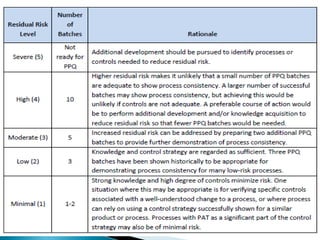
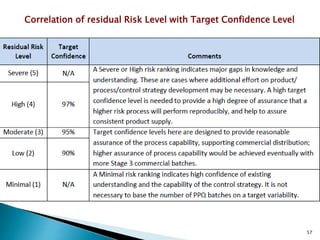
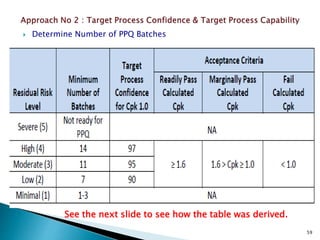
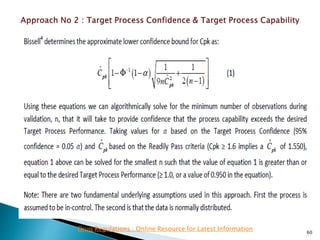
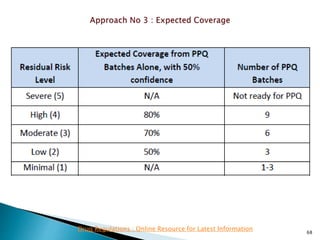
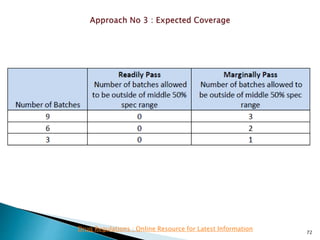
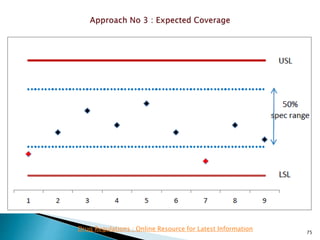
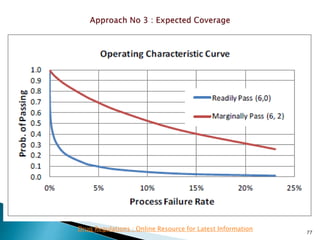
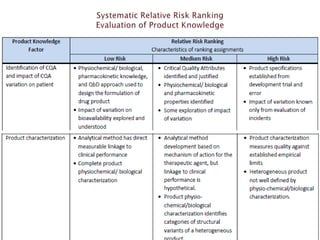
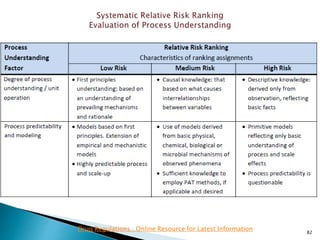
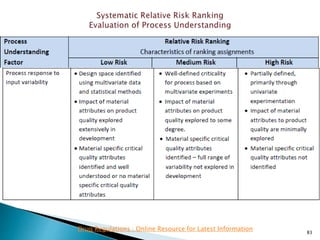
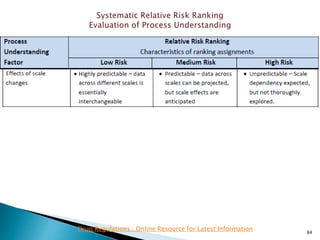
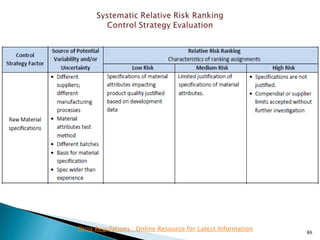
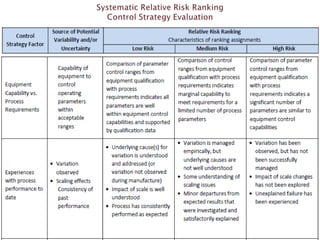
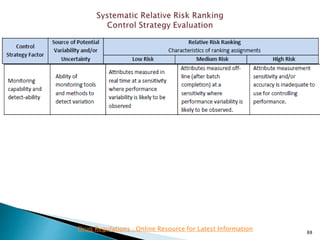
This presentation discusses approaches for determining the number of process performance qualification (PPQ) batches needed based on a risk-based assessment of product and process knowledge and the control strategy. It describes evaluating the risks associated with product attributes, process parameters, and controls. Factors that influence risk, such as raw material variability, equipment capabilities, and process performance history are reviewed. The goal is to justify the minimum number of PPQ batches required based on the level of process understanding and control.