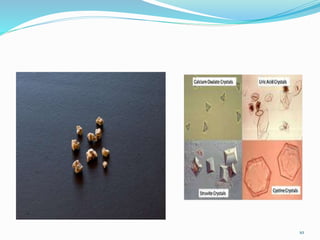
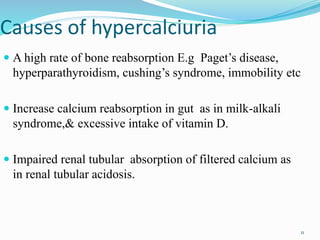
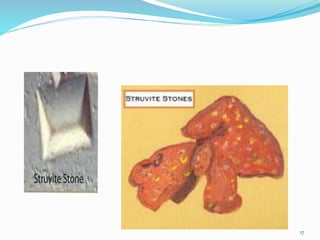
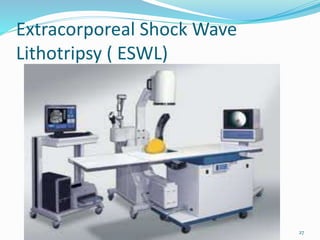
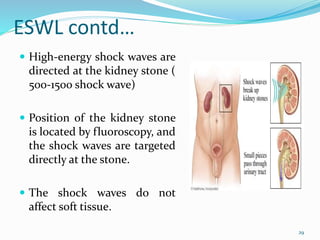
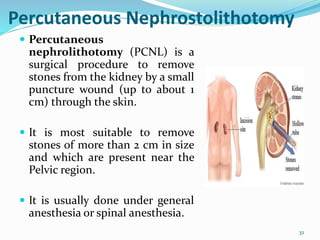
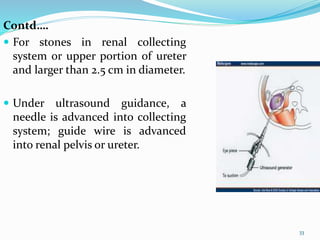
This document discusses nephrolithiasis and urolithiasis, which refer to kidney stones and urinary tract stones respectively. Stones form when substances in urine crystallize. Risk factors include hypercalcemia, dehydration, diet, genetics, and certain medical conditions. Stones are diagnosed using imaging tests and urine/blood tests. Treatment depends on stone size and location, and may include increased fluid intake, shockwave lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, or surgery to remove stones. Nursing care focuses on pain management, preventing infection and obstruction, and educating patients on prevention of recurrent stones.