Recommended
PPT
7[1].1 the respiratory process in energy production
PPT
7[1].1 the respiratory process in energy production
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Anerobic & aerobic respiration
PPT
Fcellular respiratsdjukiytrewqwfghjnbion.ppt
PPT
Fcellular respirdfghhgfdsatiofghjhgn.ppt
PPTX
Respiration_and_Aerobic_Respiration_Grade8 [Autosaved].pptx
PPTX
Respiration_and_Aerobic_Respiration_Grade8 [Autosaved].pptx
PPT
Cellular respiration .ppt
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
Aerobic-and-Anaerobic-Respiration.pptx
PPTX
RESPIRATION IN PLANTS+ class 11It helps learn to understand the concept in de...
PPTX
respiration class 10.pptx
PDF
respiration presentation by DrPriyam .pdf
PPTX
Respiration by Mr. K. S. Sontakke
PDF
ch-7respiration-120506111701-phpapp02.pdf
PPTX
1. Cellular Respiration - Final for mbbs
PPTX
Arobic and anerobic respiration
PPTX
aerobic and anaerobic respiration.pptx
PPTX
The Energy of Life: An Exploration of ATP
PDF
grade 11 first term Cellular respiration.pdf
PPTX
GEN BIO 1 (JET^J NATASHA).ppmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmtx
PPTX
anaerobic reapiratory.pptx
PPTX
PPT
PPTX
ANTI CANCER DRUGS (blood cancer) onesmus.pptx
PPTX
ivan work Diet in pregnancy/Minimumdietarydiversity.pptx
More Related Content
PPT
7[1].1 the respiratory process in energy production
PPT
7[1].1 the respiratory process in energy production
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Anerobic & aerobic respiration
PPT
Fcellular respiratsdjukiytrewqwfghjnbion.ppt
PPT
Fcellular respirdfghhgfdsatiofghjhgn.ppt
Similar to CELLULAR RESPIRATION for young science.pptx
PPTX
Respiration_and_Aerobic_Respiration_Grade8 [Autosaved].pptx
PPTX
Respiration_and_Aerobic_Respiration_Grade8 [Autosaved].pptx
PPT
Cellular respiration .ppt
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
Aerobic-and-Anaerobic-Respiration.pptx
PPTX
RESPIRATION IN PLANTS+ class 11It helps learn to understand the concept in de...
PPTX
respiration class 10.pptx
PDF
respiration presentation by DrPriyam .pdf
PPTX
Respiration by Mr. K. S. Sontakke
PDF
ch-7respiration-120506111701-phpapp02.pdf
PPTX
1. Cellular Respiration - Final for mbbs
PPTX
Arobic and anerobic respiration
PPTX
aerobic and anaerobic respiration.pptx
PPTX
The Energy of Life: An Exploration of ATP
PDF
grade 11 first term Cellular respiration.pdf
PPTX
GEN BIO 1 (JET^J NATASHA).ppmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmtx
PPTX
anaerobic reapiratory.pptx
PPTX
PPT
More from musayansa
PPTX
ANTI CANCER DRUGS (blood cancer) onesmus.pptx
PPTX
ivan work Diet in pregnancy/Minimumdietarydiversity.pptx
PPT
cell biology for young scientists level 4.ppt
PPTX
Session 1 Introduction to biostatistic.pptx
PPT
Introduction to medical physiology dcm.ppt
PDF
Onesmus history of digestive system, elucidating the major historical events.pdf
PPTX
Cancer Immunology, molecular mechanisms.pptx
PPTX
cancer and the immune system, molecular mechanisms.pptx
PPTX
MSc PHY Animal act, biomedical sciences.pptx
PPTX
Msc PHY Animal ethics in biomedical laboratories.pptx
PPTX
physiology of excitable tissues, the nerve.pptx
PPTX
history of nervous system and neurophysiology.pptx
PPTX
CANCER OF THE OVARY. .pptx
PPTX
COLON CANCER causes and Management of the disease.pptx
PPTX
1. APPROACH TO A VOMITING CHILD pediatric.pptx
PPTX
FLUID IN PAEDIATRICS PATIENTS333kk3.pptx
PPTX
Benign diseases of the breast, ANDI conditions
PPTX
Approach To Acute Limb Pain in pediatrics
PPTX
biology of evil, basic understanding of the neuropsychological basis of evil
PPTX
Recently uploaded
PPTX
CABG.pptx Coronary..heart surgery... Bypass grafting
PPTX
A Seminar Presentation on Transposable Elements
PPTX
Radially polarized THz pulses by ZnTe axicon pumped at 2060 nm
PPTX
Sedimentary basins by Team Maverick.pptx
PPTX
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS FOR HORTICULTURAL CROPS PPT.pptx
PDF
Alkene ( एल्कीन ) organic Chemistry Notes PDF Download - Irfanullah Mehar - W...
