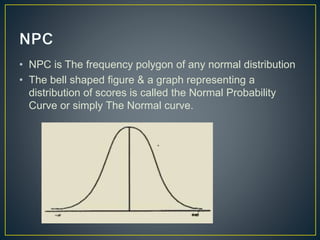
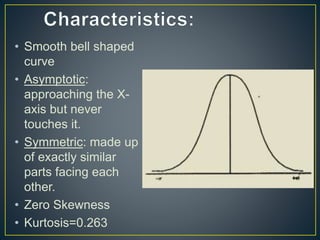
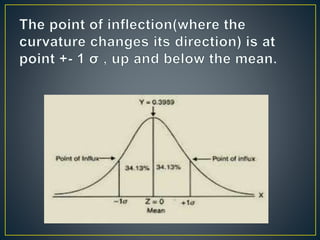
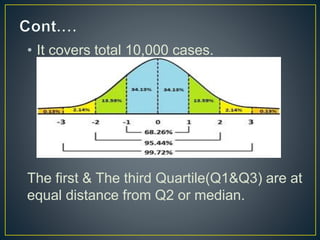
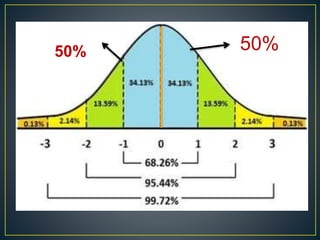
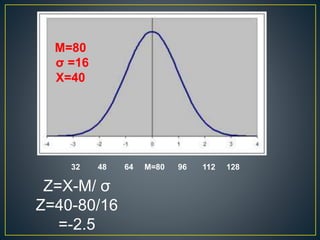
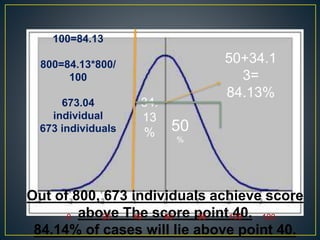
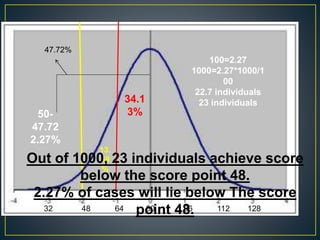
The document discusses the normal probability curve, also known as the Gaussian curve, and its characteristics including symmetry, unimodality, and specific statistical properties. It explains calculations for determining standard scores (z-scores), percentage of cases within a normal distribution, and comparisons of performance in tests across subjects. Additionally, it addresses practical applications of the normal distribution in research, measurement, and test construction.