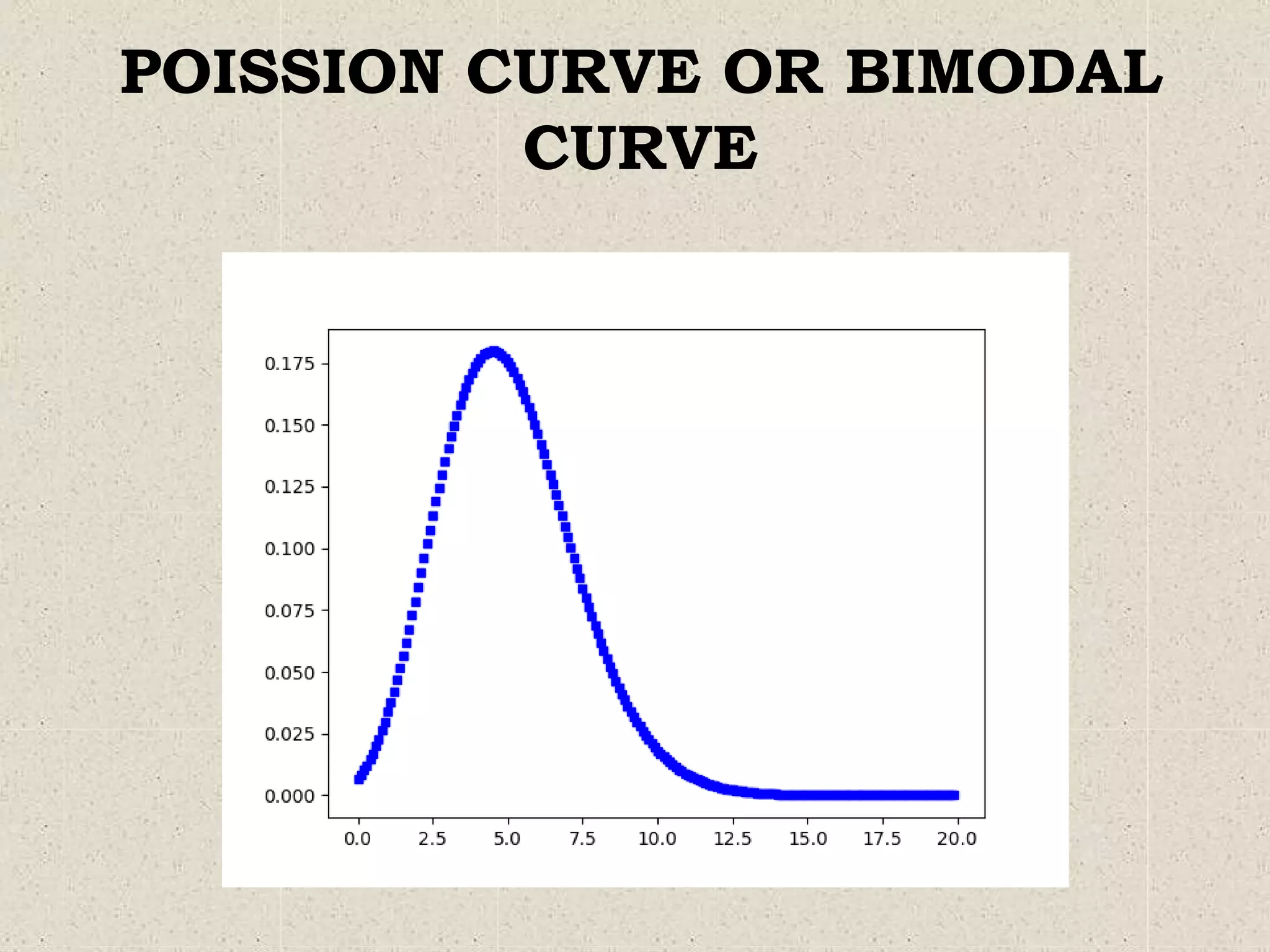
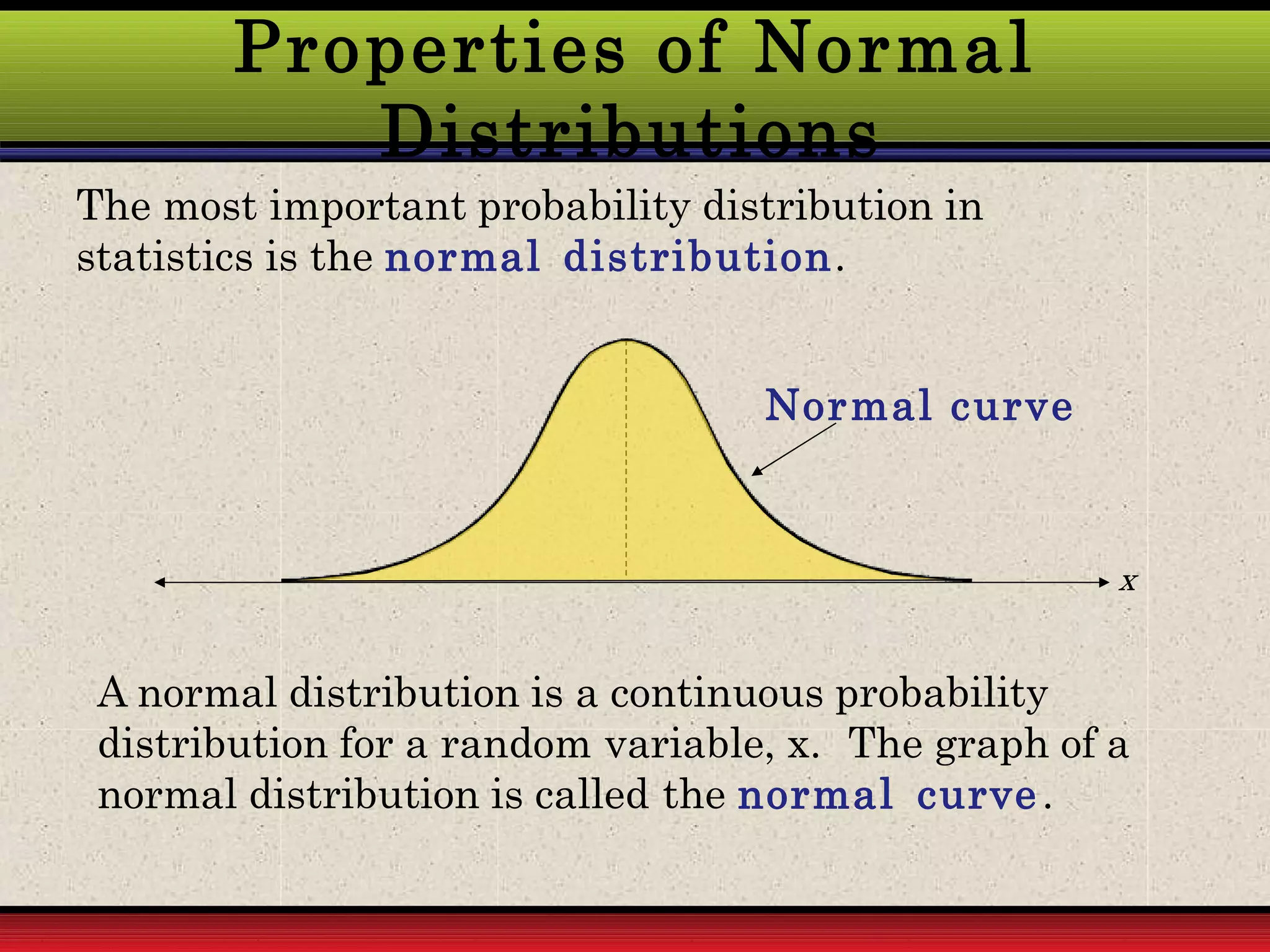
