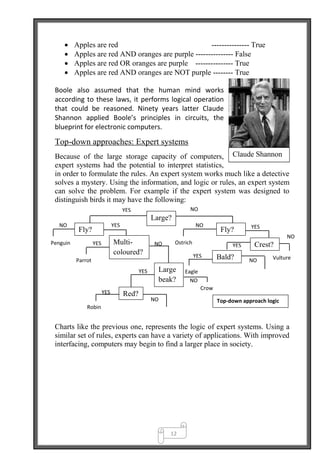
This document provides an overview of the key approaches to artificial intelligence, including neural networks, parallel computation, and top-down expert systems. It discusses how neural networks attempt to mimic the human brain by constructing electronic circuits that function like neurons. Pioneering work by McCulloch and Pitts in the 1940s linked neural processing to binary logic and laid the foundations for computer-simulated neural networks. Expert systems take a top-down approach, using stored information and rules to interpret data and solve problems in specific domains.