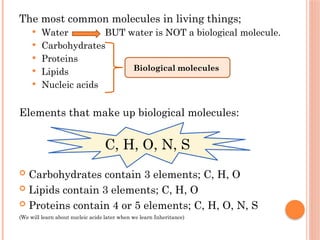
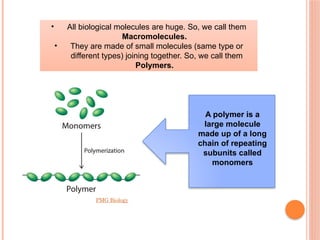
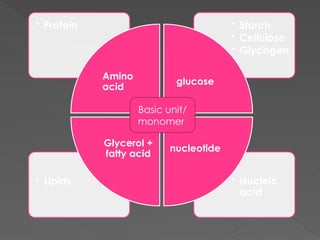
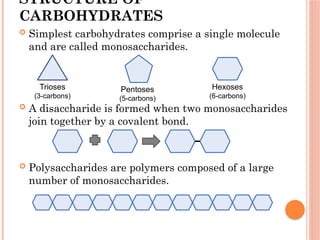
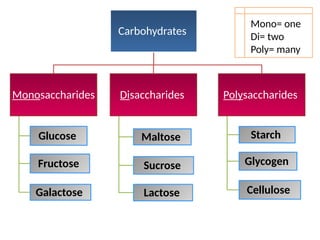
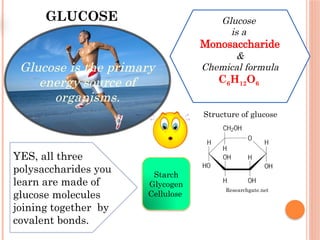
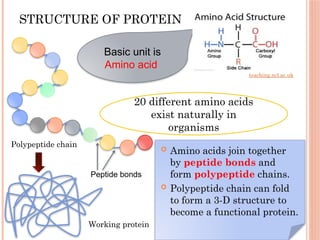
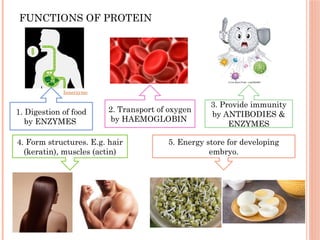
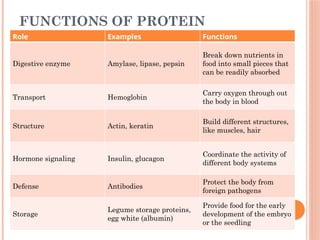
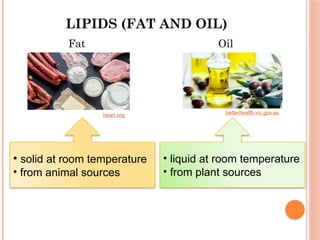
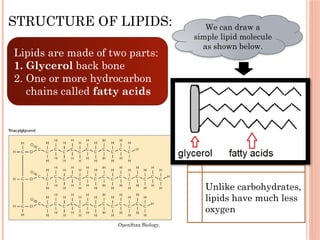
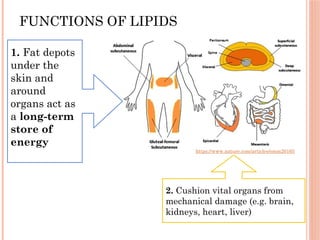
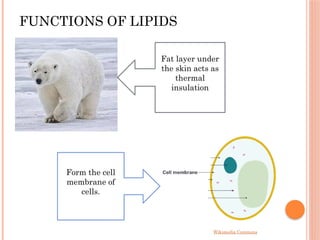
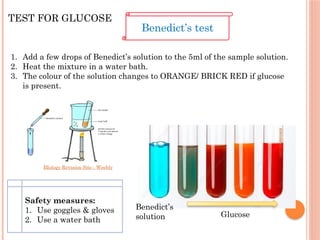
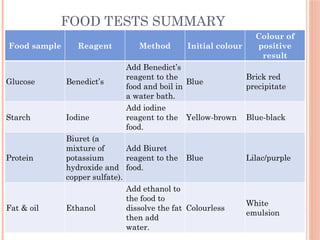
The document discusses biological molecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, outlining their chemical elements, structures, and functions. It also details practical tests for identifying the presence of glucose, starch, protein, and fats in food samples. Additionally, it describes the role of various biological molecules in living organisms and provides safety measures for conducting these tests.