Embed presentation
Download as PPSX, PPTX
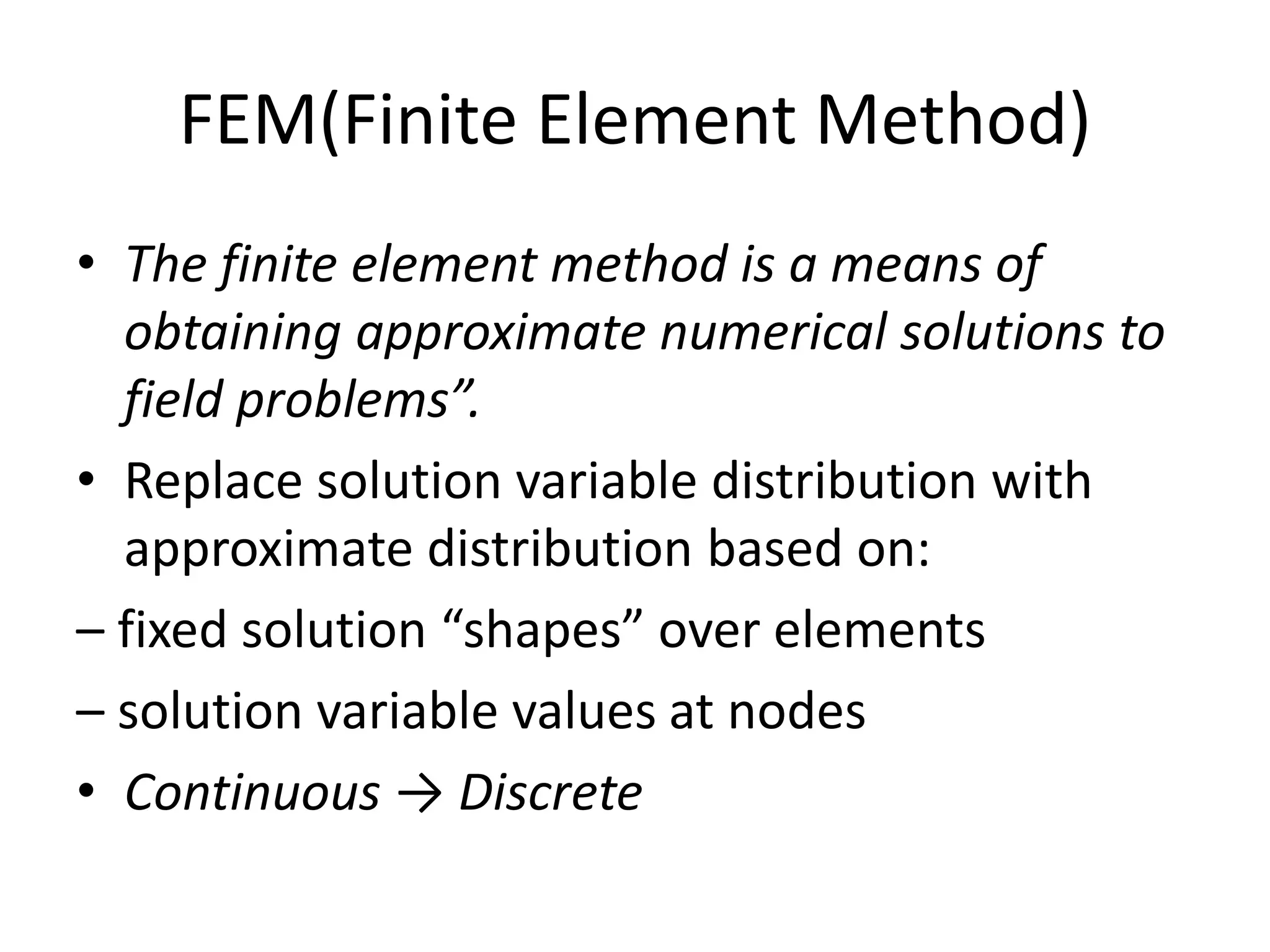