PDF
Alkane ( एल्केन ) - Notes PDF Download Hindi Medium - IRFANULLAH MEHAR.pdf
PPTX
Psychopathology and mental Disorders.pptx
PPTX
CAM pathway in plants (unique pathway found in Xerophytes).pptx
PPT
Ch04uiuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuukkkkkkklh.ppt
PPTX
SCIENCE Quiz Bee 2025-School - Based.pptx
PPT
human_digestive_system_ppt.ppt9thgradebiology
PDF
Benzene ( बेंजीन ) - Organic Chemistry Notes PDF Download Slide - Irfanullah ...
PDF
Origin Of Life & Evolution || BIOLOGY || CBSE & CHSE
PPTX
Photosynthesis (Light dependent reaction and Calvin cycle).pptx
PDF
Animal Classification - Grade of Organisation, Symmetry, Coelom, Embryogeny ...
PPTX
C4 cycle in plants (Hatch and Slack Pathway).pptx
PDF
Betterszie | Exploring Dendrimer Generations Using the BeSEC
PDF
Hematology-1-Lesson_About_Hematopoiesis_and_erythropoetin
PPTX
Week 3 - Microbes - Pathogens & Infection (1).pptx
CELLULAR RESPIRATION for young science.pptx 1. 2. Definition
• Is a series of enzyme-controlled reactions in which
chemical energy is released during the breakdown
of glucose.
• It occurs at a cellular level
• Main source of energy is Glucose.
• Reaction : C6H12O6+O2== 6CO2 +6H2O+ ATP
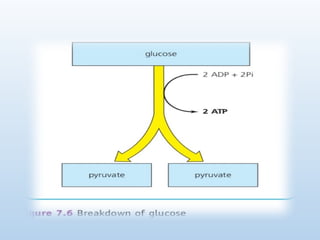
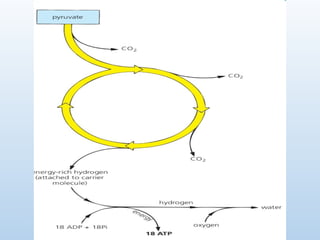
3. 4. Stages
I. Glycolysis
-Occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
-Occurs in the presence or absence of O2.
- Glucose is broken down to 2 pyruvate molecules
and 2 ATPs molecules are produced.
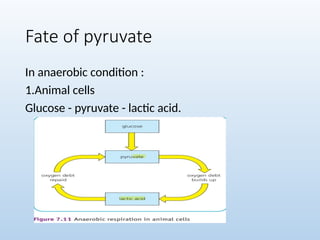
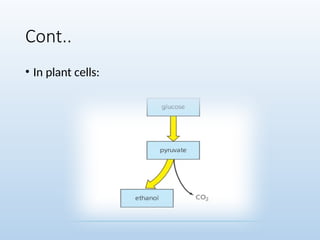
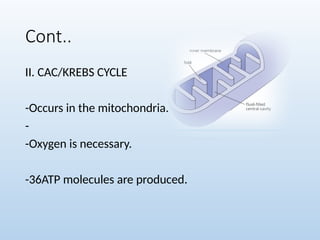
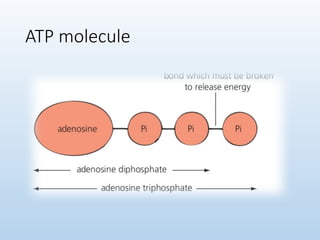
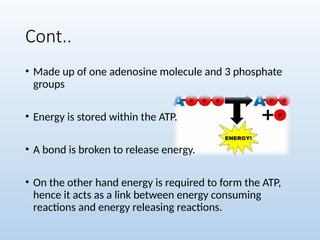
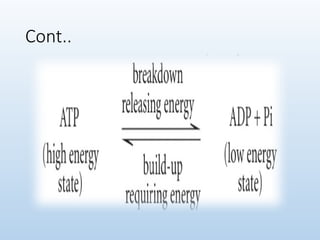
6. 7. 8. 10. 11. Cont..
• Made up of one adenosine molecule and 3 phosphate
groups
• Energy is stored within the ATP.
• A bond is broken to release energy.
• On the other hand energy is required to form the ATP,
hence it acts as a link between energy consuming
reactions and energy releasing reactions.
12. 13. Uses of ATP
• Cell division
• Protein synthesis
• Transmission of nerve impulse
• Muscle contraction.
• Active uptake of ions and molecules.
• CO2 fixation during photosynthesis.
14.