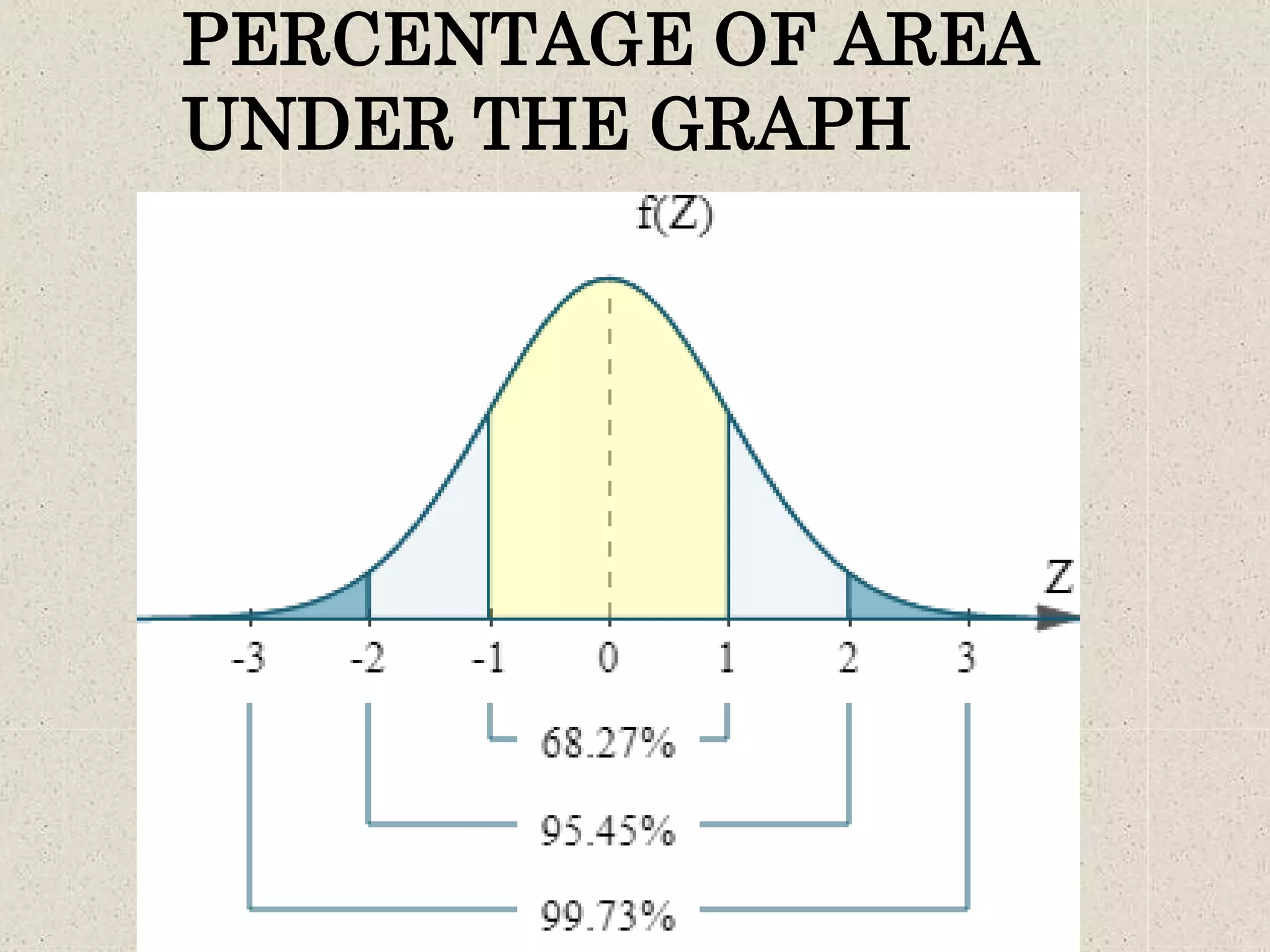
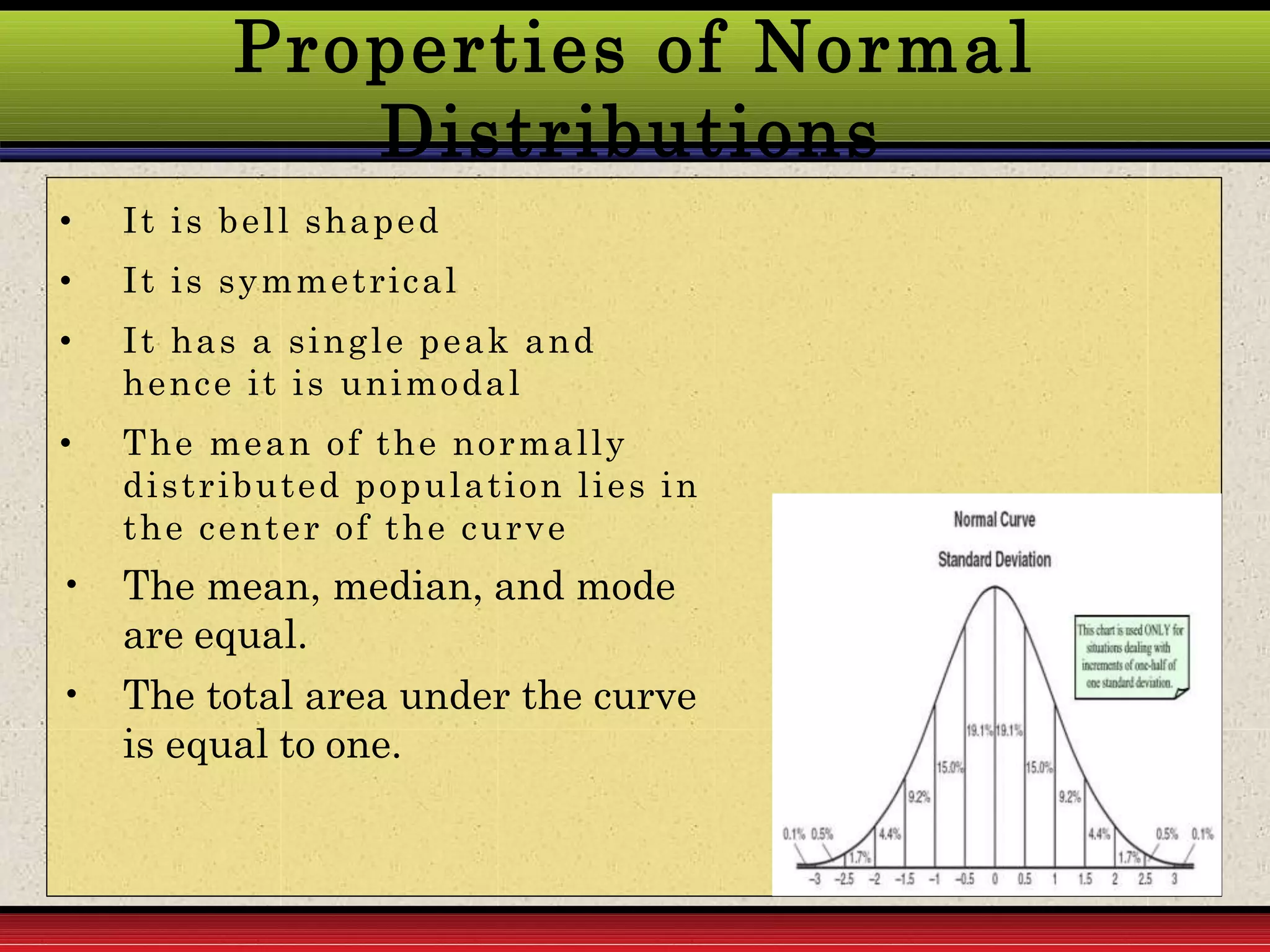
This document