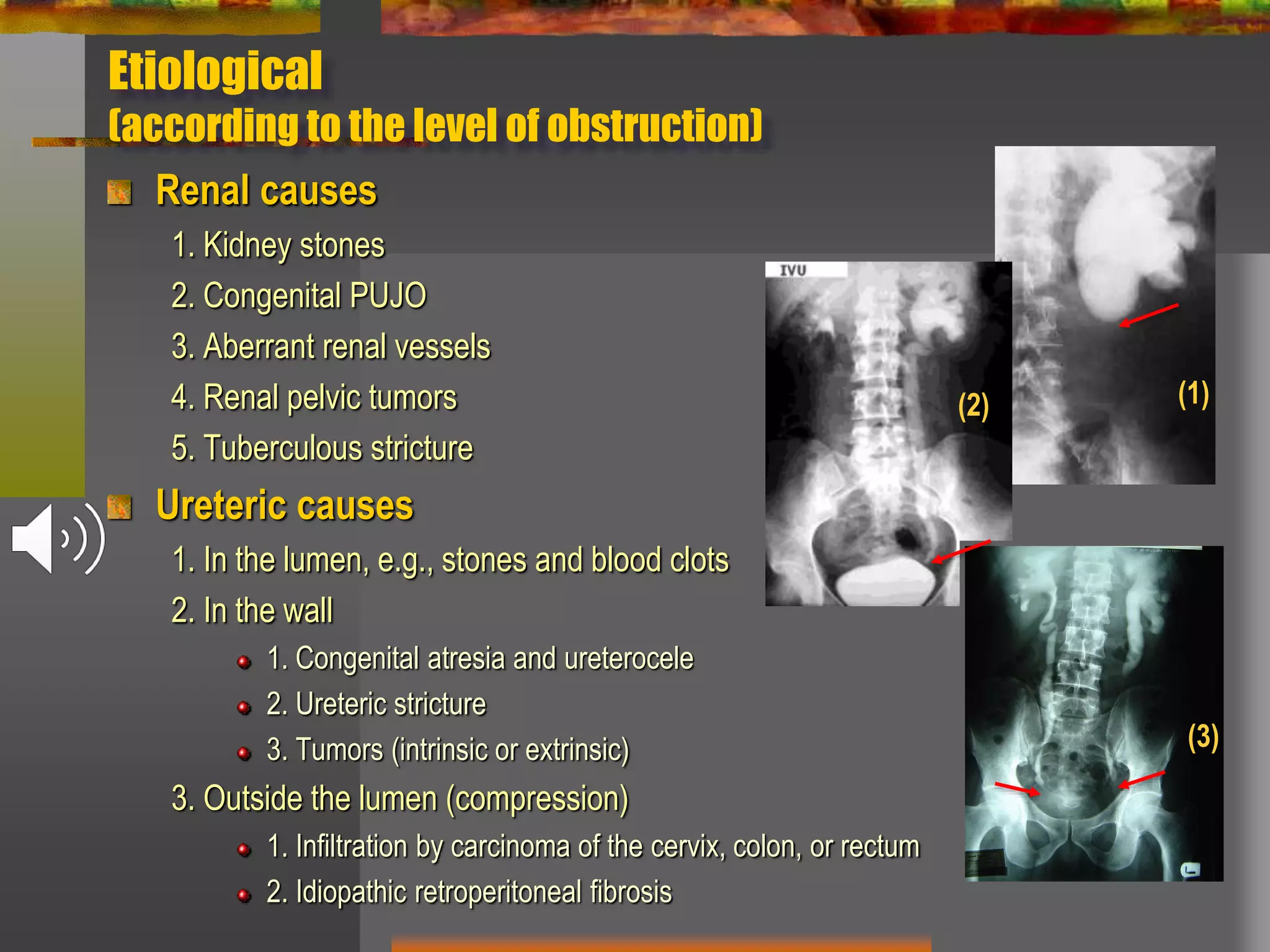
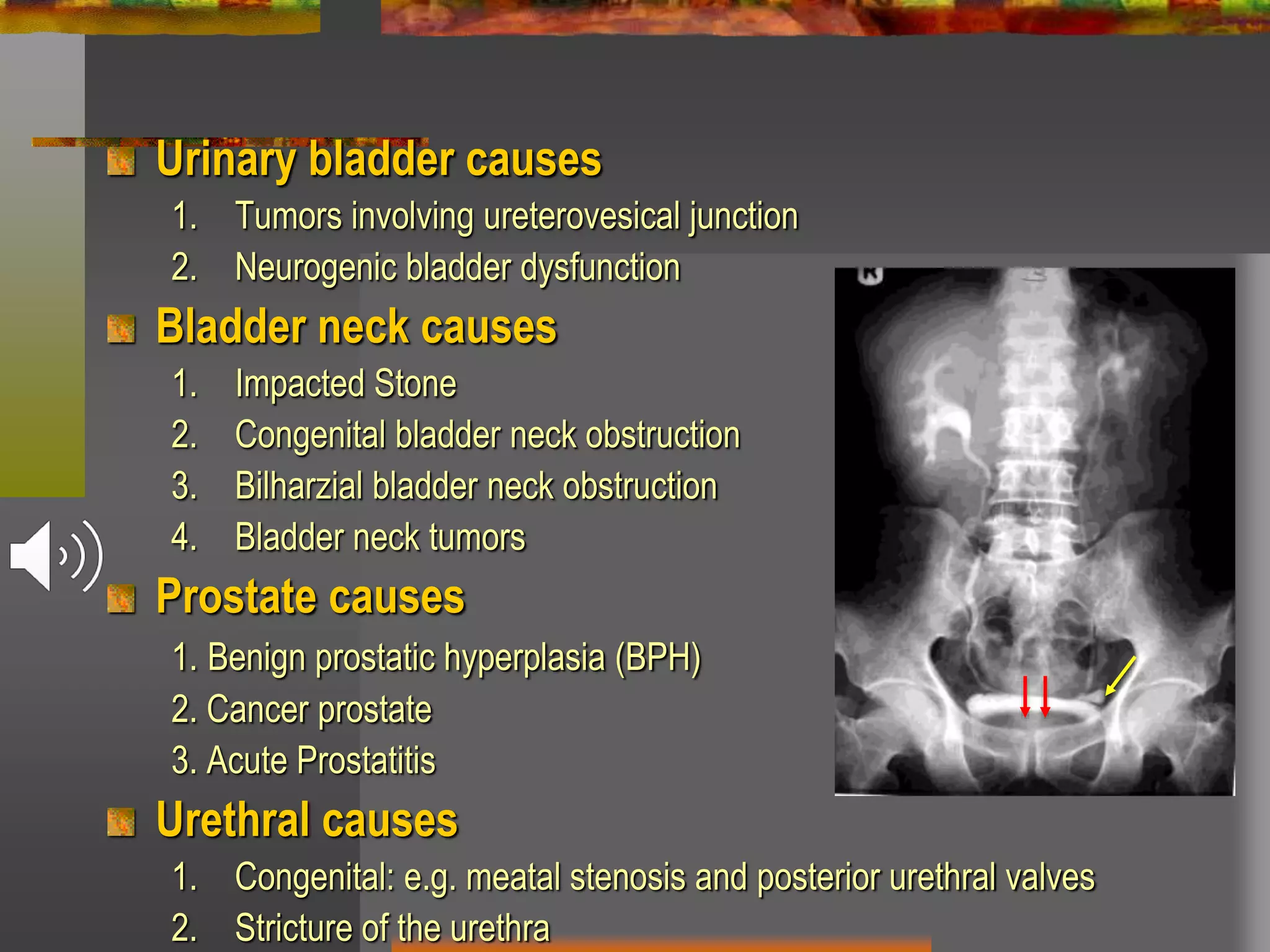
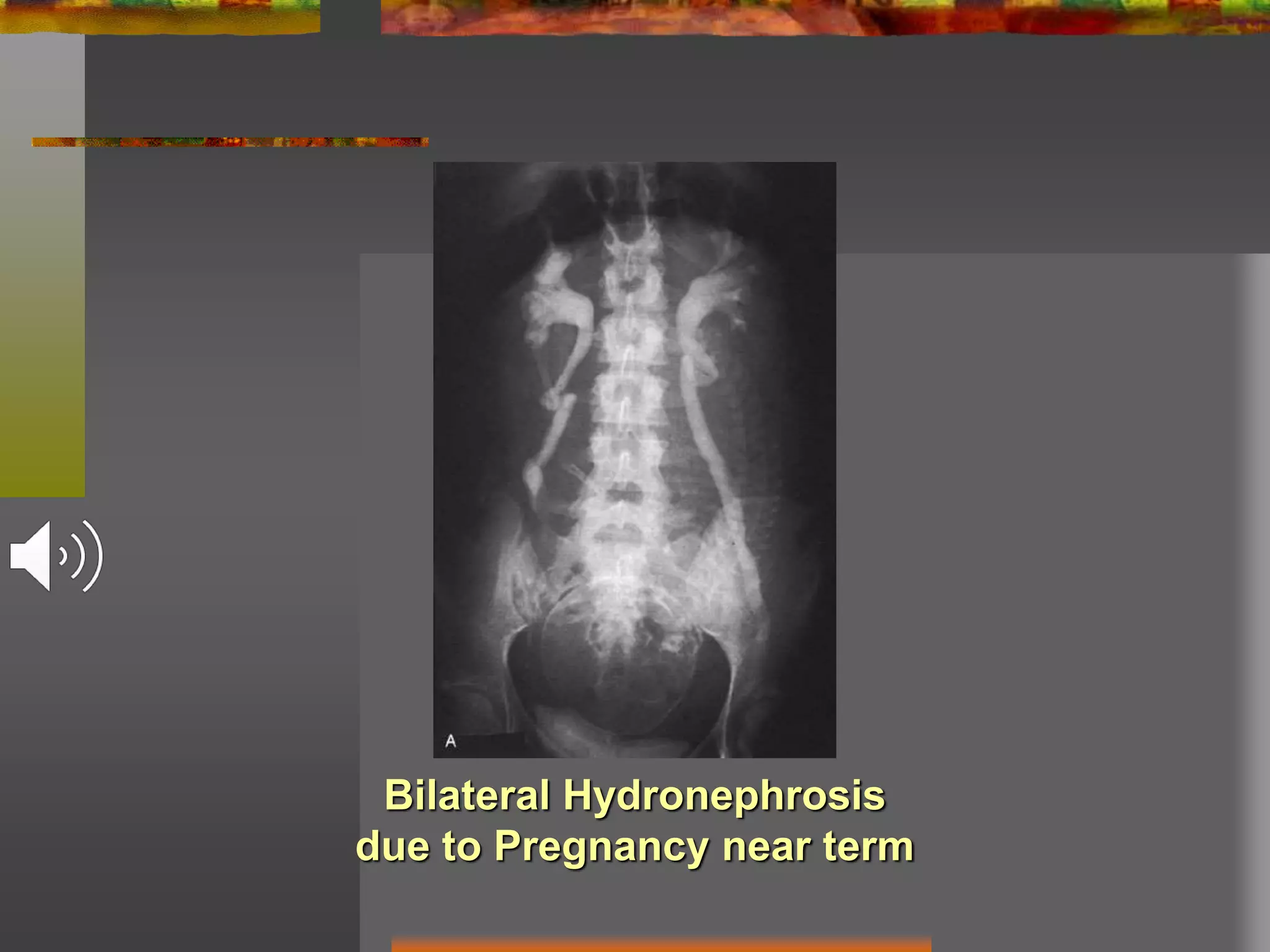
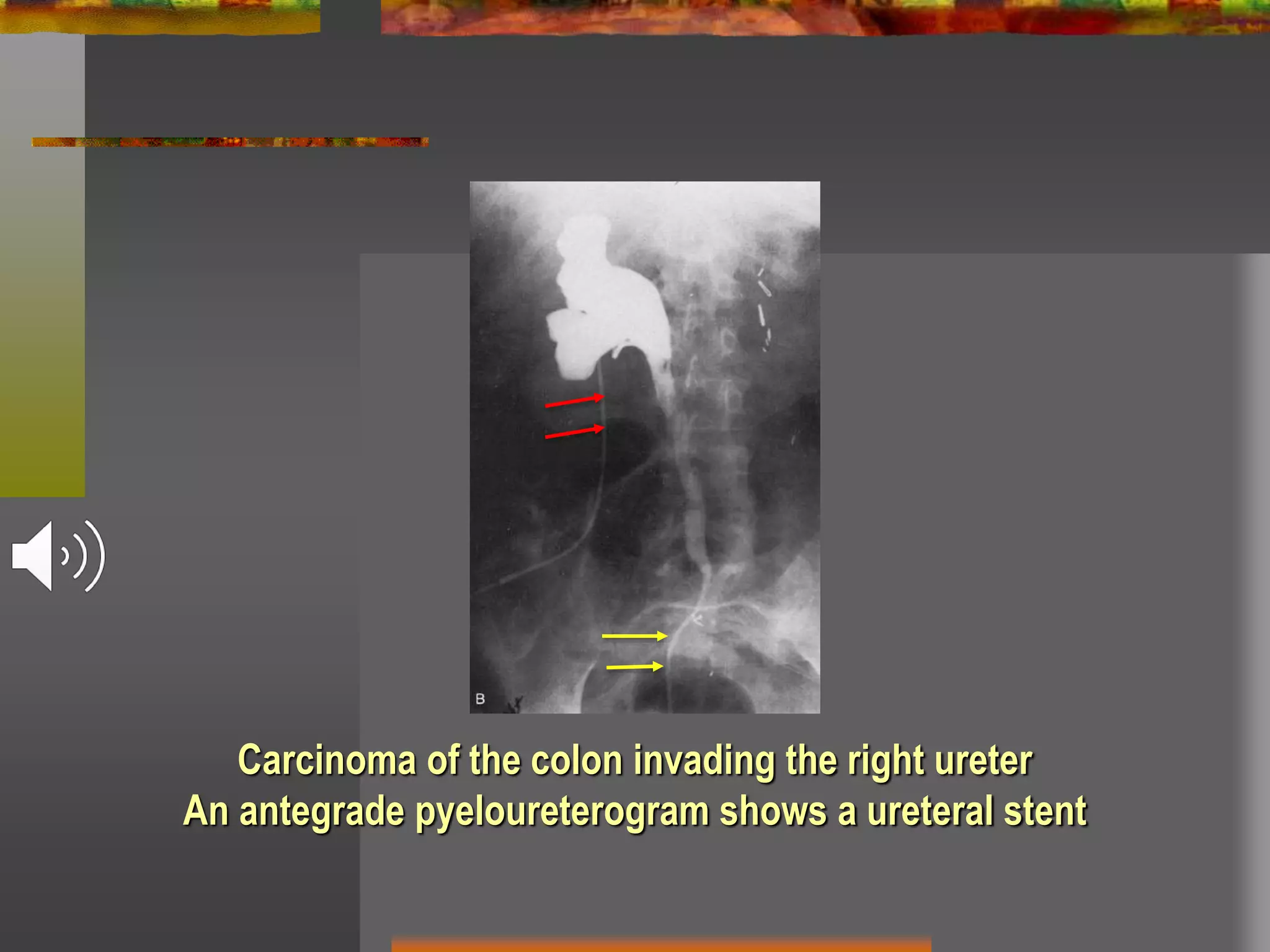
