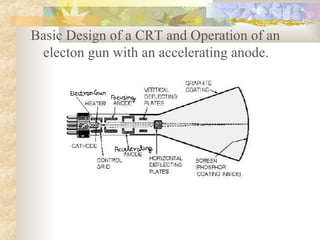
Video monitors use cathode ray tubes to display output. In a cathode ray tube, an electron gun fires a beam of electrons that is focused and deflected to hit phosphor on the screen, causing it to glow. The beam rapidly redraws the image to keep the screen illuminated, in a process called refresh. Key components of the electron gun include a heated cathode that emits electrons, an accelerating anode that speeds up the electrons, and control and focusing systems that shape the beam. When electrons hit phosphor, their energy causes the phosphor to glow briefly.