provides an overview of the normal probability curve. Some key points:
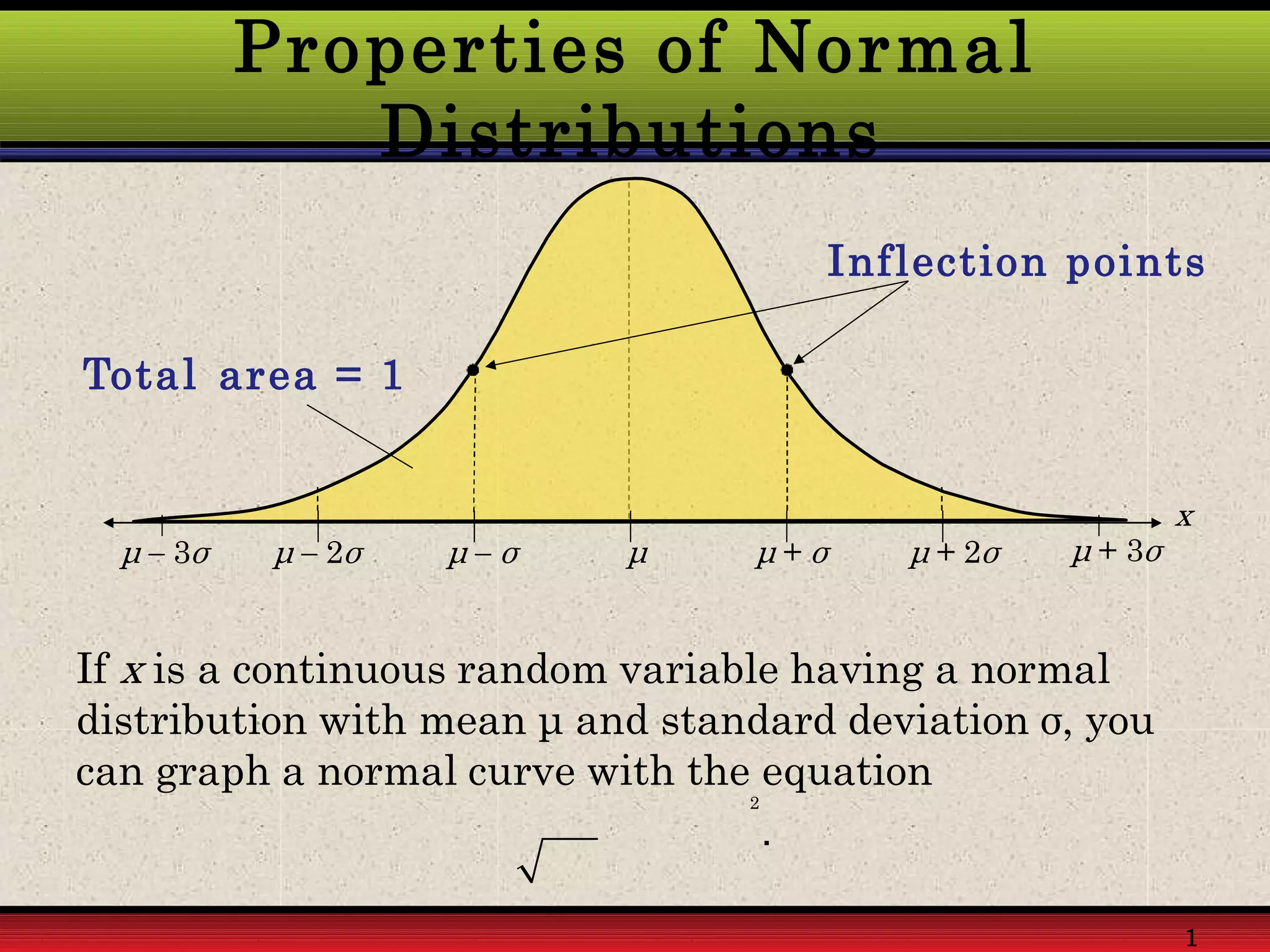
