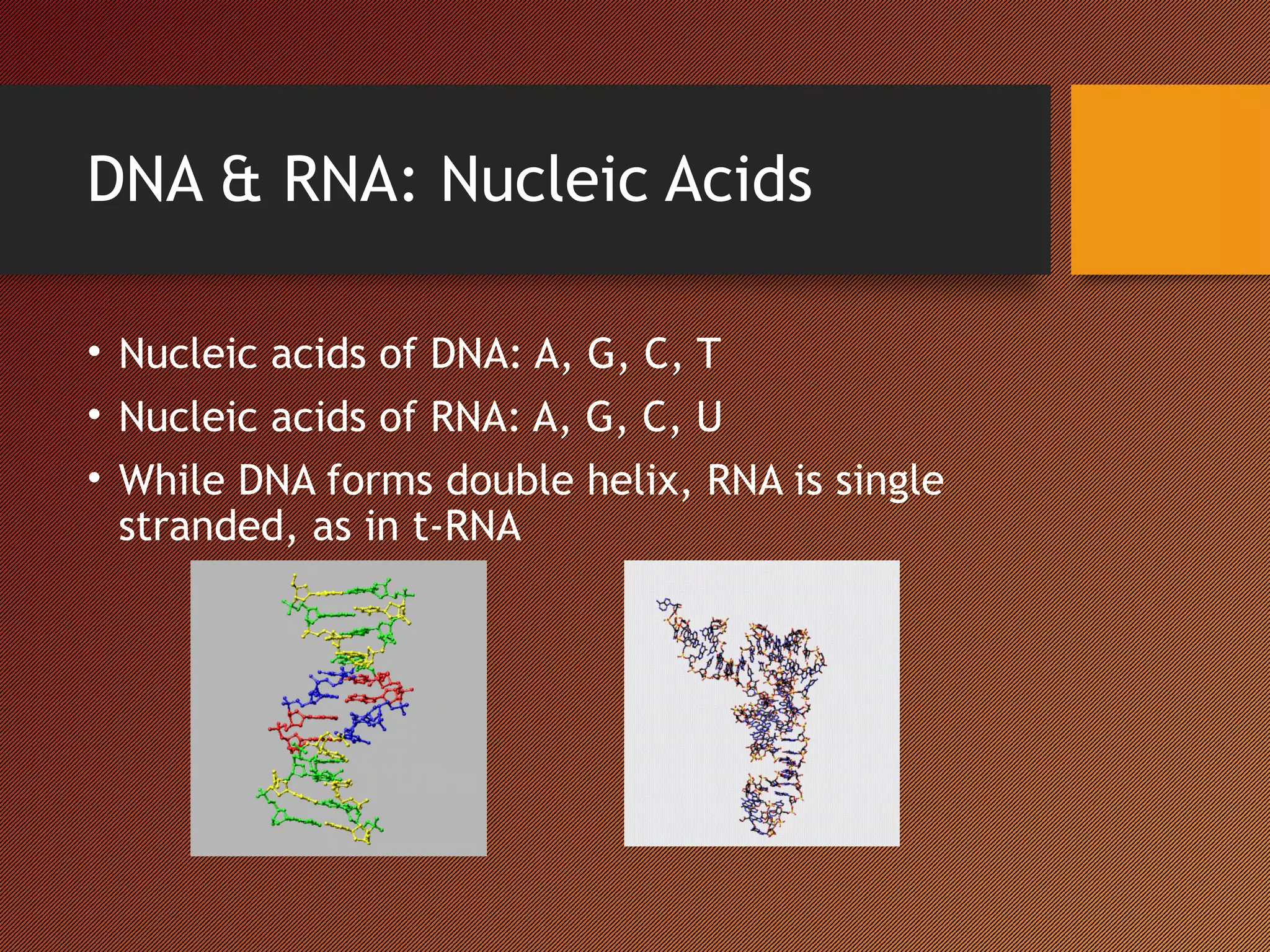
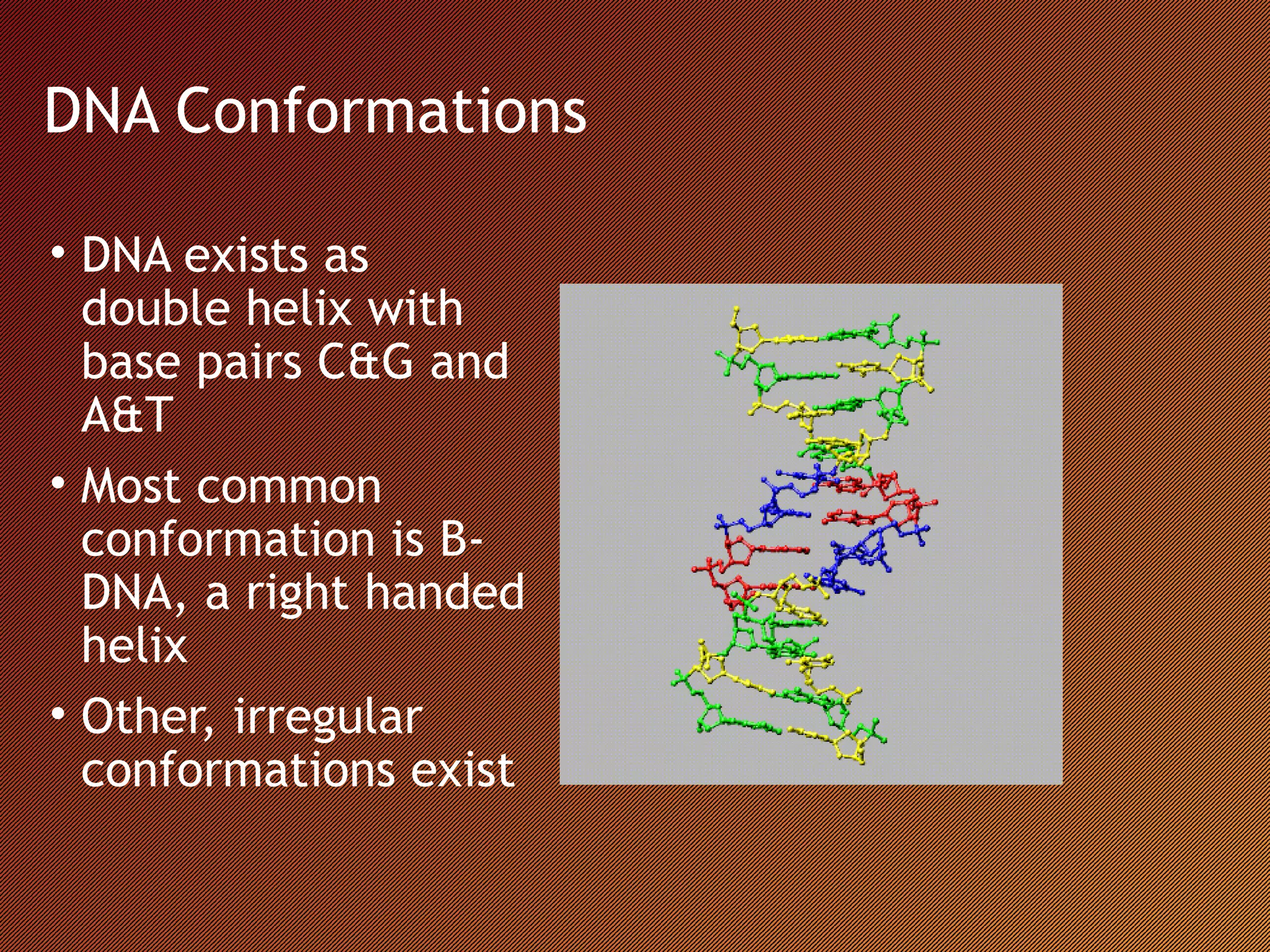
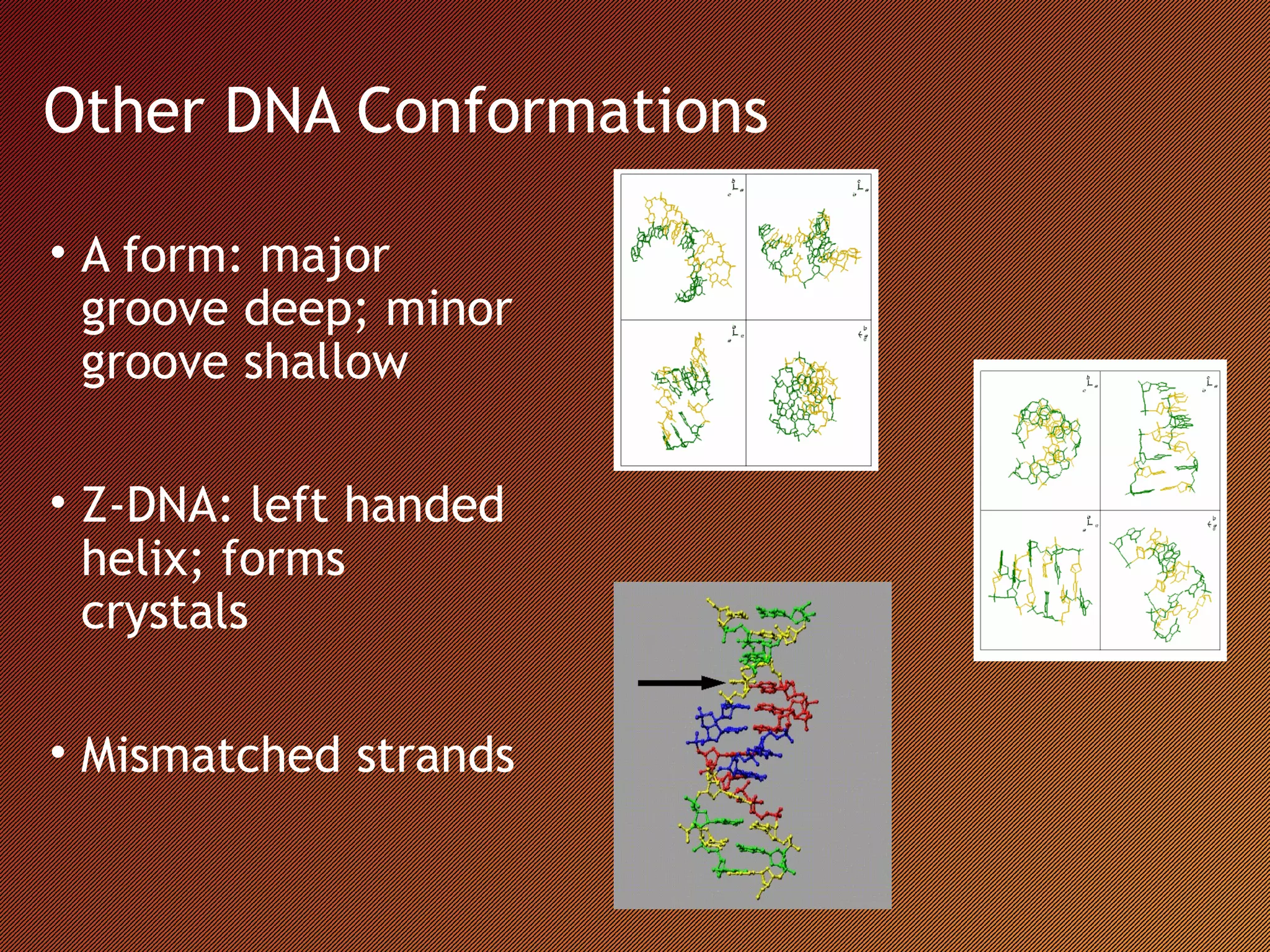
The Nucleic Acid Database provides structural references and a search engine for DNA and RNA structures. It depicts structures through systematic design based on biological data in tools like the RNA Viewer, Base Pair Viewer, and ATLAS. It also examines structures through innovative methods like the Musical Atlas, which uses musical algorithms to represent DNA structures as instrumental songs.