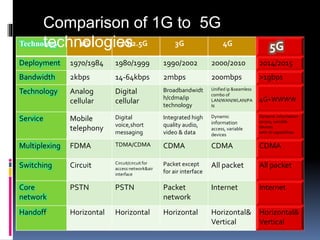
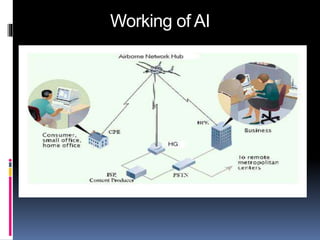
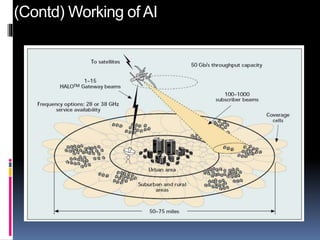
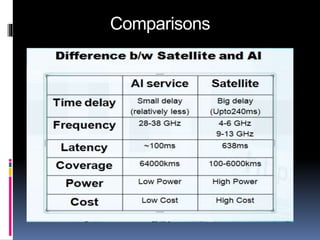
The document discusses Airborne Internet (AI), which provides internet access to aircraft. AI uses high-altitude planes, blimps, and drones stationed 60,000 feet above ground to function as flying cell towers, creating a wireless network for aircraft and users on the ground. It operates similarly to satellite internet but without transmission delays. Three companies have proposed implementations using planes, drones, and blimps to provide coverage over hundreds of cities. AI would benefit aviation services and allow passengers to access internet during flights, including in remote areas.