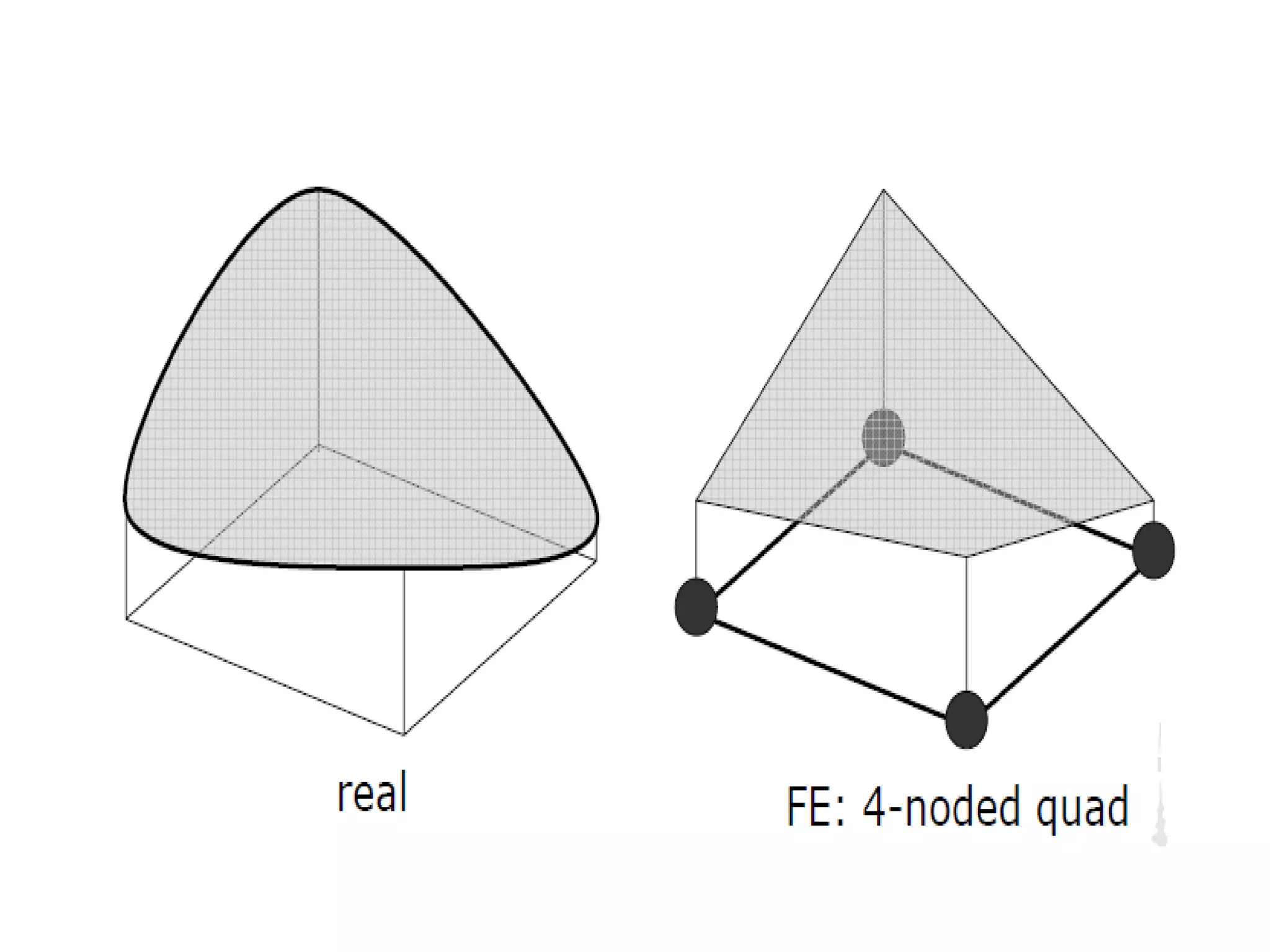
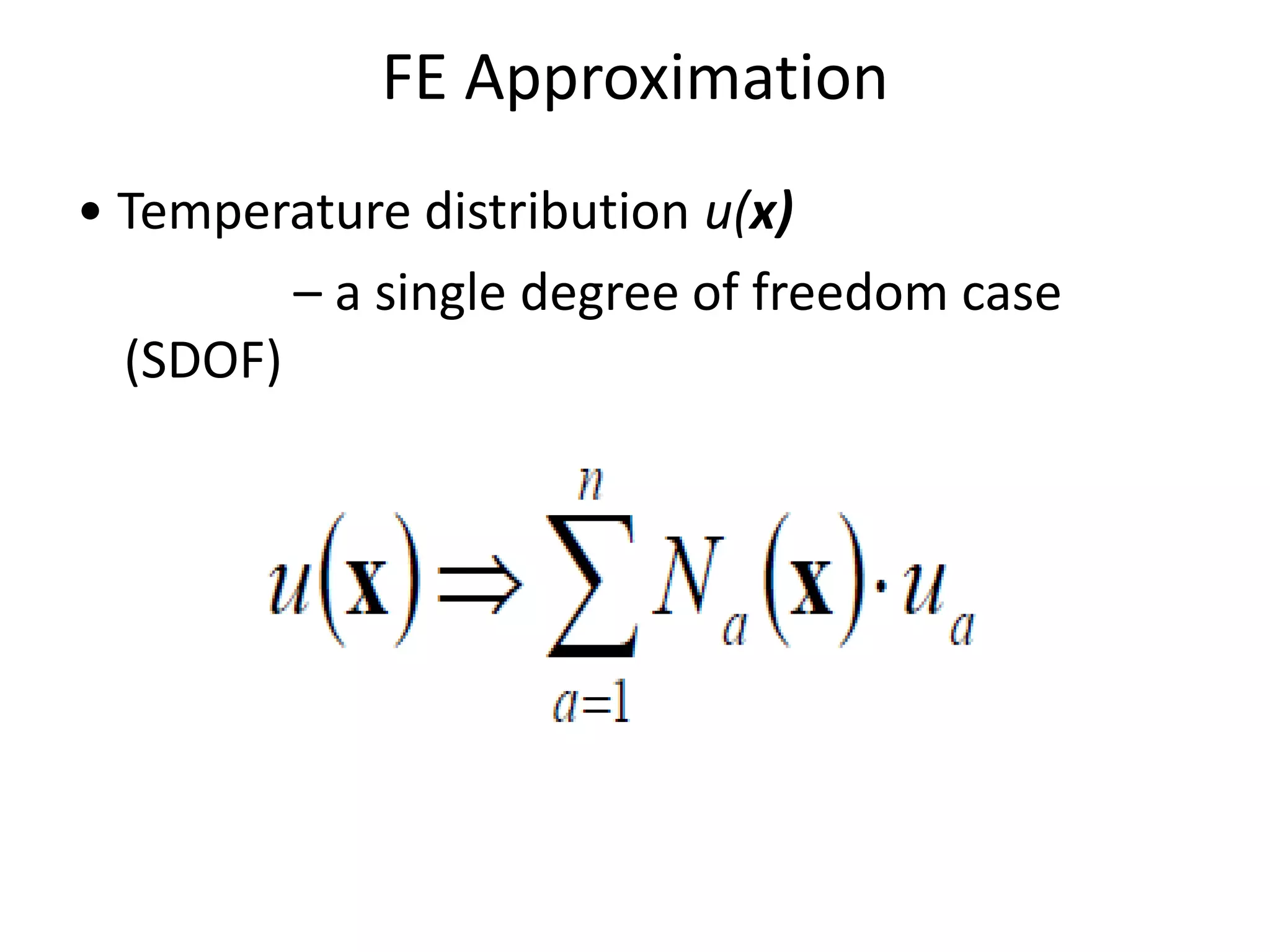

