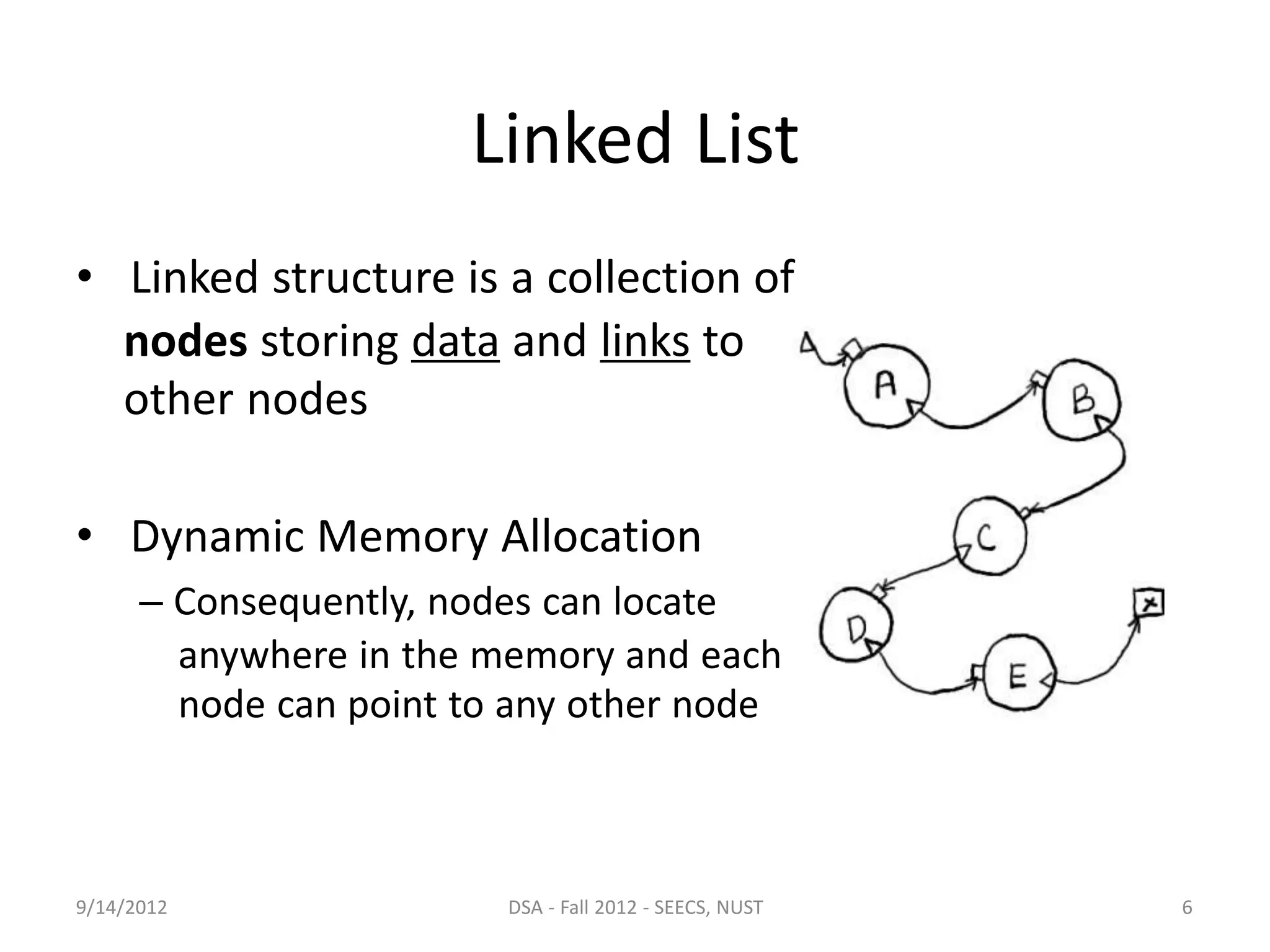
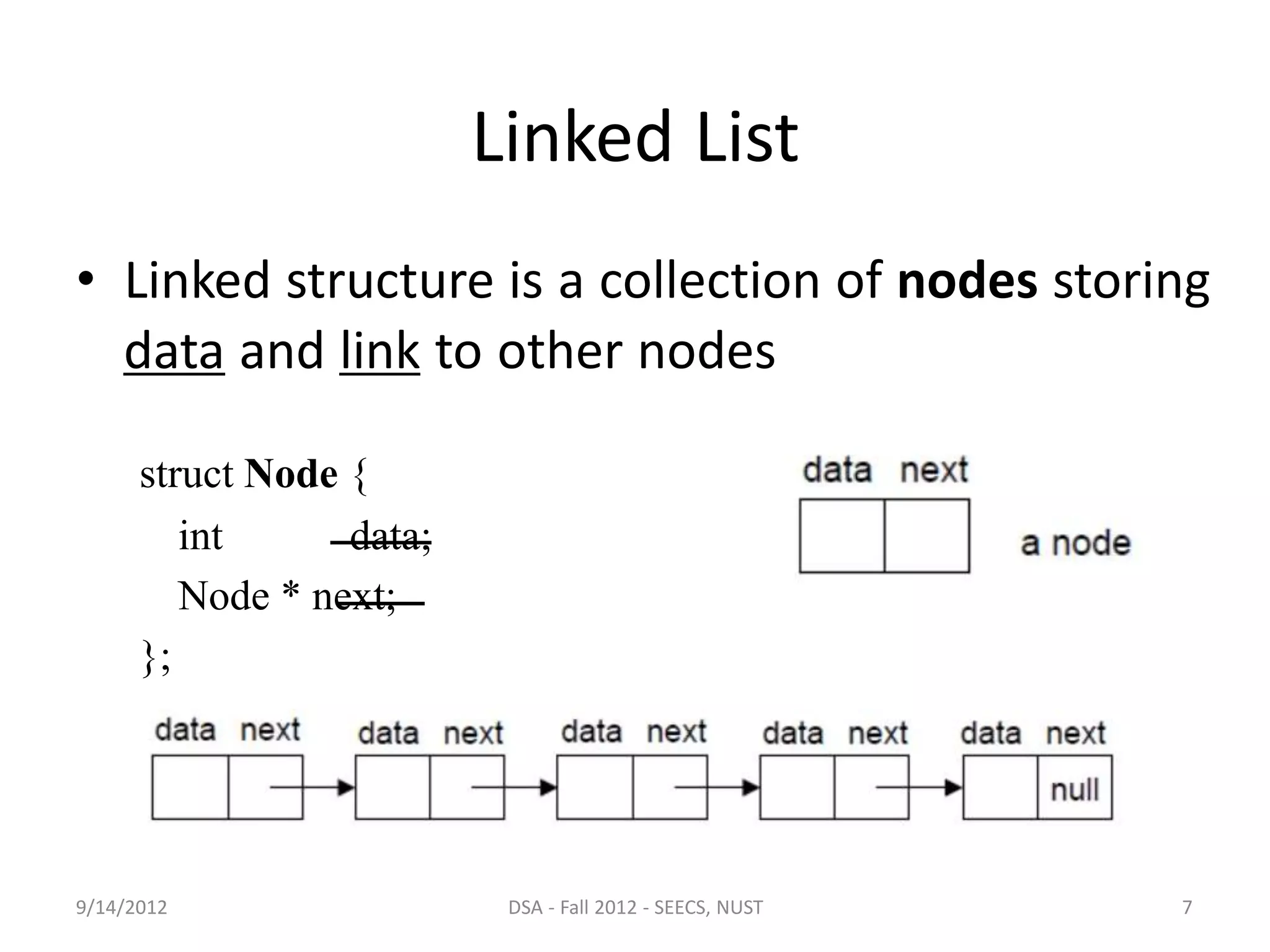
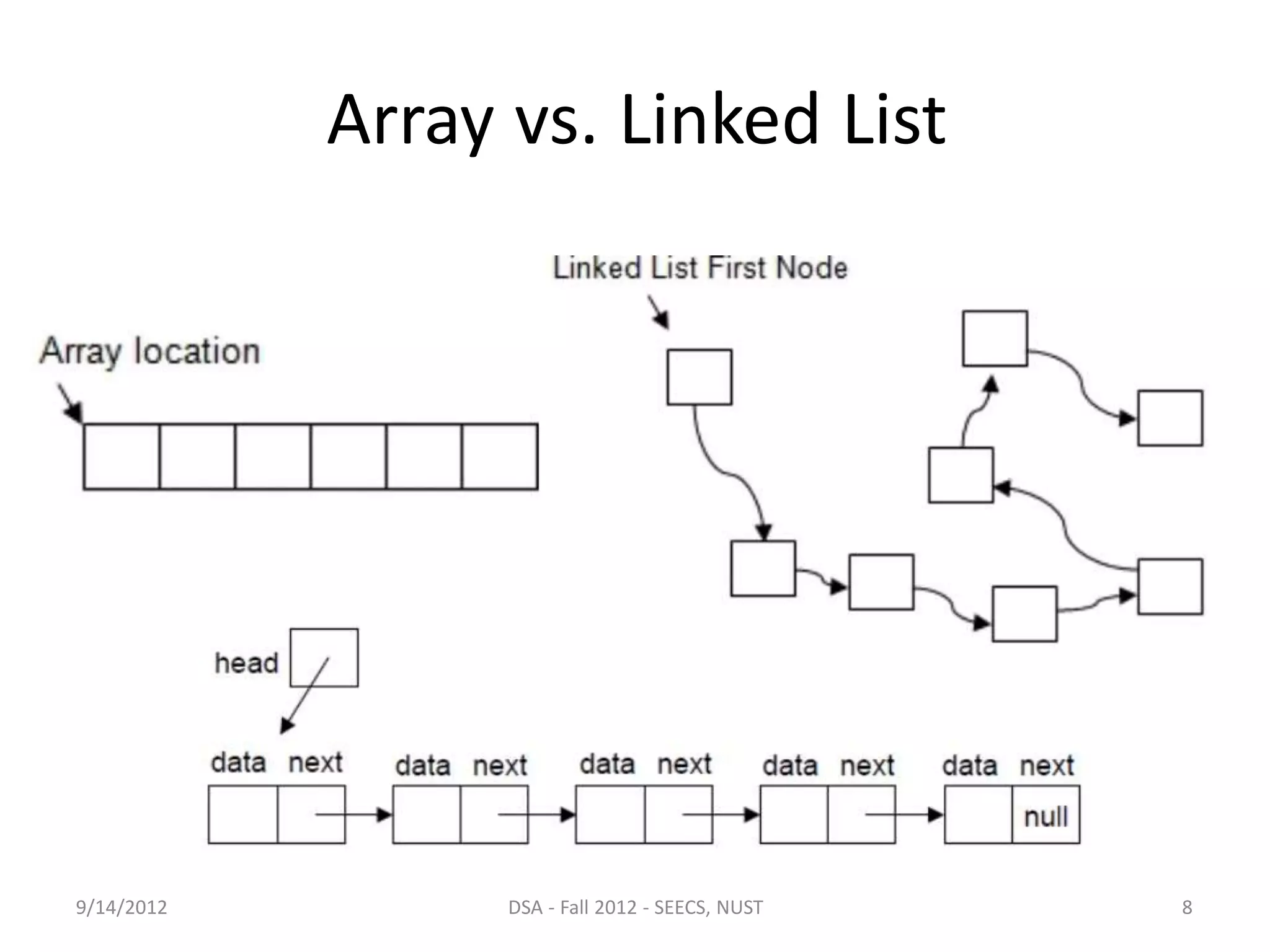
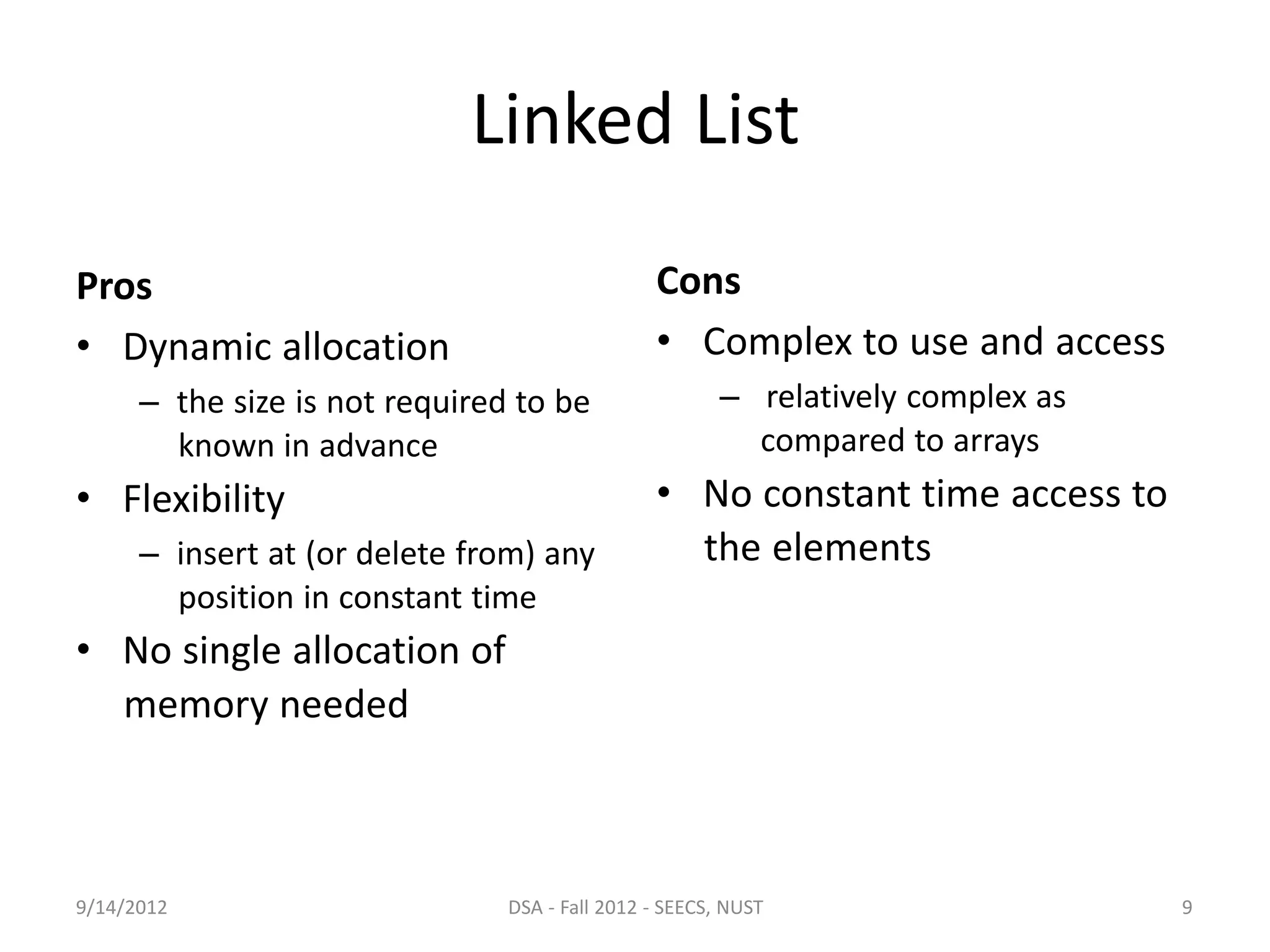
This document discusses arrays and linked lists as data structures. It outlines the pros and cons of arrays, which have fixed size and allow constant time access but require contiguous memory. Linked lists are introduced as a solution, using dynamic memory allocation so nodes can be anywhere in memory. Each linked list node stores data and a link to the next node. Linked lists provide flexibility for insertion and deletion at any position in constant time but are more complex to use than arrays.