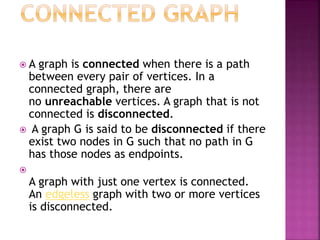
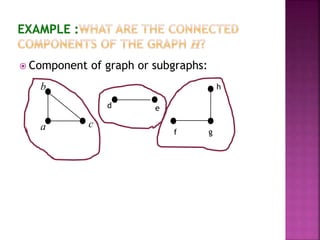
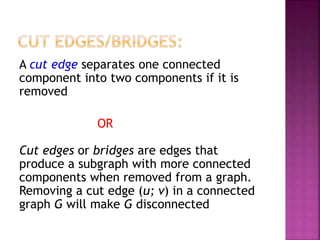
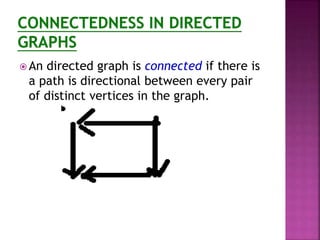
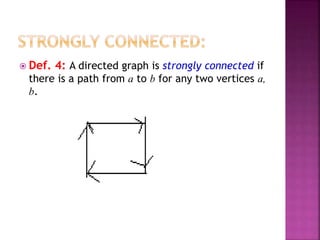
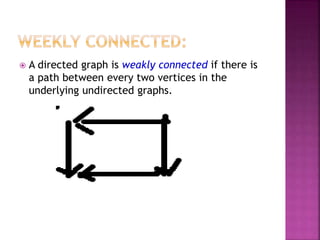
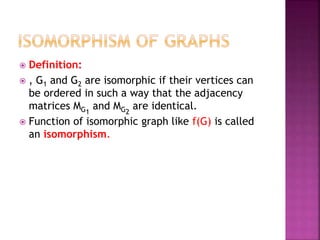
The document discusses various concepts related to connectivity in graphs. It defines what makes a graph connected versus disconnected. Key points include: a connected graph has a path between all vertex pairs; removing vertices or edges can disconnect a graph; connected components are maximal connected subgraphs; cut vertices and edges disconnect the graph when removed. Graph isomorphism is also discussed, where two graphs are isomorphic if their adjacency matrices are identical.










![Def.
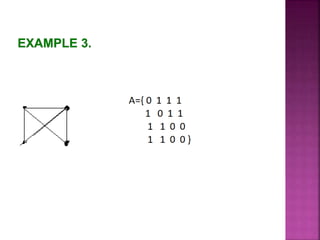
G=(V, E) : simple graph, V={v1,v2,…,vn}. (Order doesn't matter)
A matrix A is called the adjacency matrix of G
if A=[aij]nn , where aij = 1, if {vi,vj}E,
0, otherwise.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/connectivityofgraphs-180109113113/85/Connectivity-of-graphs-20-320.jpg)