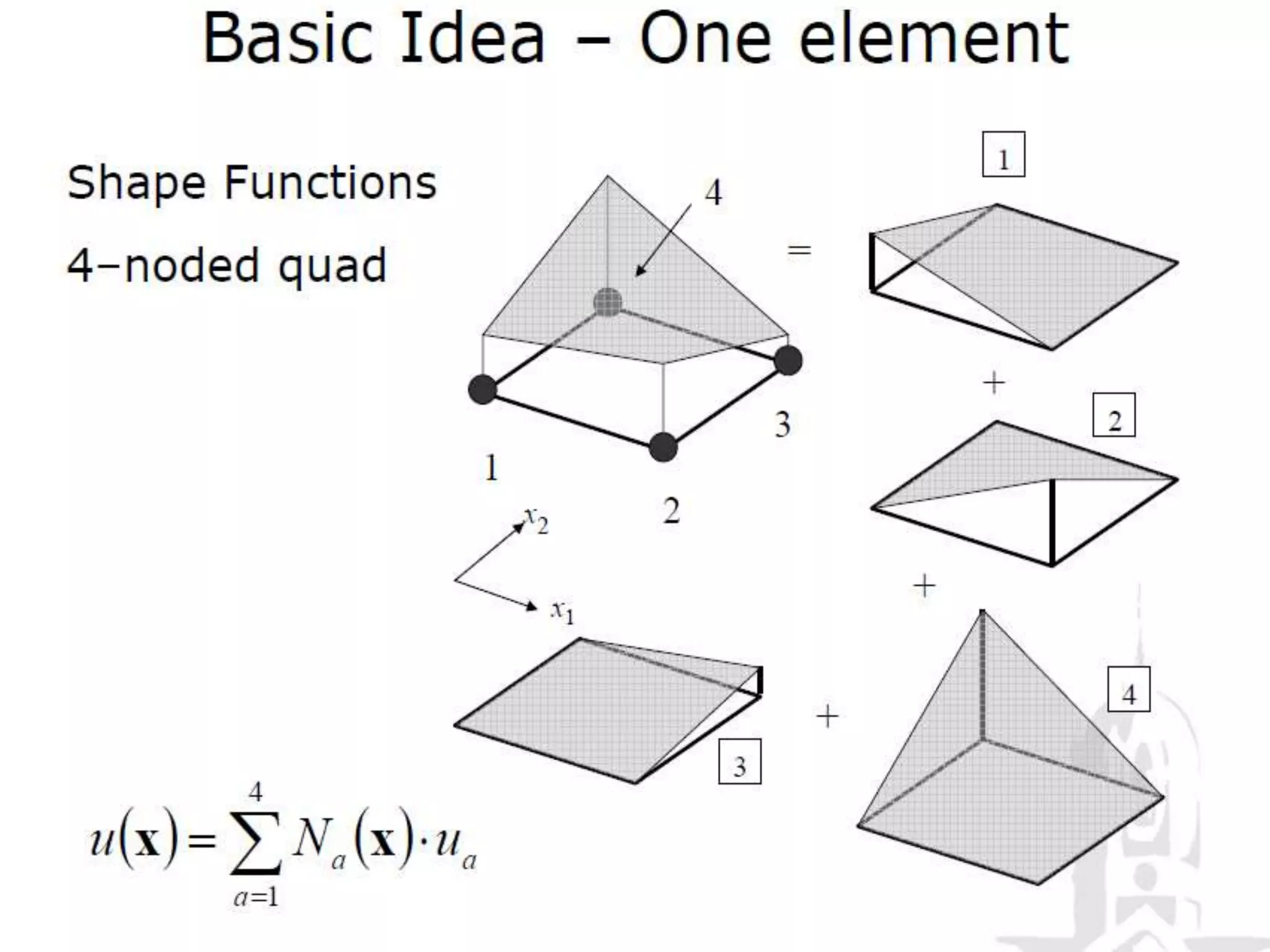
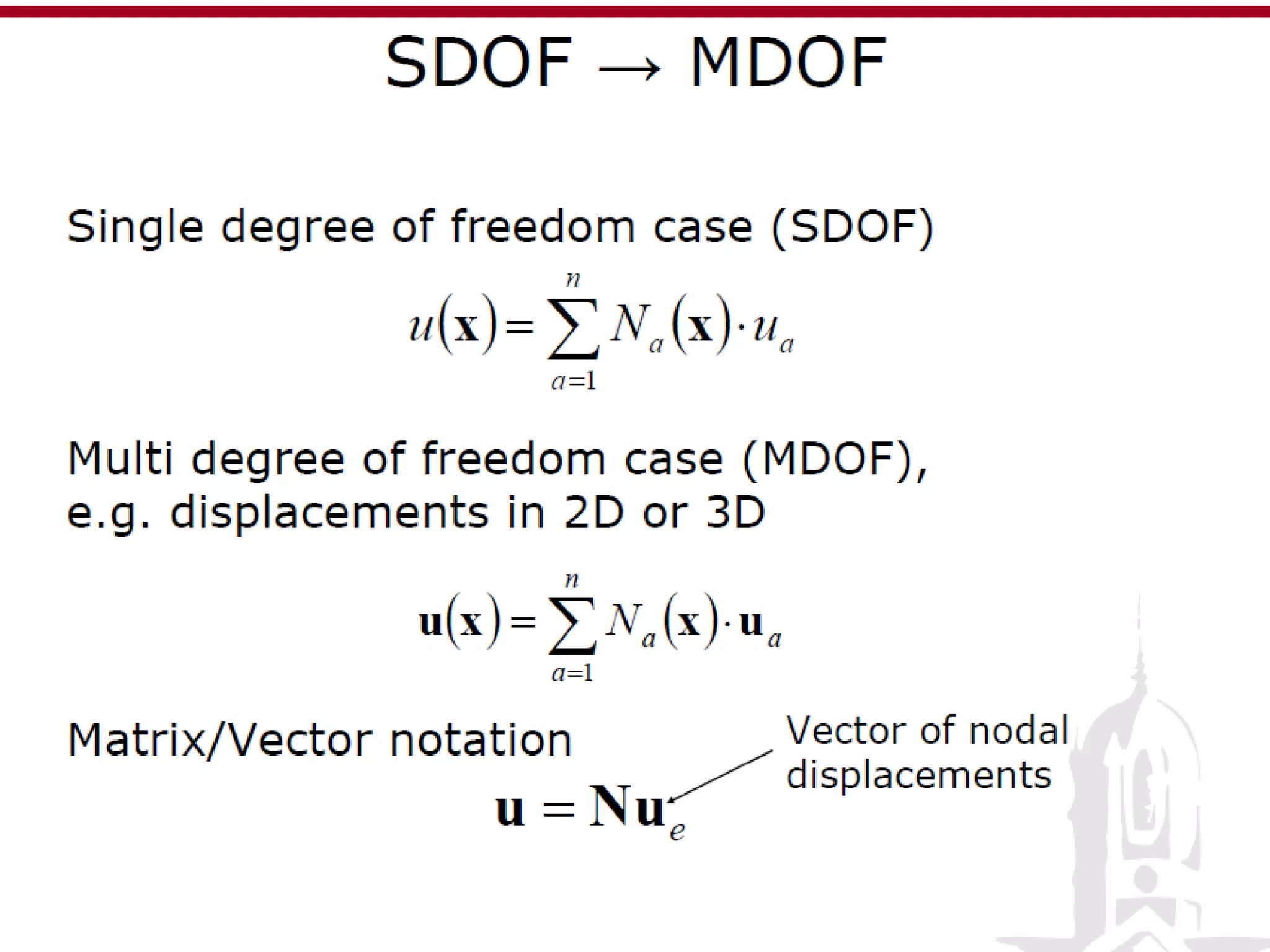
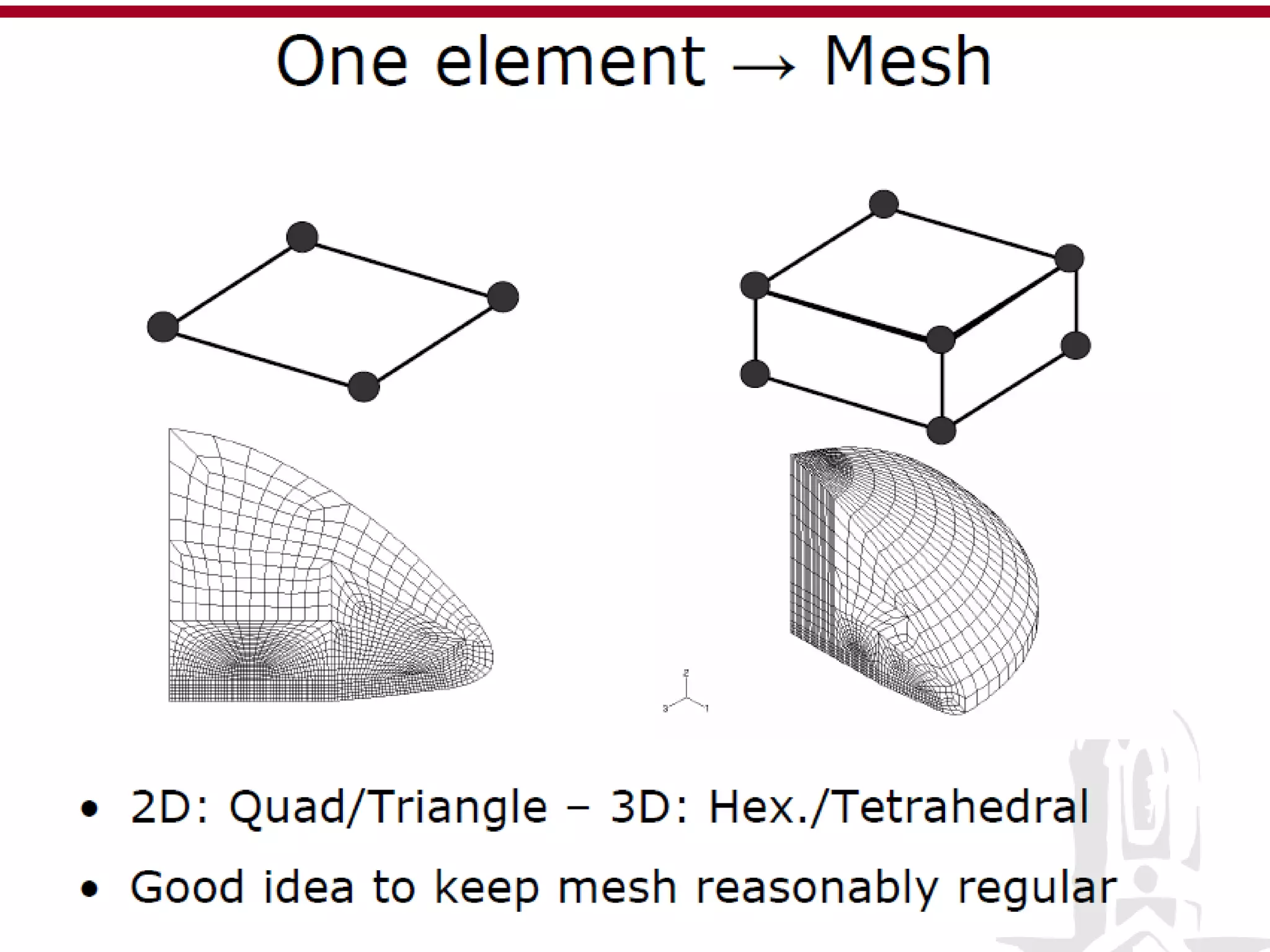
