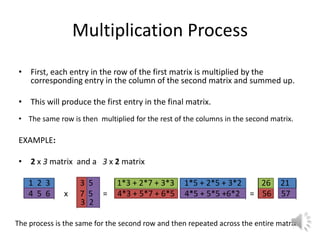
To multiply matrices, the number of columns in the first matrix must equal the number of rows in the second matrix. Each entry in a row of the first matrix is multiplied by the corresponding entry in a column of the second matrix and summed. This process is repeated for each row and column to populate the final matrix. The dimensions of the final matrix will be the number of rows in the first matrix and the number of columns in the second.