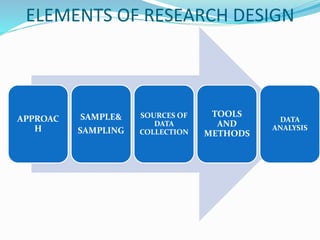
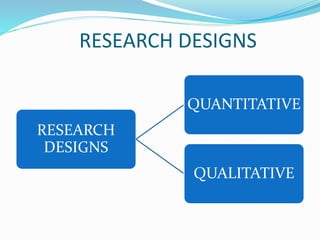
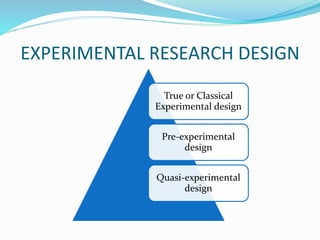
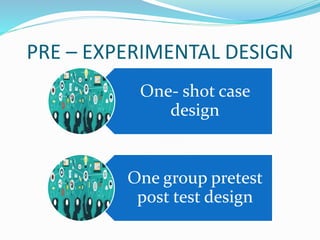
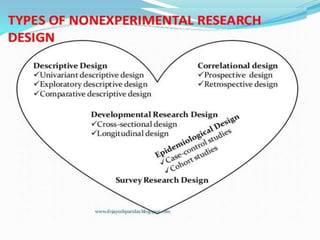
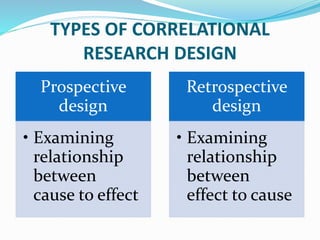
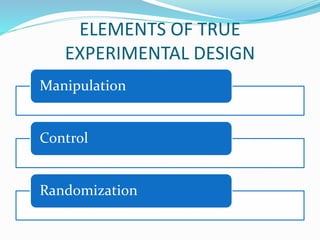
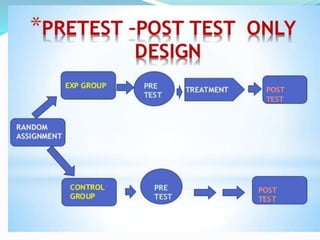
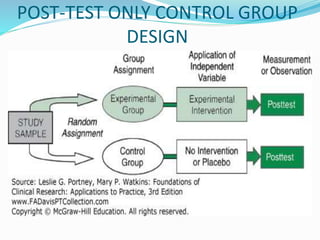
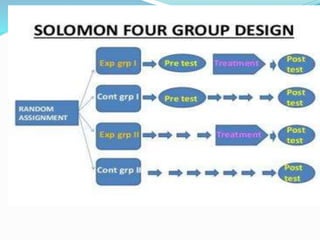
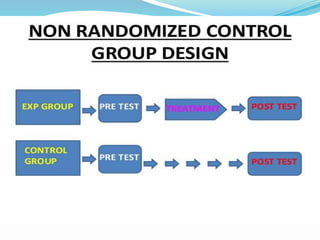
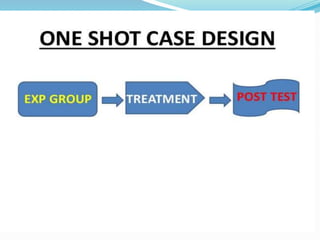
This document discusses research design in nursing. It defines research design and outlines its purposes and characteristics. The key elements of research design are identified as approach, sampling, data collection/analysis. Quantitative and qualitative designs are examined, including experimental, non-experimental, and other approaches. Specific designs like descriptive studies, correlational studies, true experiments, quasi-experiments, and pre-experiments are defined and their advantages/disadvantages discussed. Factors influencing design choice and current challenges in nursing research designs are also summarized.