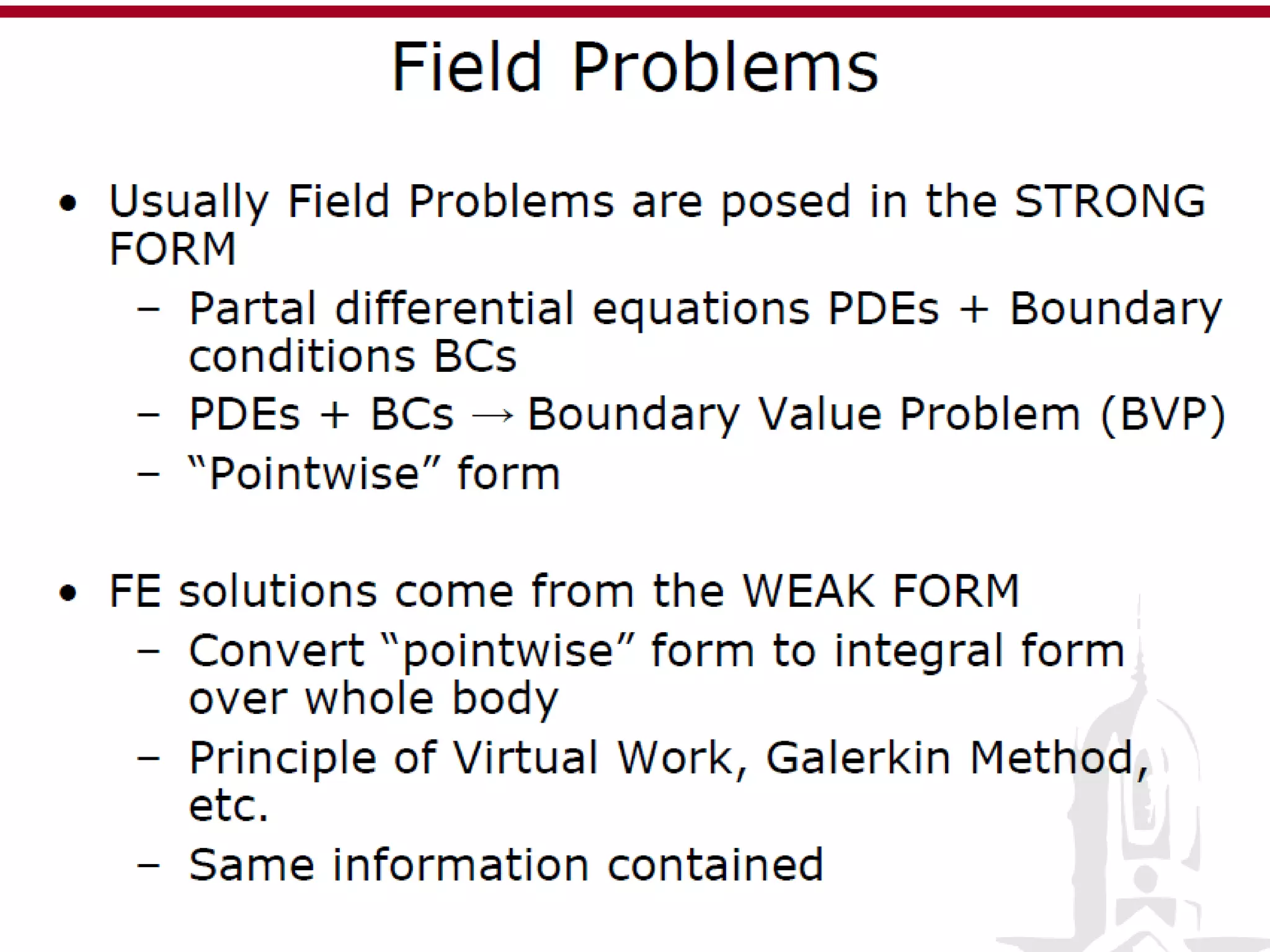
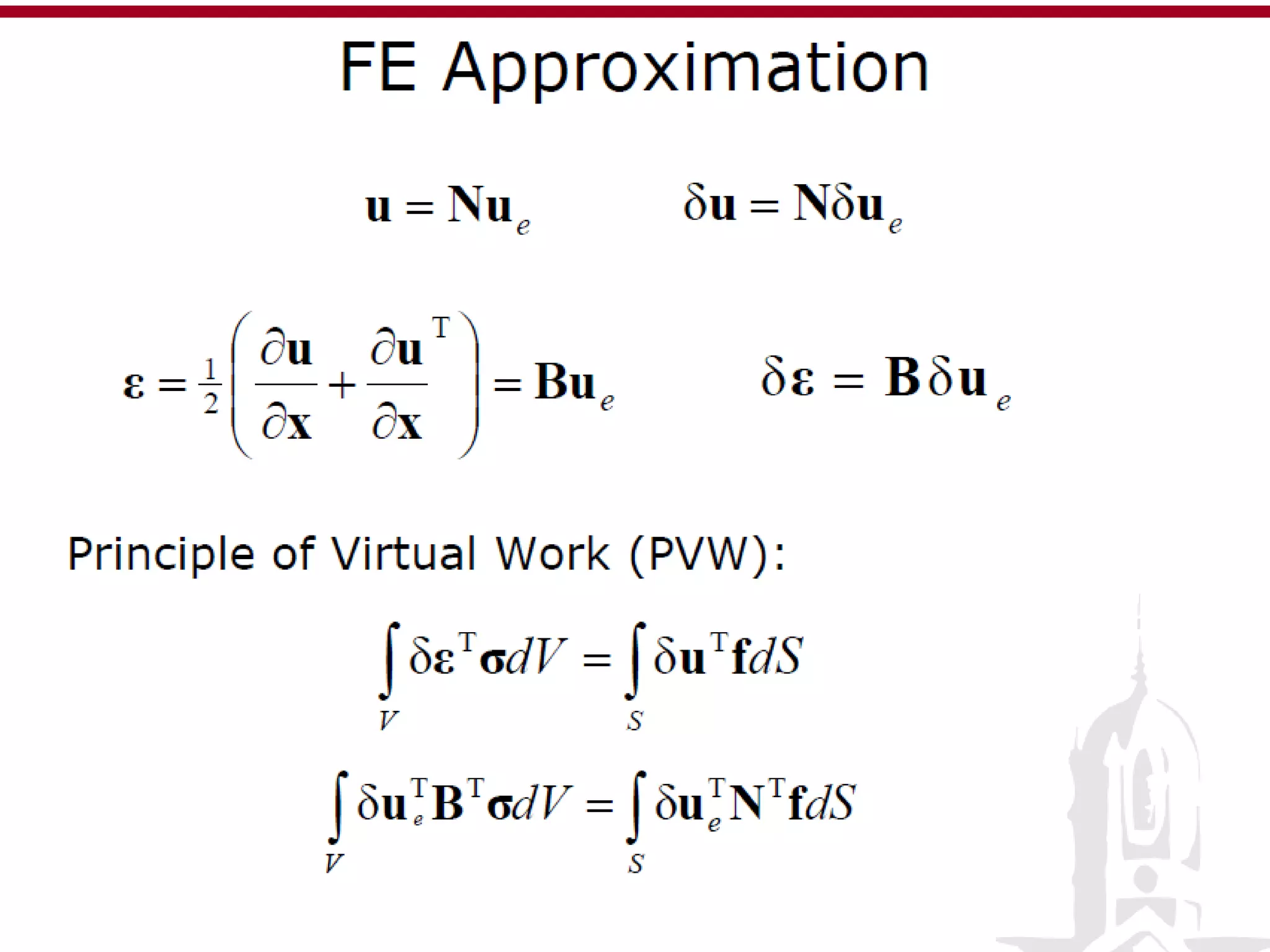
