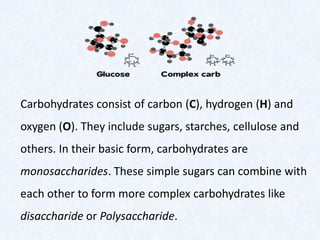
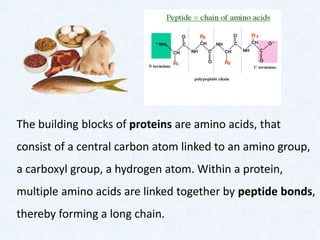
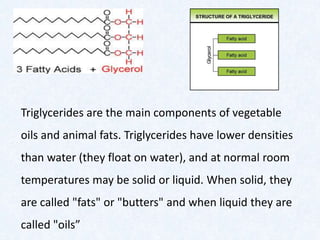
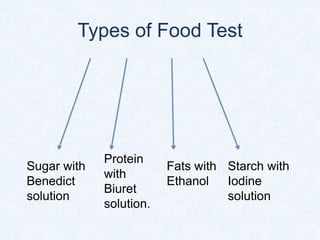
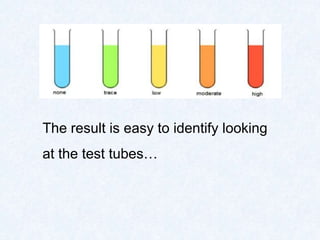
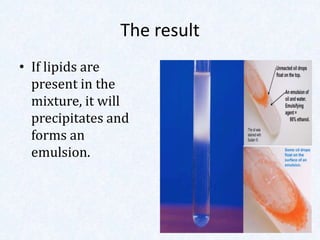
Large molecules are composed of smaller units that combine. Carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and cellulose, and are made from monosaccharides. Proteins are made from amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Fats are triglycerides composed of fatty acids and glycerol. Food tests can identify these macromolecules using Benedict's solution for sugars, Biuret reagent for proteins, iodine for starches, and ethanol for fats. The document provides details on procedures and results for each of these common food tests.











![BIBLIOGRAPHY
• Available on- http://brilliantbiologystudent.weebly.com/ethanol-
emulsion-test-for-lipids.html [on-line] accessed on- 31st October
• Available on-
http://www.biosci.ohiou.edu/introbioslab/Bios170/170_2/biuret.ht
m [on-line] accessed on- 4th November
• Available on- http://dev.nsta.org/ssc/pdf/v4-TS_33.pdf [on-line]
accessed on- 8th November
• Available on- http://www.bayerpharma.com/en/research-and-
development/technologies/small-and-large-molecules/index.php
[on-line] accessed on- 8th November
• Google images accessed on 12th November.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/foodtest-140520070631-phpapp02/85/Food-test-18-320.jpg)