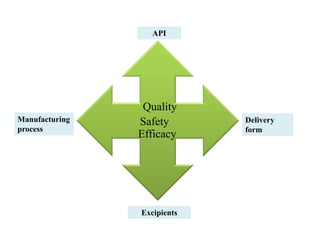
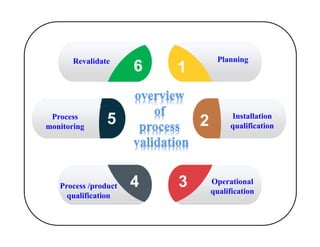
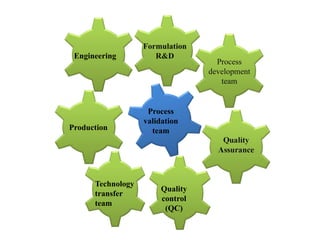
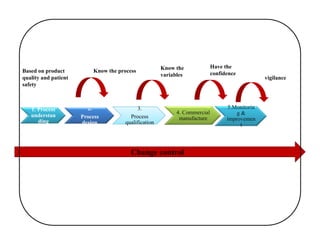
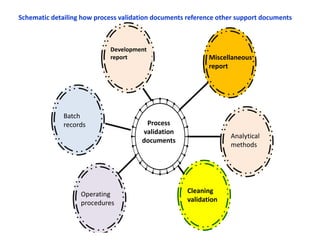
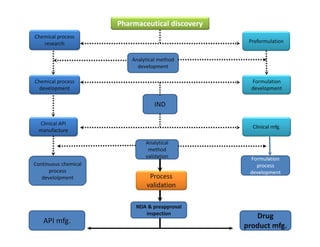
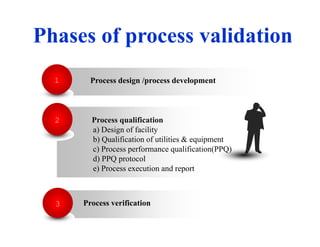
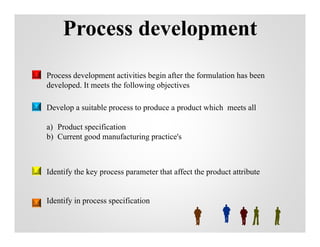
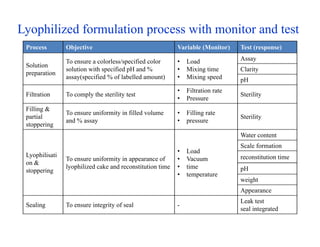
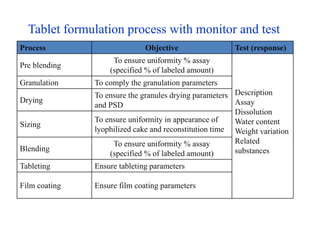
This document discusses process validation. It defines process validation as establishing documented evidence that a process will consistently produce a product meeting its predetermined specifications. The key aspects of process validation are to obtain consistent and reliable data, demonstrate that the process remains in control, and show the process works as intended. There are different types of process validation including prospective, retrospective, and concurrent validation. Process validation involves multiple phases from process design and qualification to process verification and monitoring. It is important for quality, safety, efficacy and compliance with global regulatory agencies.