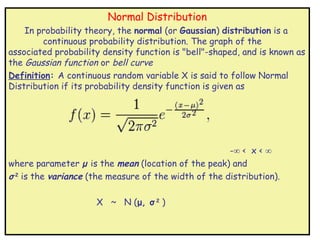
The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is symmetric and bell-shaped. It is defined by two parameters: the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ). The standard normal distribution refers to a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and standard deviation of 1. The normal distribution and standard normal distribution have many useful properties and applications in statistics. Tables of the standard normal distribution are often used to find probabilities associated with the normal distribution.


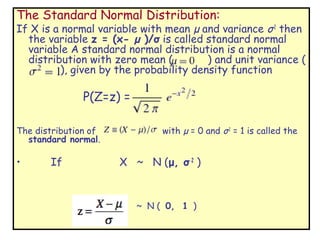






![Normal Probability:
1] As normal distribution is continuous distribution,
probability at a point is zero i.e. P ( z = a ) = 0
2] As the standard normal distribution is symmetric about
mean (=0). P (z < 0 ) = P ( z > 0 ) = ½
3] P ( 0 < z < a) then table value for a gives the required
probability.
4] P (-a < z < 0) = P ( 0 < z < a) as the curve is symmetric
about 0.
5] P( z < -a) = P ( z > a) = P ( z > 0 ) - P ( 0 < z < a)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/normaldistri-130125003135-phpapp02/85/Normal-distri-11-320.jpg)
![• 1]Question: What is the relative frequency of observations
below 1.18?
• That is, find the relative frequency of the event Z < 1.18. (Here
small z is 1.18.) (Or P(Z < 1.18 )
• P( z < 1.18) = P( z < 0 ) + P ( 0 < z < 1.18)
• = 0.5 + 0.3810
• = 0.8810](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/normaldistri-130125003135-phpapp02/85/Normal-distri-12-320.jpg)
![2] P(z<-0.63) = P(z>0.63) = P(z>0) – P(0<z<063) = 0.2643
3] P(z>-1.48) = P(z>0) + P(0<z<1.48) = 0.9306](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/normaldistri-130125003135-phpapp02/85/Normal-distri-13-320.jpg)
![4] P( -1.65 < z < 1.65 ) = 2 P ( 0< z < 1.65 )
5] P(z<0.84) = 0.8000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/normaldistri-130125003135-phpapp02/85/Normal-distri-14-320.jpg)

![• Example 1
An average light bulb manufactured by the Acme
Corporation lasts 300 days with a standard deviation of
50 days. Assuming that bulb life is normally distributed,
what is the probability that an Acme light bulb will last
at most 365 days?
• Example 2
Suppose scores on an IQ test are normally distributed.
If the test has a mean of 100 and a standard deviation
of 10, what is the probability that a person who takes
the test will score between 90 and 110?
[P( 90 < X < 110 ) = P( X < 110 ) - P( X < 90 )
P( 90 < X < 110 ) = 0.84 - 0.16
P( 90 < X < 110 ) = 0.68
• Thus, about 68% of the test scores will fall between 90
and 110.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/normaldistri-130125003135-phpapp02/85/Normal-distri-16-320.jpg)
![• Problem 3
• Molly earned a score of 940 on a national achievement
test. The mean test score was 850 with a standard
deviation of 100. What proportion of students had a
higher score than Molly? (Assume that test scores are
normally distributed.)
• [z = (X - μ) / σ = (940 - 850) / 100 = 0.90
• we find P(Z < 0.90) = 0.8159.
Therefore, the P(Z > 0.90) = 1 - P(Z < 0.90) = 1 - 0.8159
= 0.1841. Thus, we estimate that 18.41 percent of the
students tested had a higher score than Molly. ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/normaldistri-130125003135-phpapp02/85/Normal-distri-17-320.jpg)


![• Answer:
• Mean = [600 + 470 + 170 + 430 + 300]/5 = 1970/5 = 394
•
• so the mean (average) height is 394 mm. Let's plot this on the
chart:
• Now, we calculate each dogs difference from the Mean:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/normaldistri-130125003135-phpapp02/85/Normal-distri-20-320.jpg)
![• To calculate the Variance, take each difference, square it, and then average the
result:
• Variance: σ2 = [2062 + 762 + (-224)2 + 362 + (-94)2 ]/5 = 108,520/5 = 21,704
• So, the Variance is 21,704.
• And the Standard Deviation is just the square root of Variance, so:
• Standard Deviation: σ = √21,704 = 147.32... = 147 (to the nearest mm)
•
• And the good thing about the Standard Deviation is that it is useful. Now we can
show which heights are within one Standard Deviation (147mm) of the Mean:
• So, using the Standard Deviation we have a "standard" way of knowing what is
normal, and what is extra large or extra small.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/normaldistri-130125003135-phpapp02/85/Normal-distri-21-320.jpg)