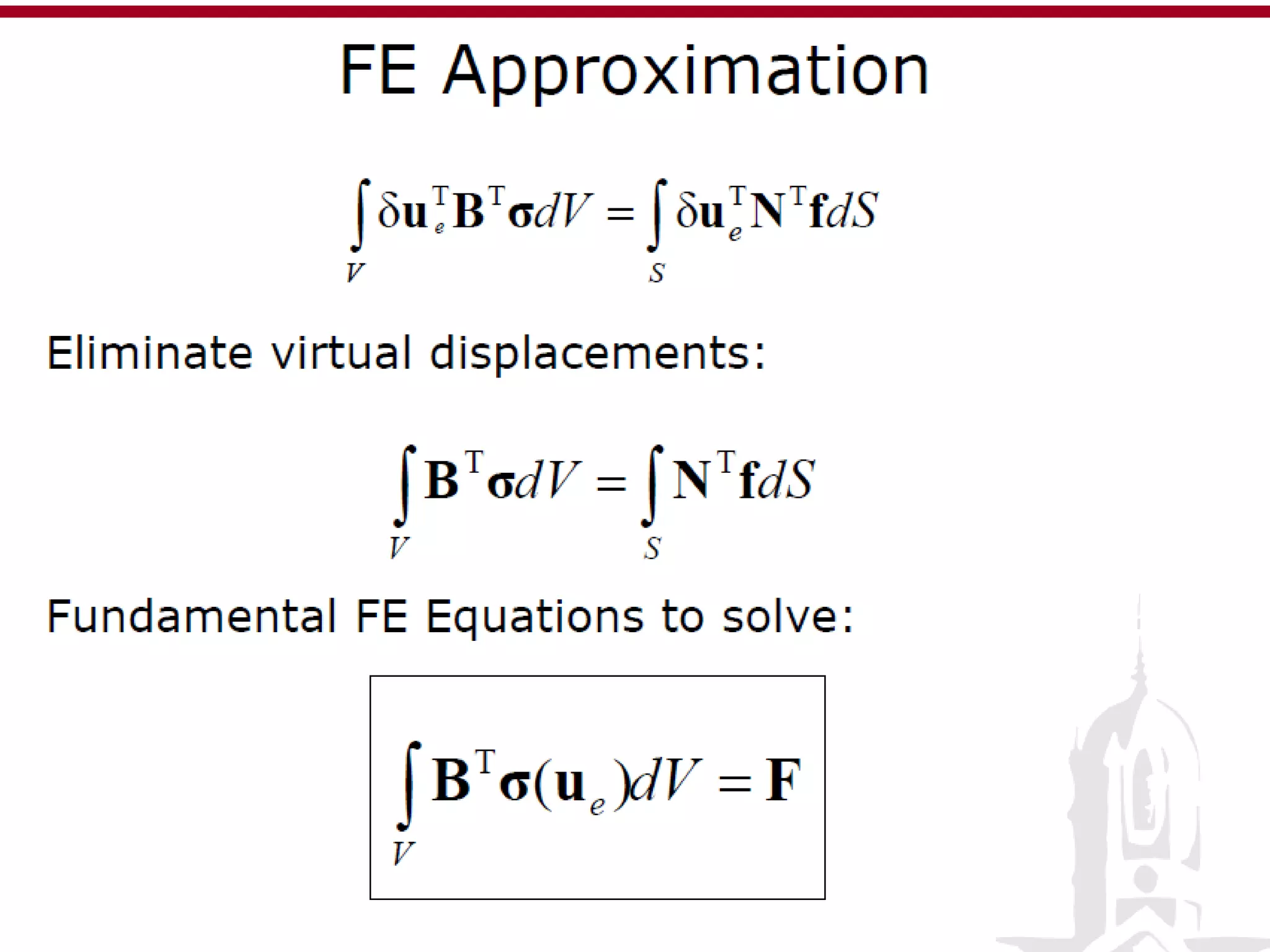
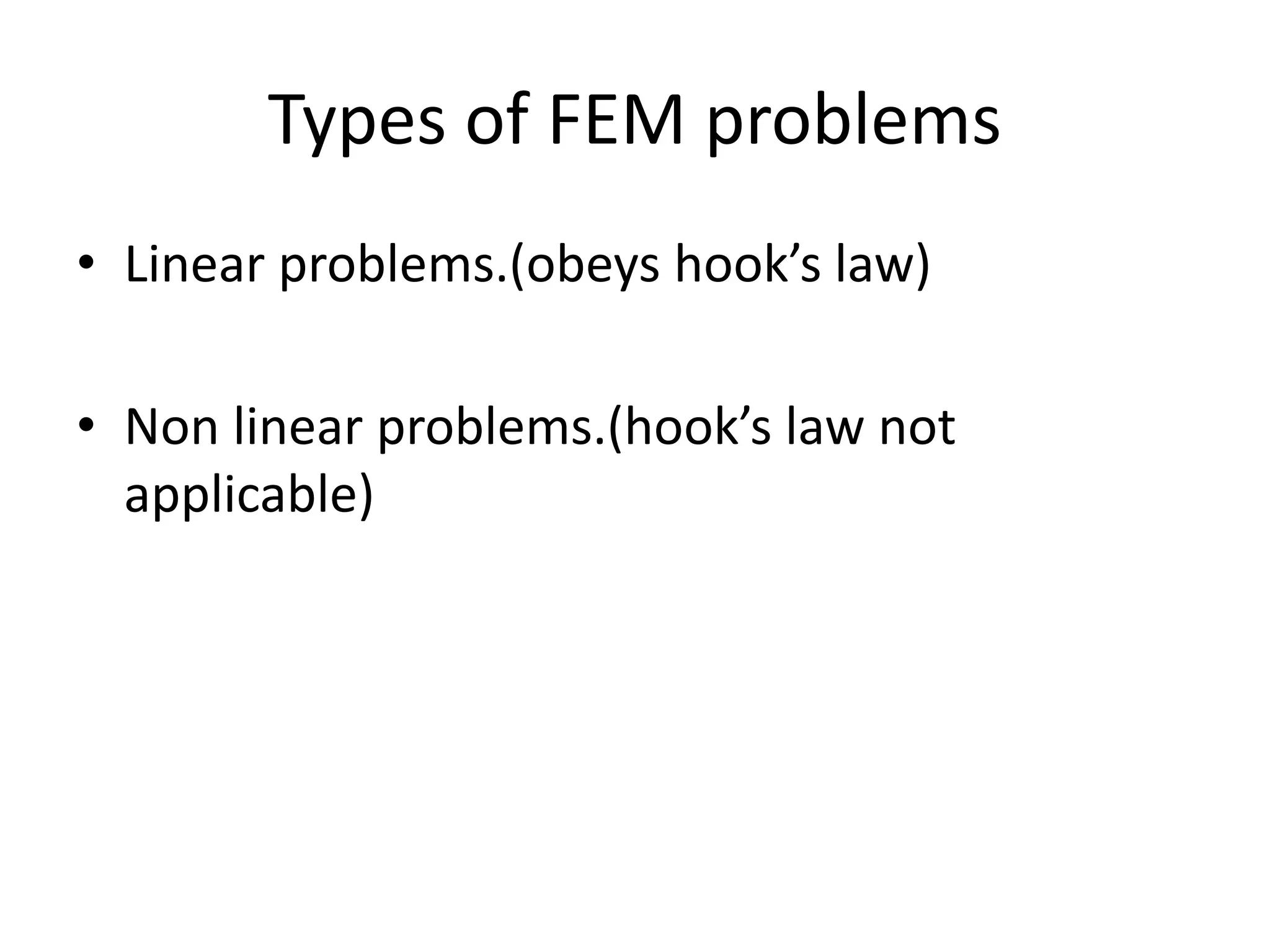
