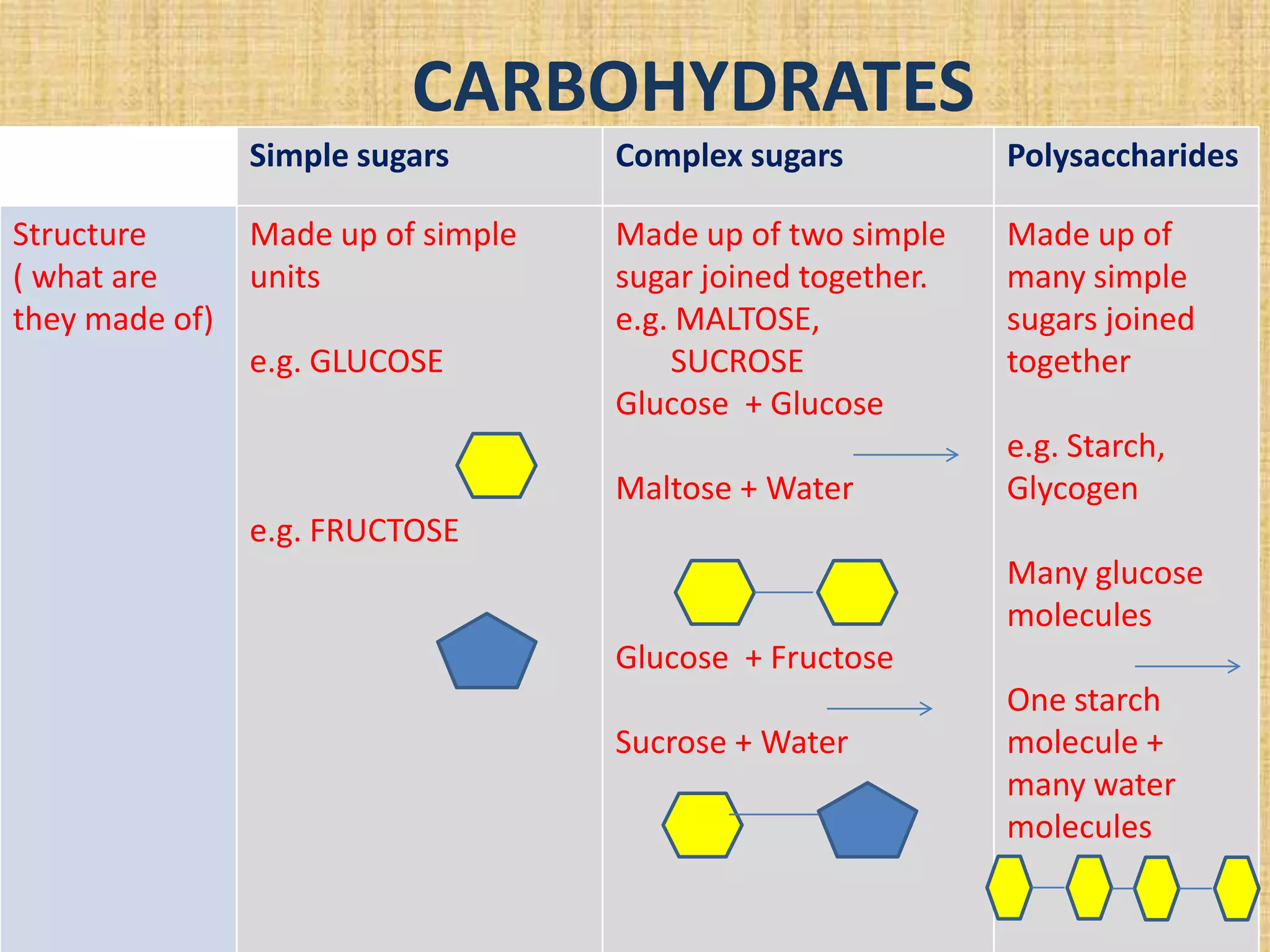
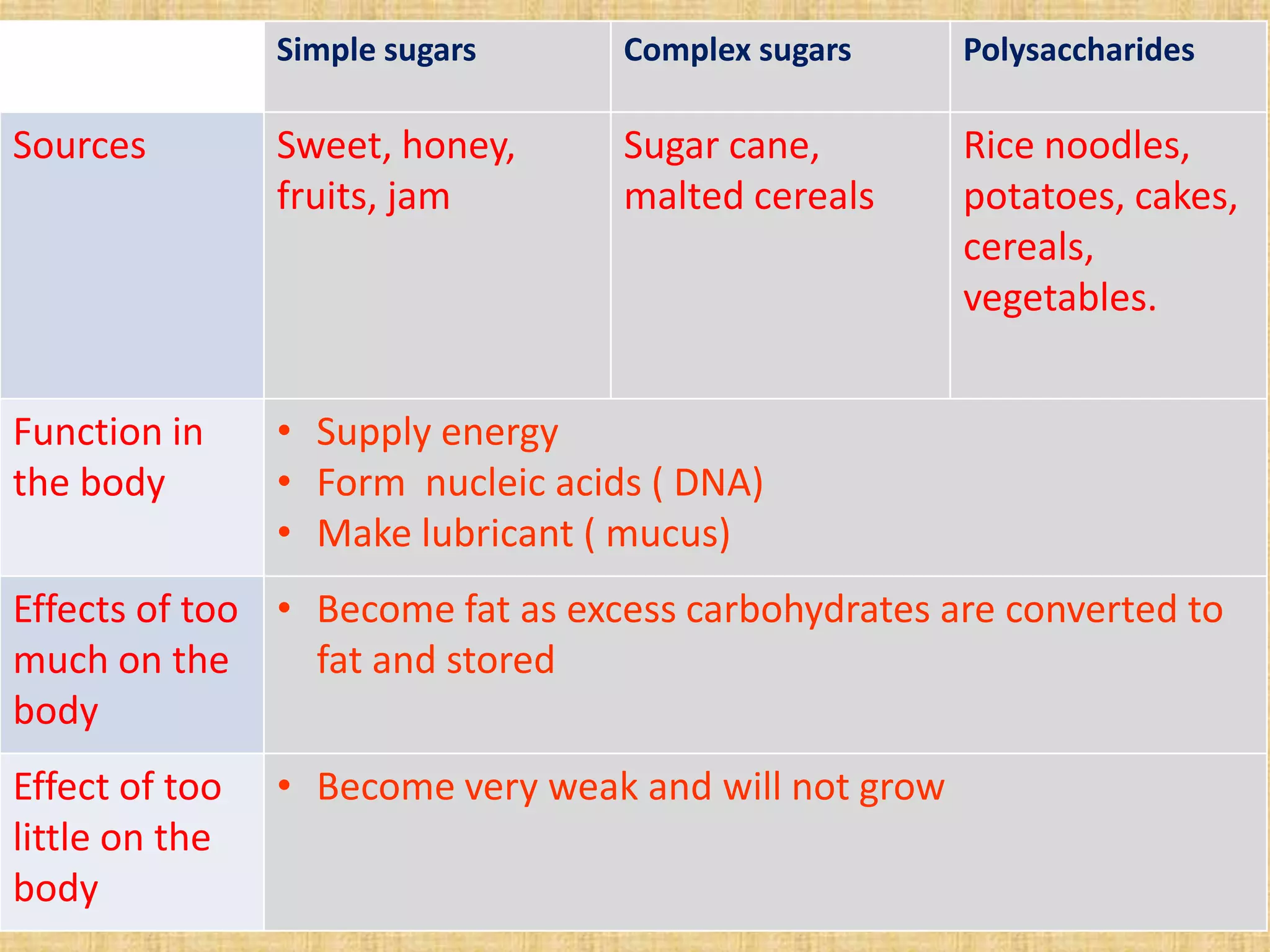
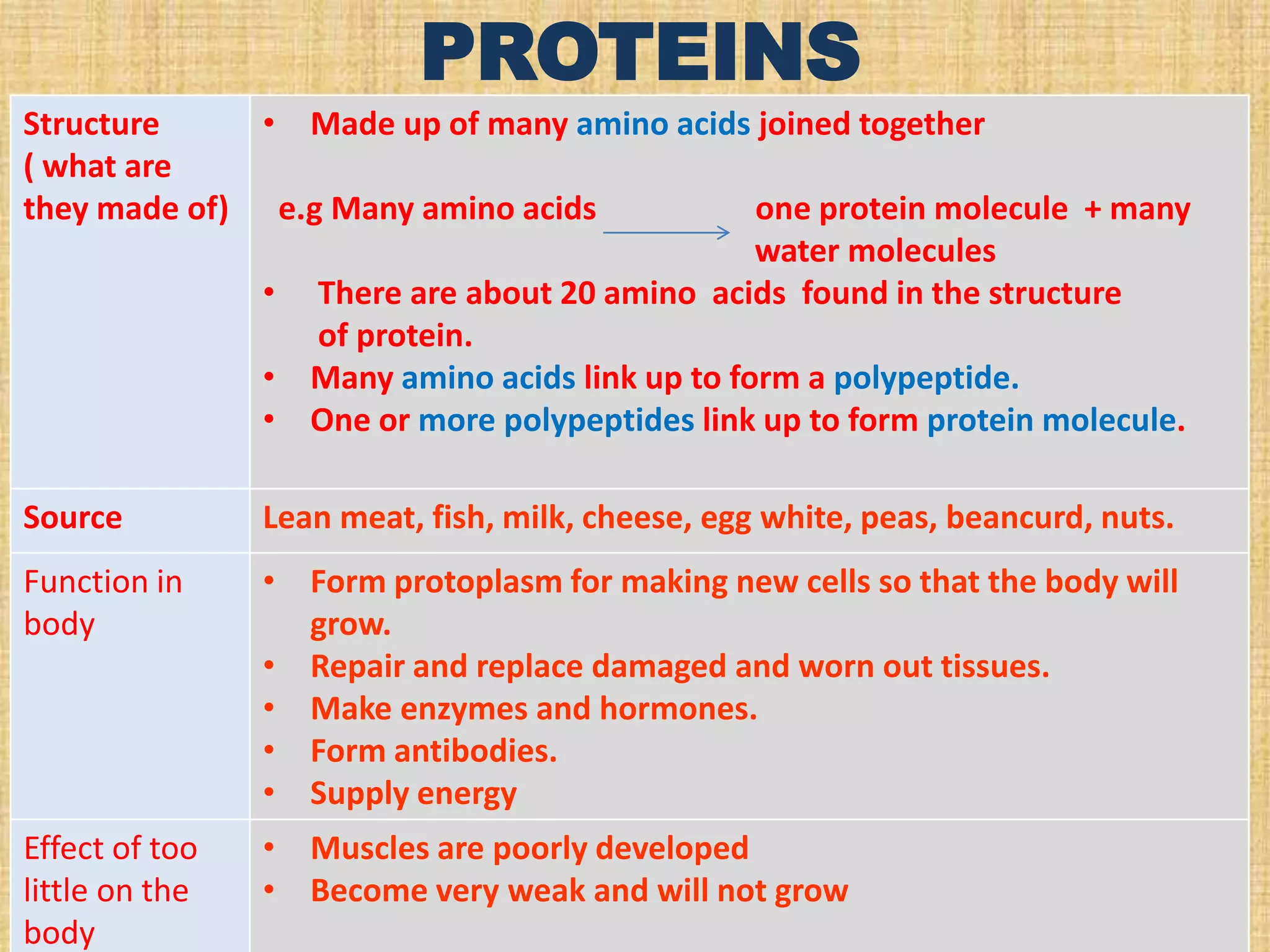
This document discusses nutrients and why we need food. It explains that we need food for energy, growth, repair, and health. The main nutrients provided by food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Carbohydrates include simple sugars, complex sugars, and polysaccharides. Proteins are made of amino acids and are important for growth, tissue repair, and enzyme/hormone production. Fats provide energy, form cell membranes, and carry fat-soluble vitamins. The document also describes tests to identify starches, sugars, proteins and fats in food.