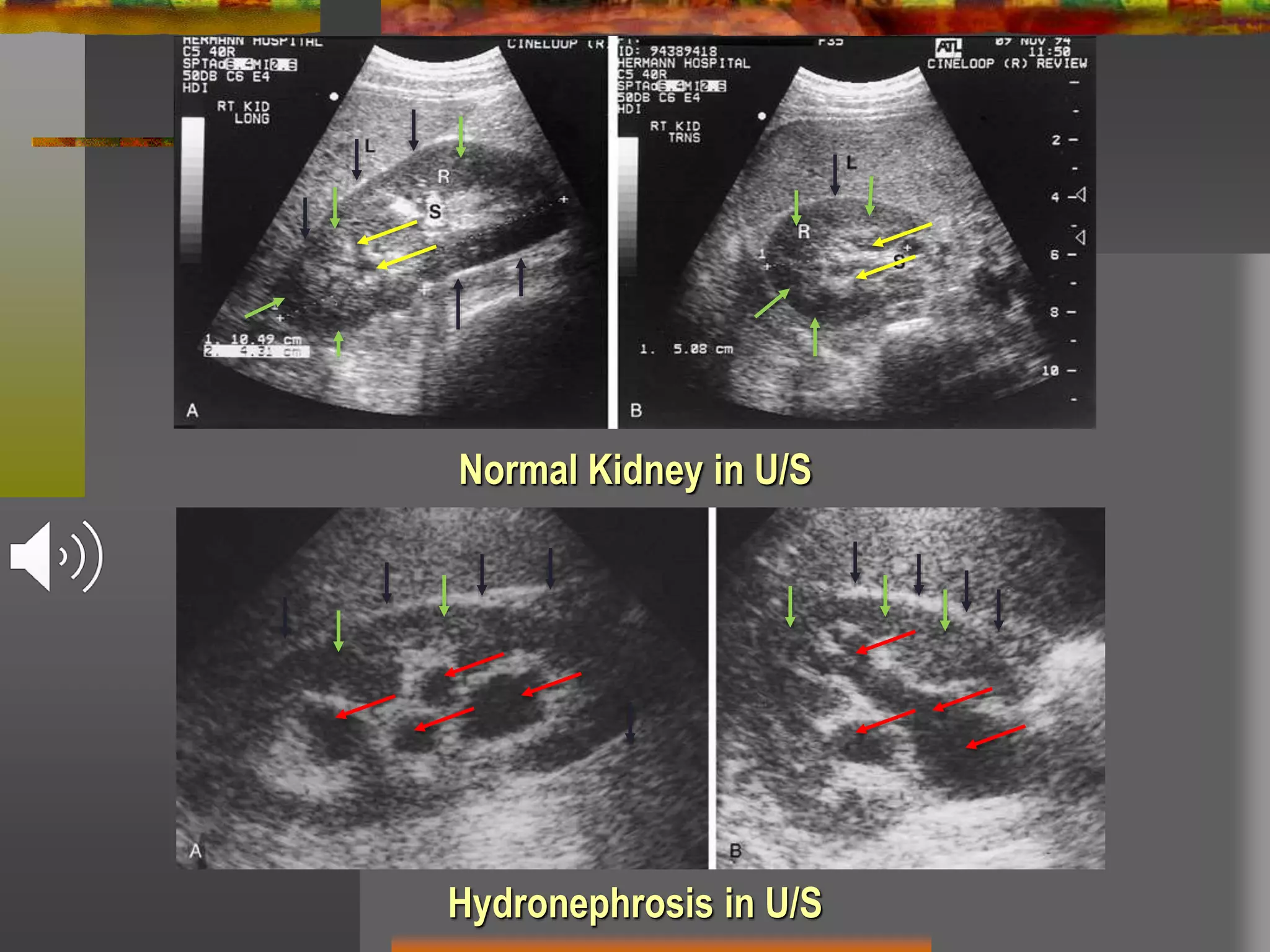
Obstructive uropathy refers to any obstruction in the urinary tract. It can cause changes including hydronephrosis (distension of the kidneys and ureters) and hydroureteronephrosis (distension of the kidneys, ureters and bladder). The document discusses the classification, causes, pathology, investigations and management of various types of obstructive uropathy including ureteric strictures and retroperitoneal fibrosis. Surgical intervention is often needed to relieve the obstruction and treat associated complications.