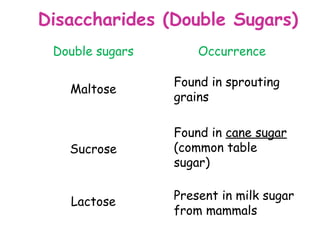
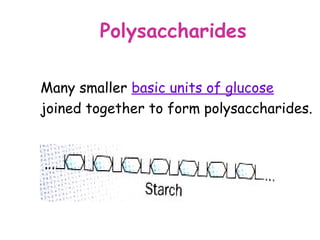
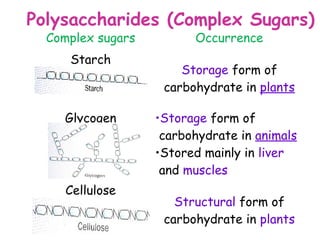
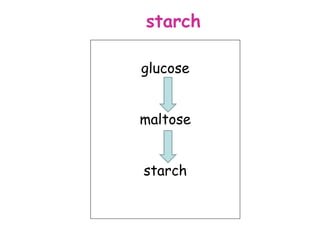
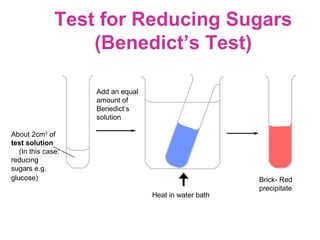
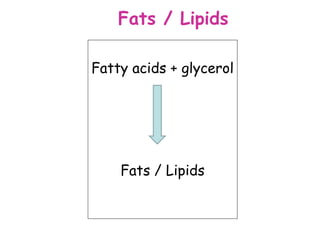
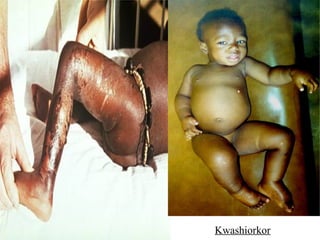
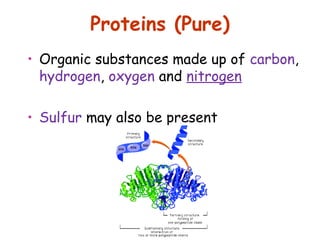
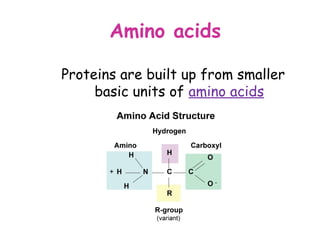
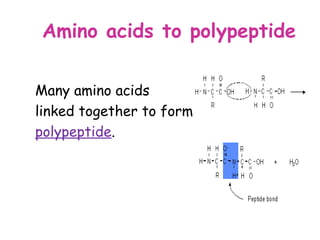
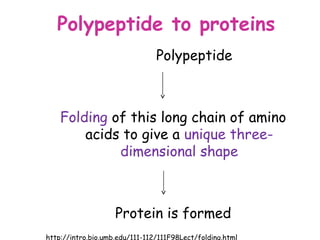
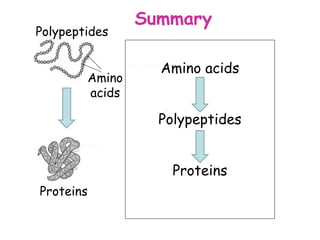
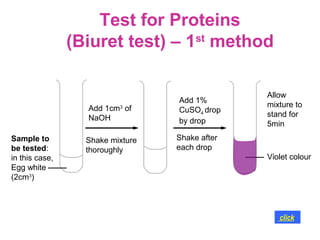
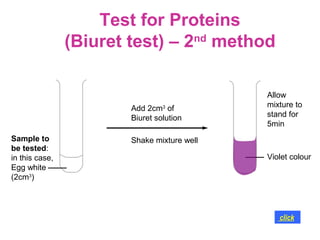
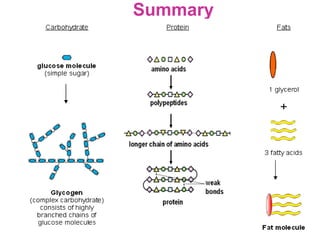
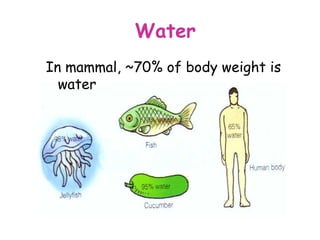
The document discusses the key nutrients that make up living organisms - carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and water. Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and include sugars like glucose. Proteins are composed of amino acids. Fats are formed from fatty acids and glycerol. Tests are described to identify each nutrient. Water makes up about 70% of the human body and is essential for transport, chemical reactions, and controlling temperature.