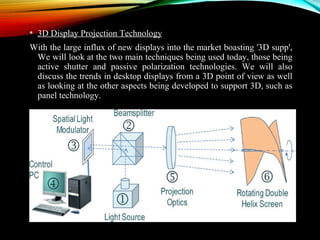
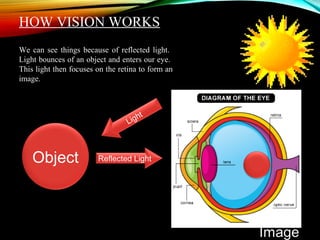
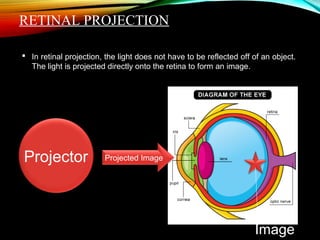
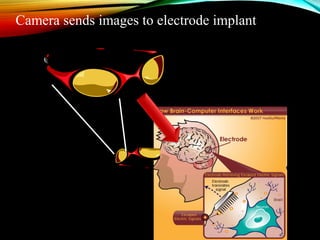
Screenless displays are an emerging technology that aims to transmit information without traditional screens or projectors, with potential applications such as augmented reality glasses and brain-computer interfaces for the visually impaired. Various types of screenless displays include visual images, retinal projections, and synaptic interfaces, each offering distinct advantages like security and portability. This technology is expected to significantly influence future media consumption, software development, and the lifestyles of individuals with visual impairments.