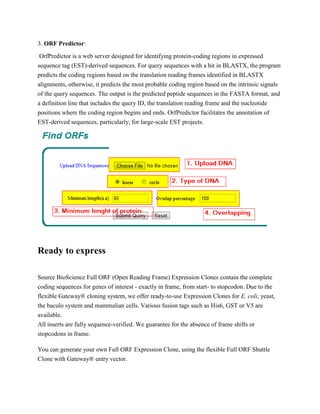
An open reading frame (ORF) is a part of a reading frame that contains no stop codons. ORFs are used as evidence to identify potential protein-coding genes in DNA sequences. The presence of a long ORF with codon usage matching the organism is used by some gene prediction algorithms to identify candidate protein-coding regions, but an ORF alone is not conclusive proof that a gene exists. Tools like ORF Finder, ORF Investigator, and ORF Predictor can be used to locate ORFs in DNA sequences.