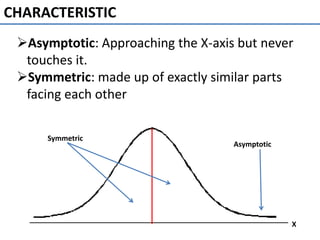
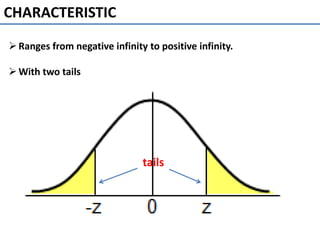
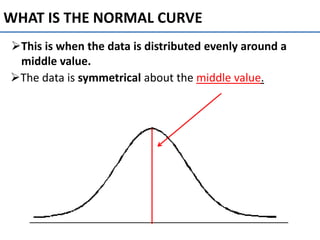
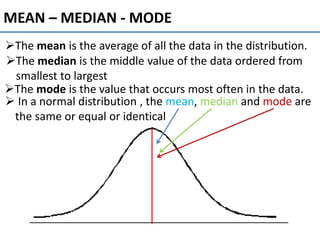
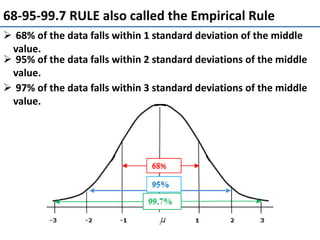
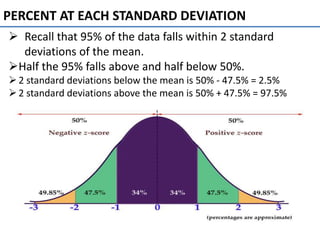
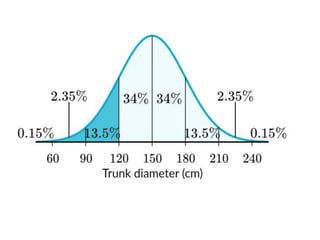
The normal curve, also called the bell curve, is an important probability distribution that is symmetric and asymptotic. It originated in the 18th century with the work of de Moivre and Laplace. The normal distribution is significant because psychological and educational variables often follow it approximately and it is easy for statisticians to work with mathematically. Key characteristics include being symmetric, ranging from negative to positive infinity, and following the 68-95-99.7 rule where most values fall within 1-3 standard deviations of the mean. The mean, median and mode are equal for a normal distribution.