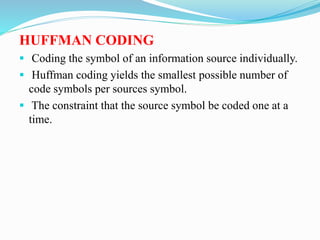
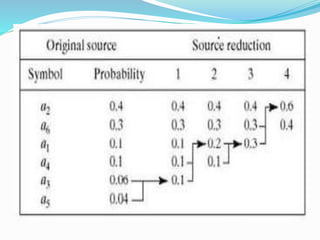
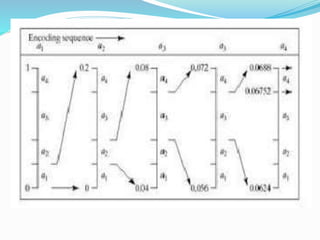
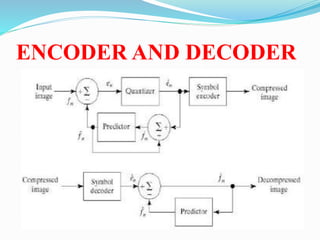
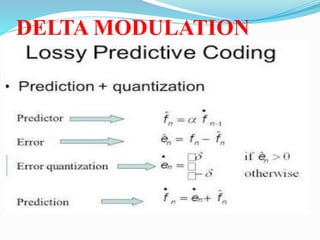
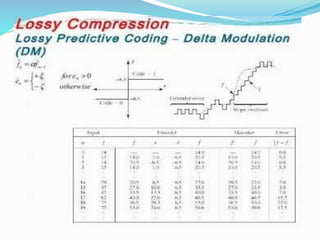
This document discusses different types of error free compression techniques including variable-length coding, Huffman coding, and arithmetic coding. It then describes lossy compression techniques such as lossy predictive coding, delta modulation, and transform coding. Lossy compression allows for increased compression by compromising accuracy through the use of quantization. Transform coding performs four steps: decomposition, transformation, quantization, and coding to compress image data.