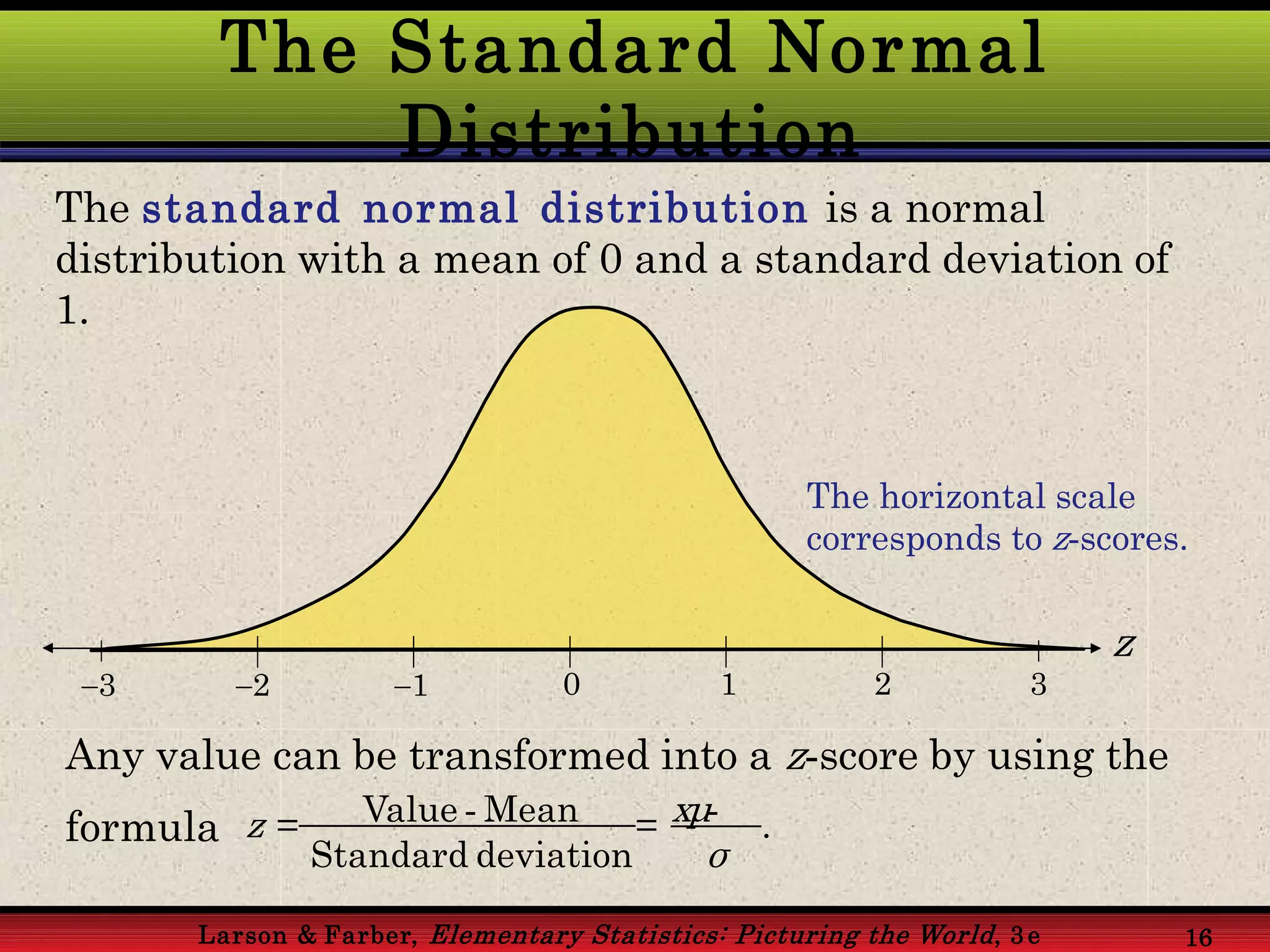
1. A normal probability curve, also called a normal distribution, shows how continuous data is distributed with the mean in the center. Most observations will be near the mean and fewer will be at the extremes.
