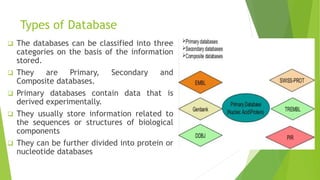
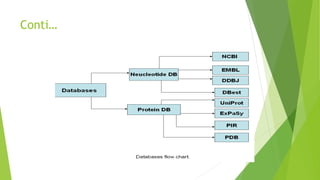
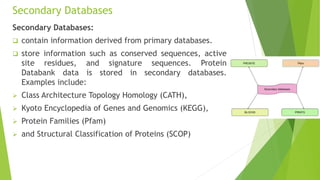
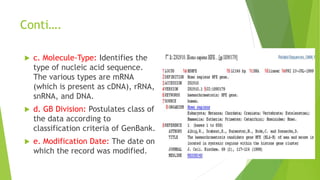
A database is a structured collection of data that can be easily accessed, managed, and updated. It consists of files or tables containing records with fields. Database management systems provide functions like controlling access, maintaining integrity, and allowing non-procedural queries. Major databases include GenBank, EMBL, and DDBJ for nucleotide sequences and UniProt, PDB, and Swiss-Prot for proteins. The NCBI maintains many biological databases and provides tools for analysis.