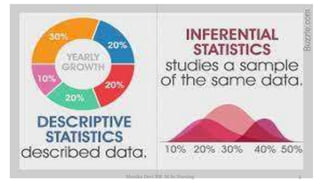
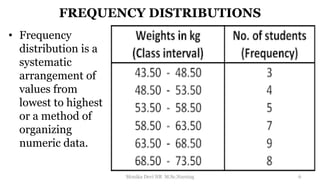
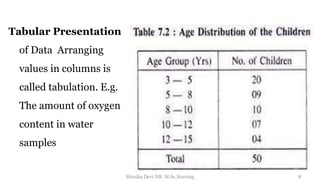
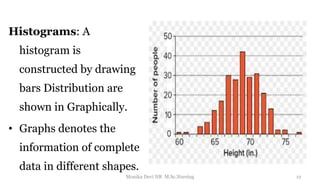
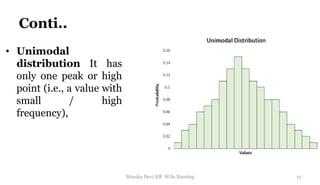
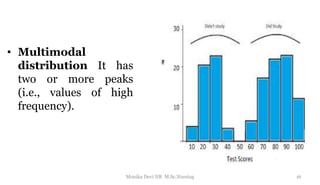
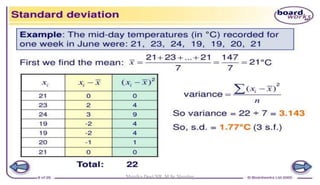
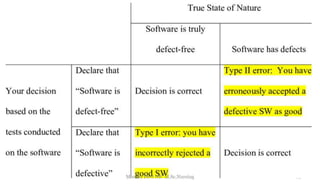
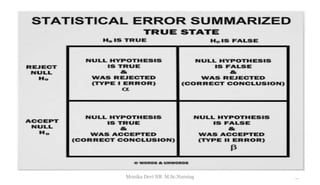
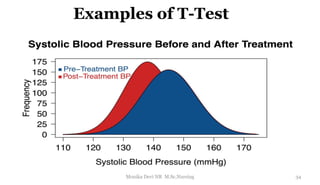
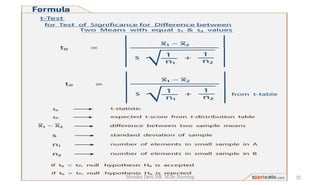
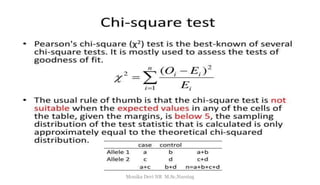
The document provides an overview of statistics as used in nursing research. It defines statistics as the science of making effective use of numerical data through collection, analysis, and interpretation. There are two main types of statistics: descriptive statistics which organize and summarize sample data, and inferential statistics which help determine if study outcomes are due to planned factors or chance. Key concepts covered include frequency distributions, measures of central tendency, variability, correlation, hypothesis testing, estimation, t-tests, chi-square tests, and analysis of variance procedures.