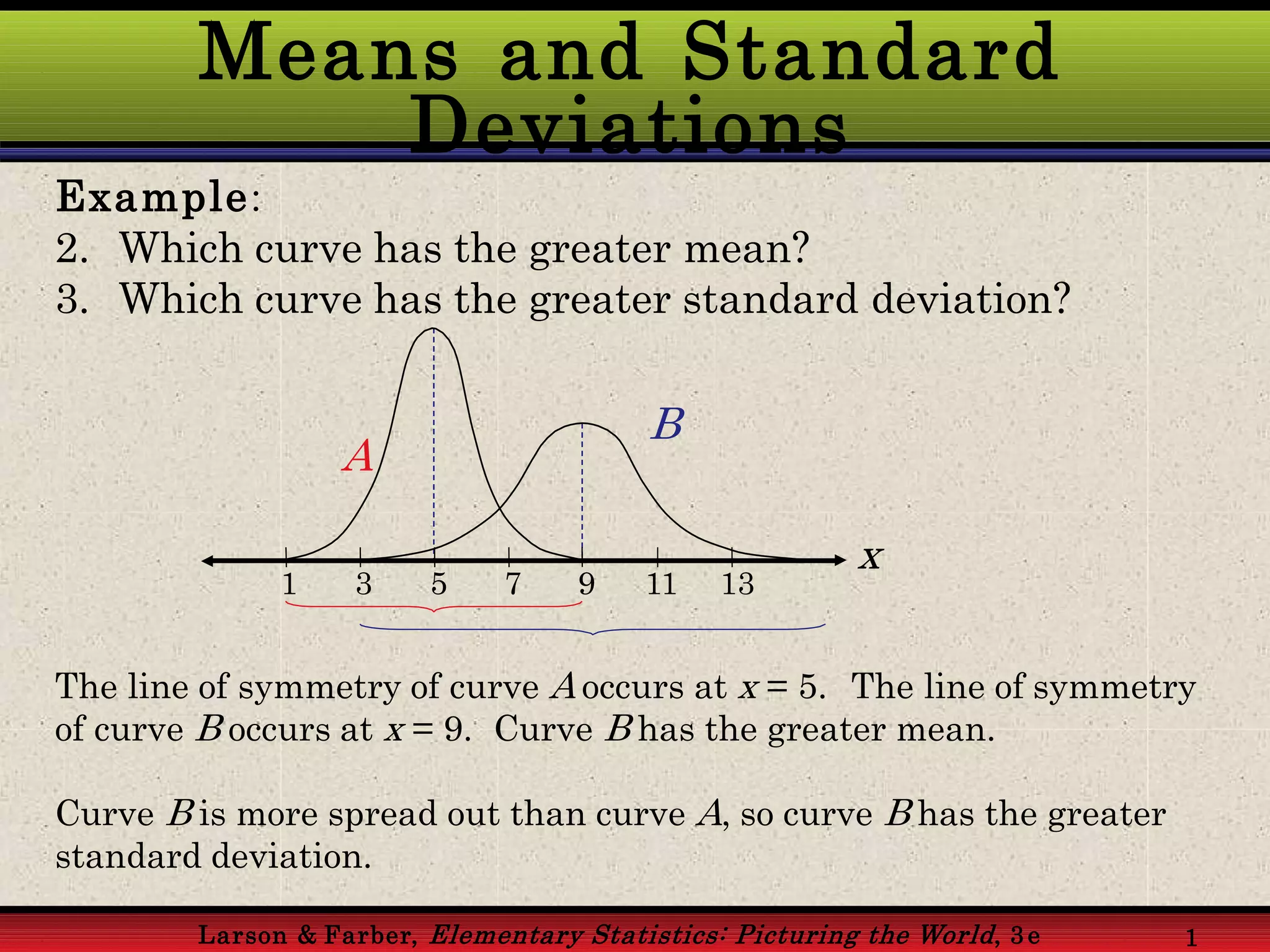
2. The curve is symmetrical and bell-shaped. It has a single peak and the mean, median, and mode are equal. Half the observations are on each side of the mean.