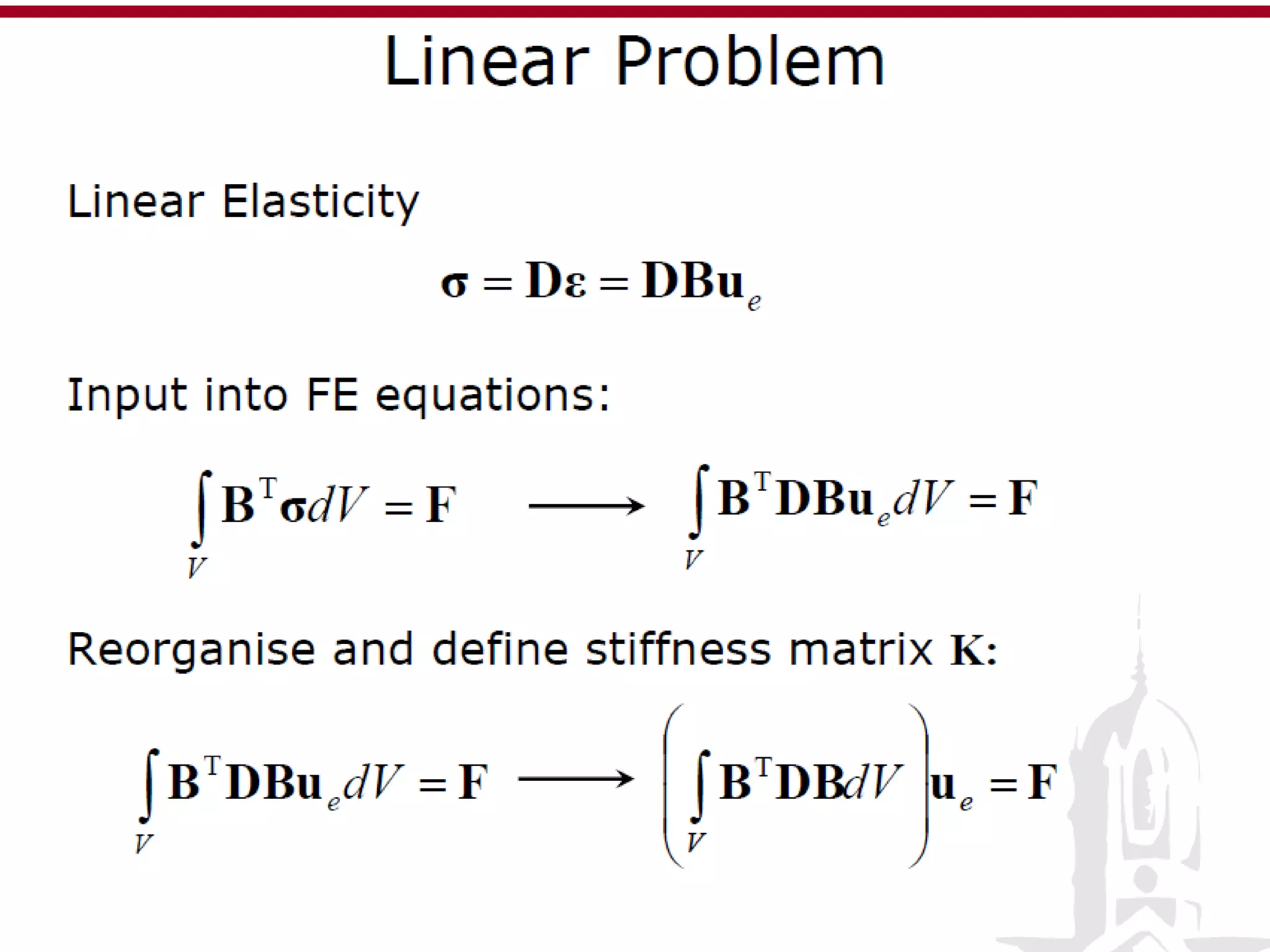
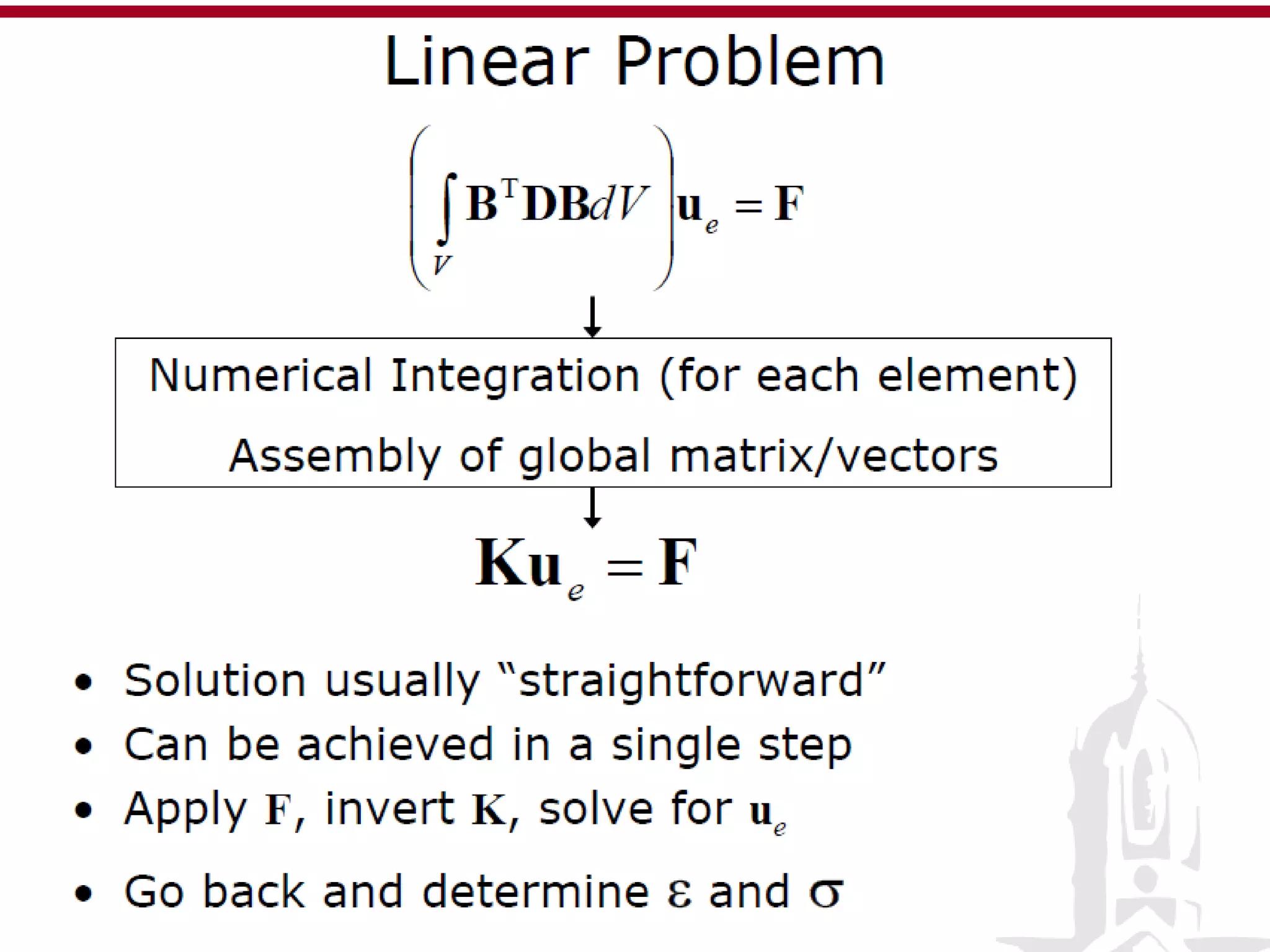
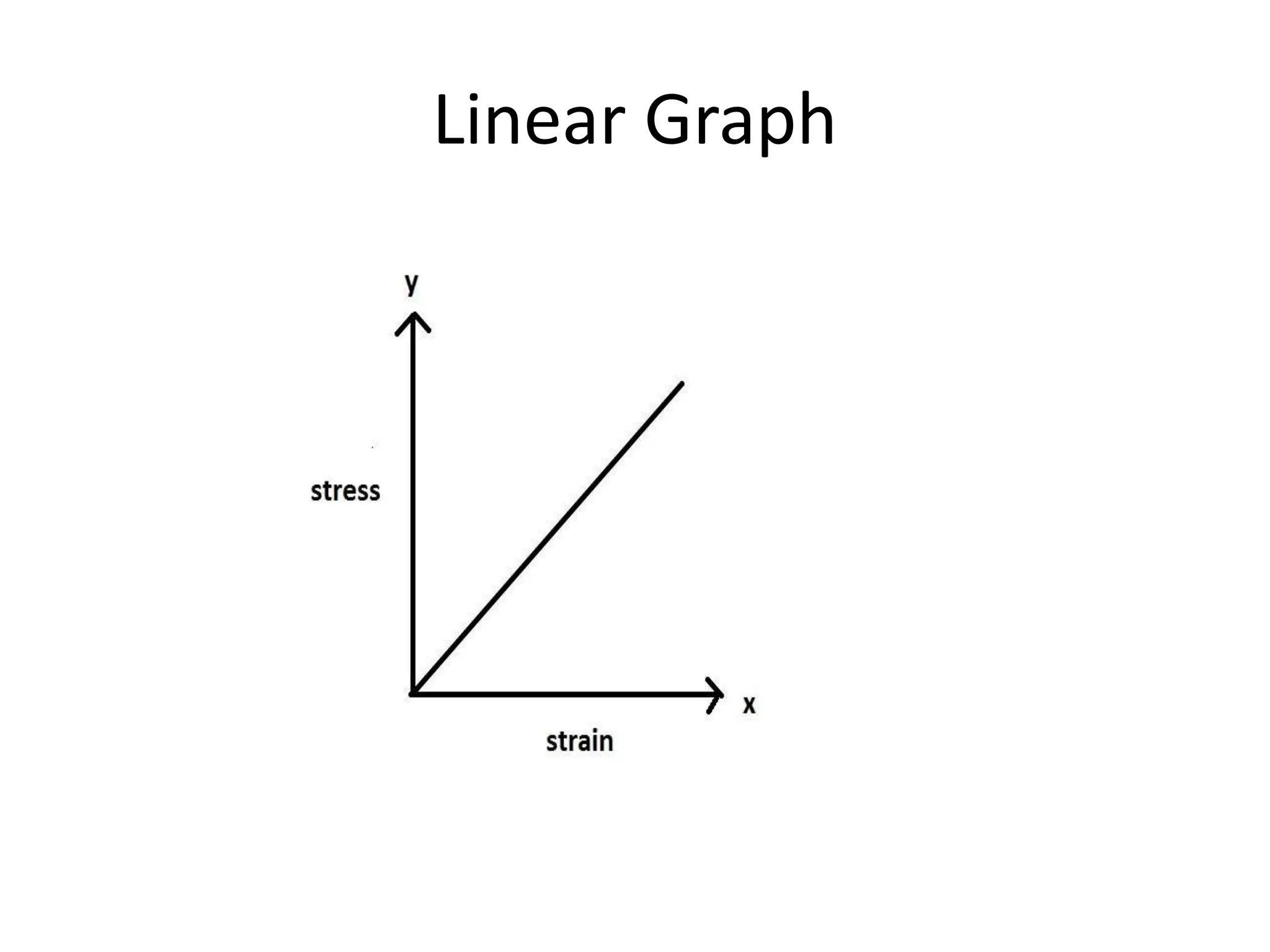
