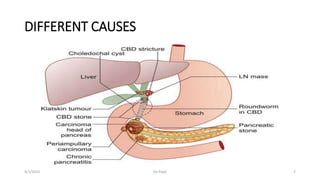
The document discusses obstructive jaundice, including its causes, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, investigations, and treatment. The most common causes are gallstones and cancer of the head of the pancreas. Obstructive jaundice results from the blockage of bile flow from the liver to the small intestine, leading to increased bilirubin levels and yellowing of the skin and eyes. Investigations include blood tests, imaging like ultrasound and CT/MRCP, and invasive procedures such as ERCP. Surgical treatment aims to relieve the obstruction by removing gallstones or tumors.