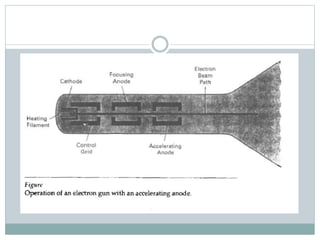
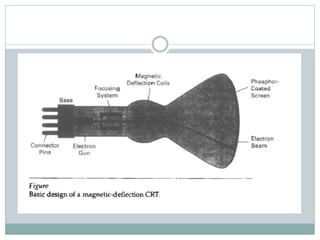
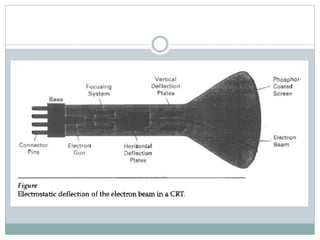
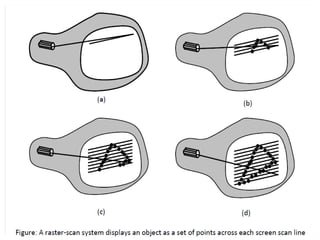
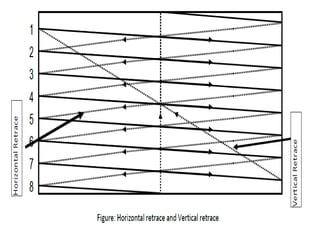
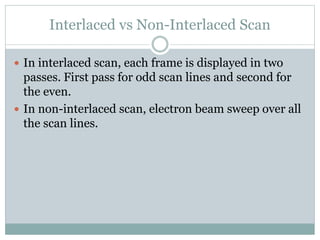
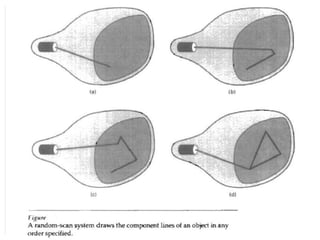
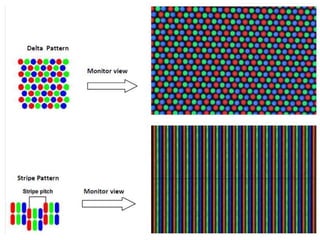
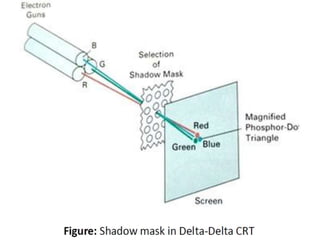
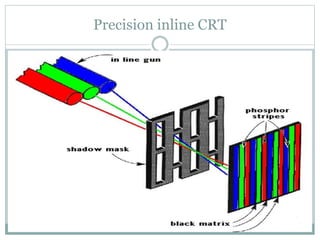
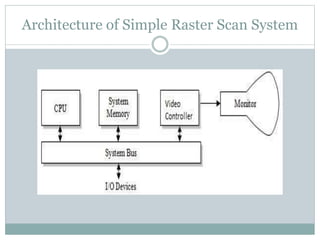
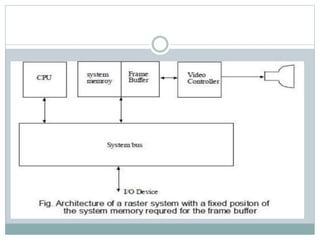
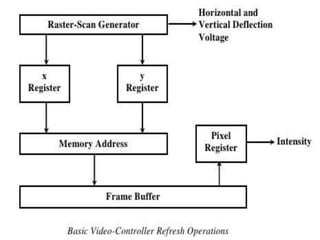
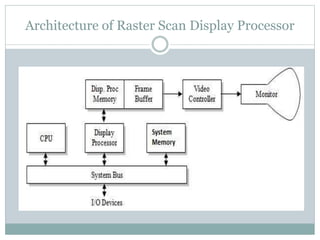
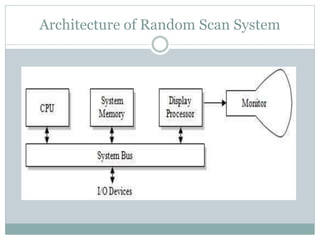
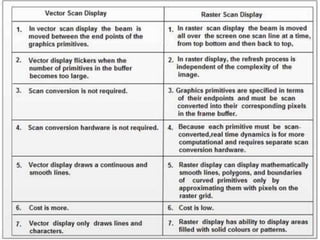
The document provides an overview of various display technologies, focusing on raster and random scan systems, detailing how cathode ray tubes function, the types of phosphors used, and the concepts of resolution and refresh rates. It also discusses color CRT monitors, including beam penetration and shadow mask techniques, and mentions the advantages of flat panel displays in terms of weight and power efficiency. Lastly, it introduces graphics software classifications and hard-copy devices for producing image prints.