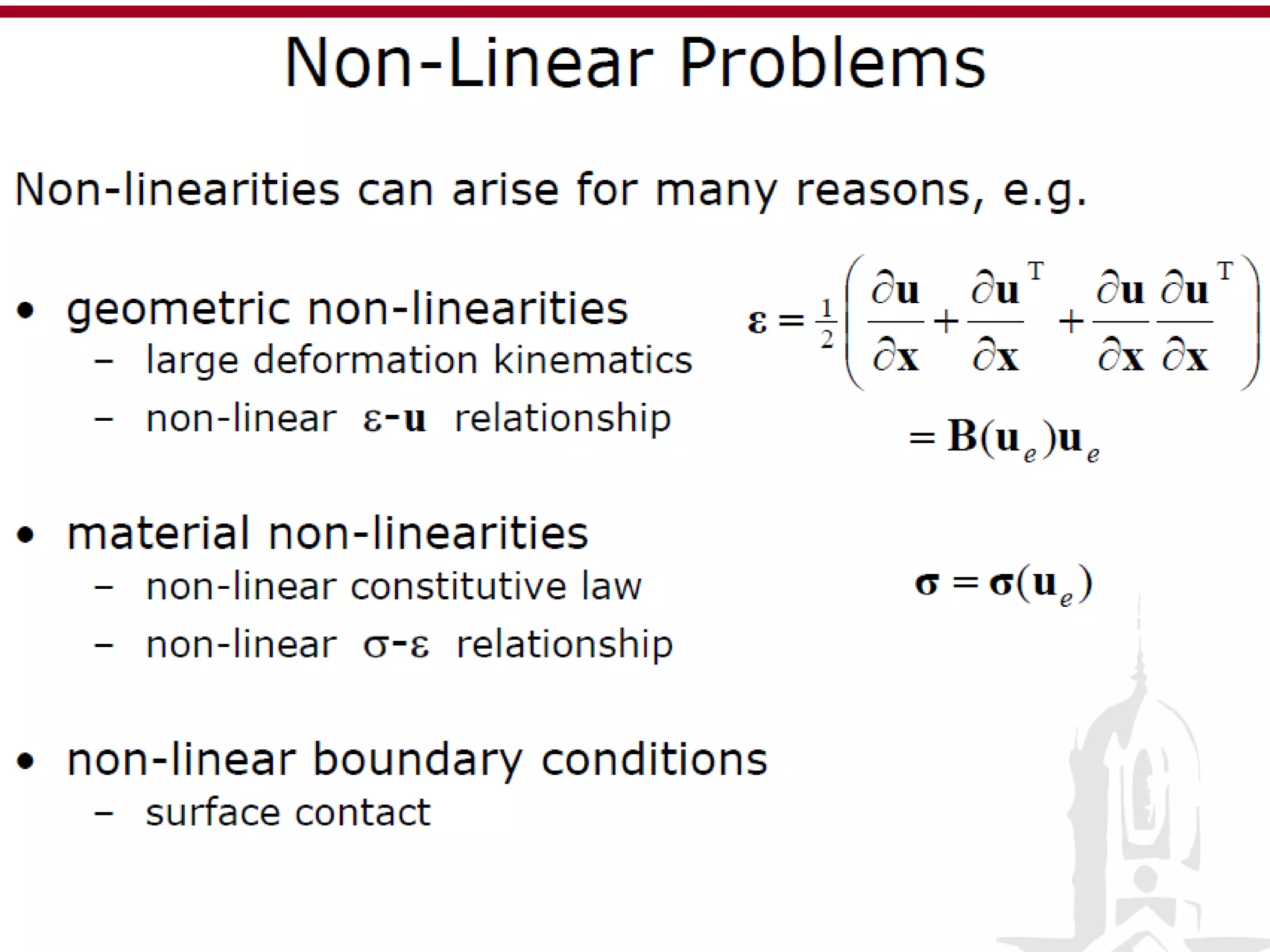
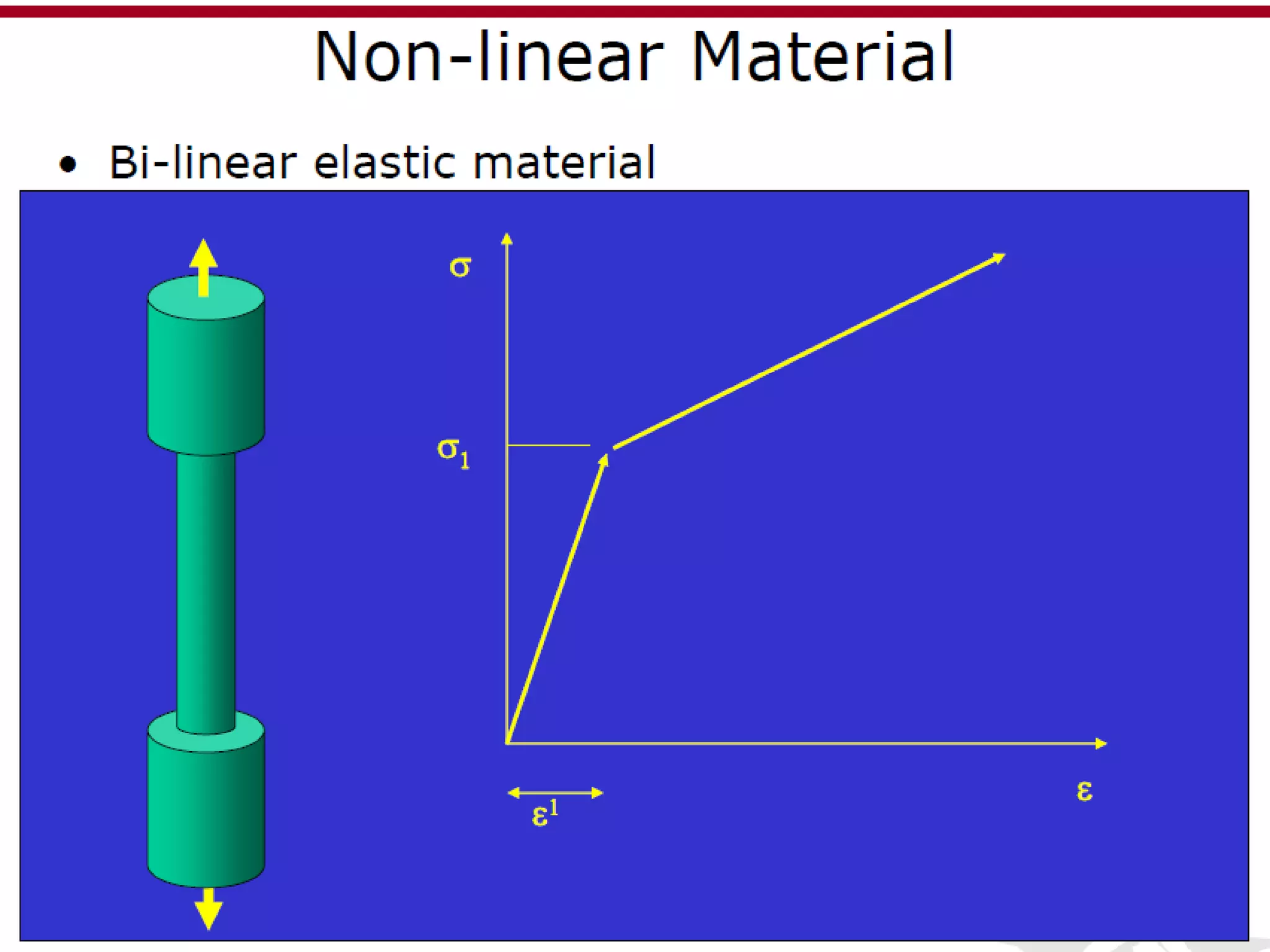