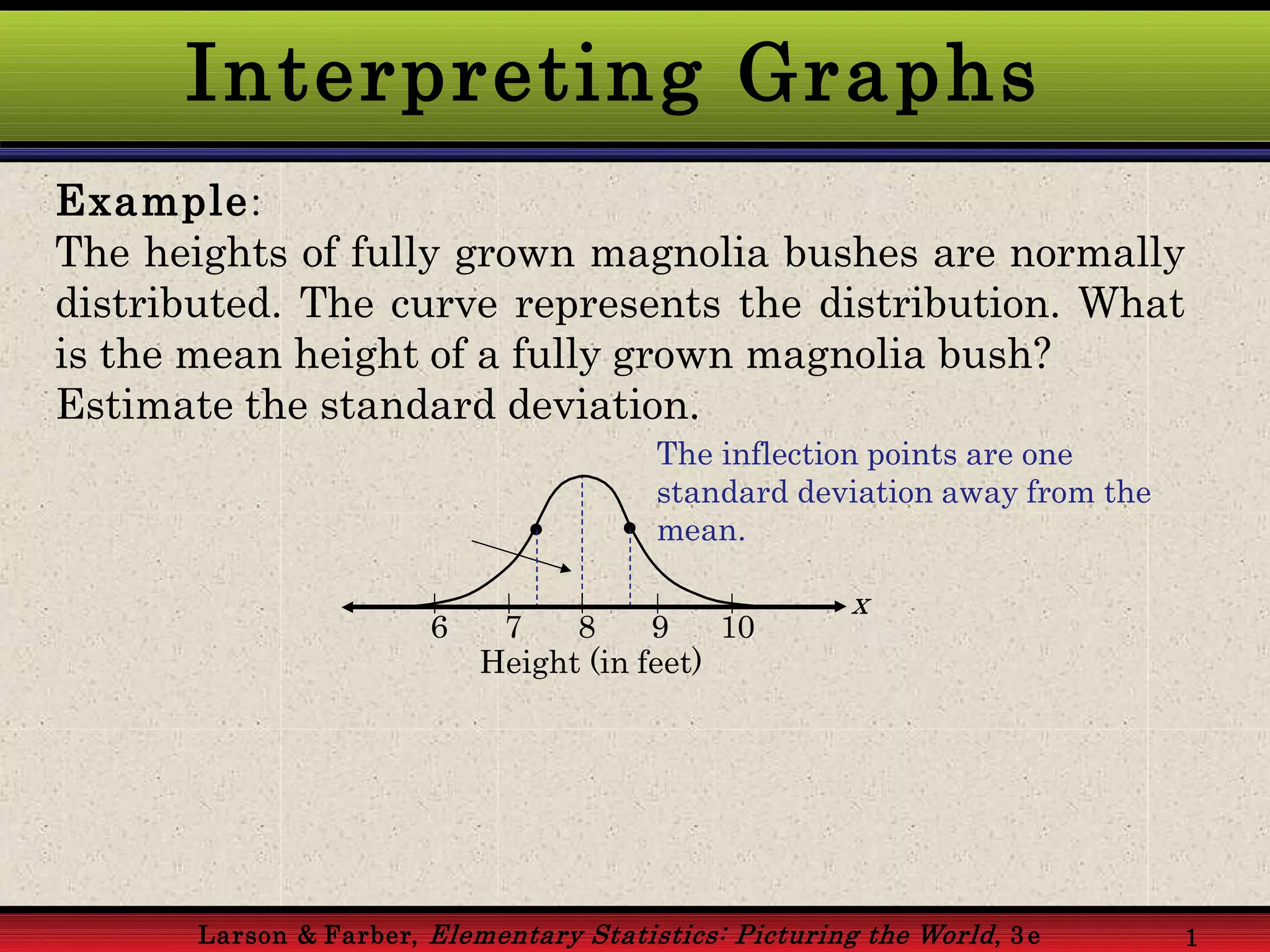
3. The curve approaches but never touches the x-axis as it extends from the mean. Between one standard deviation of the mean, the curve curves downward, and outside it curves upward.