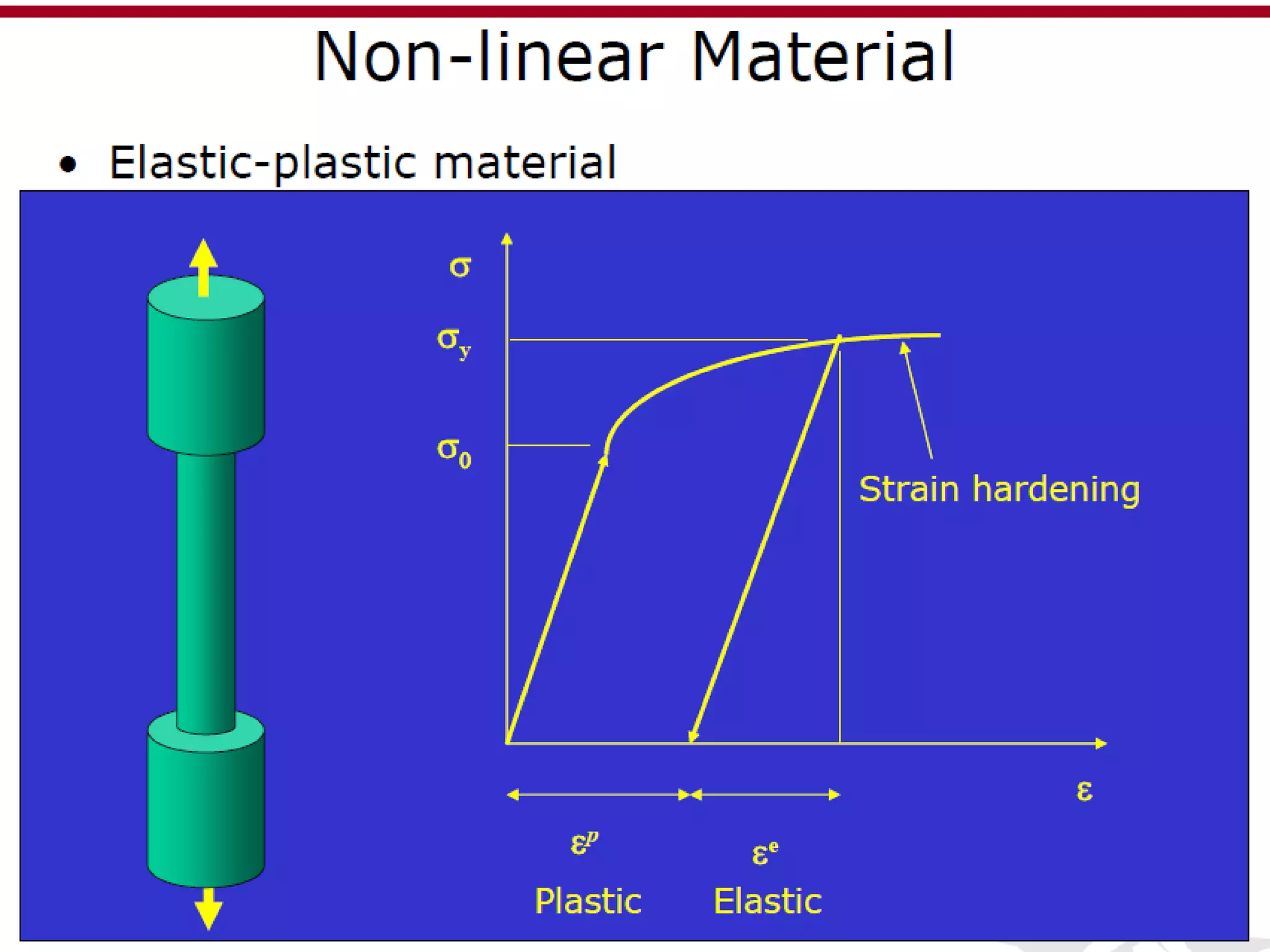


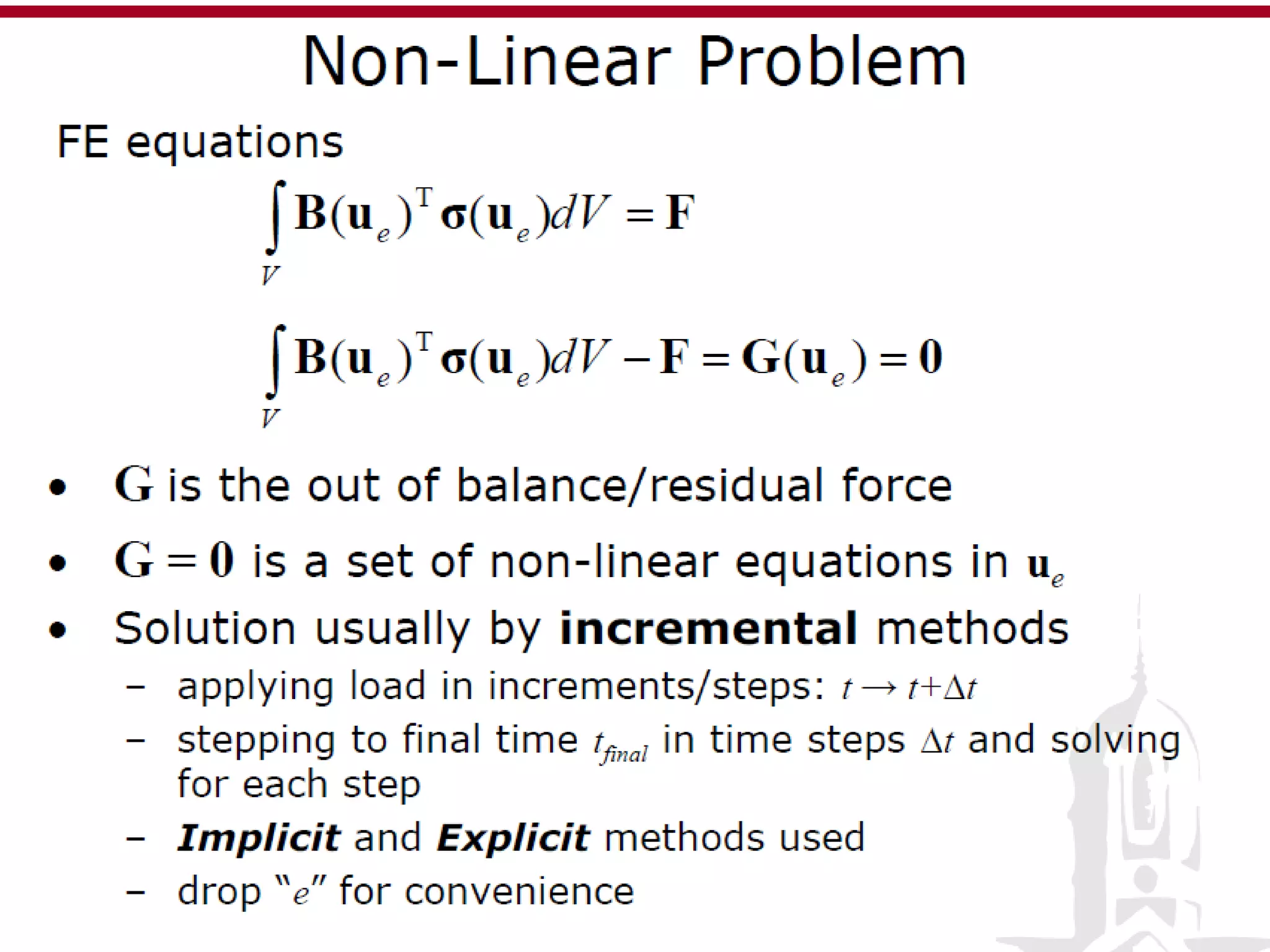
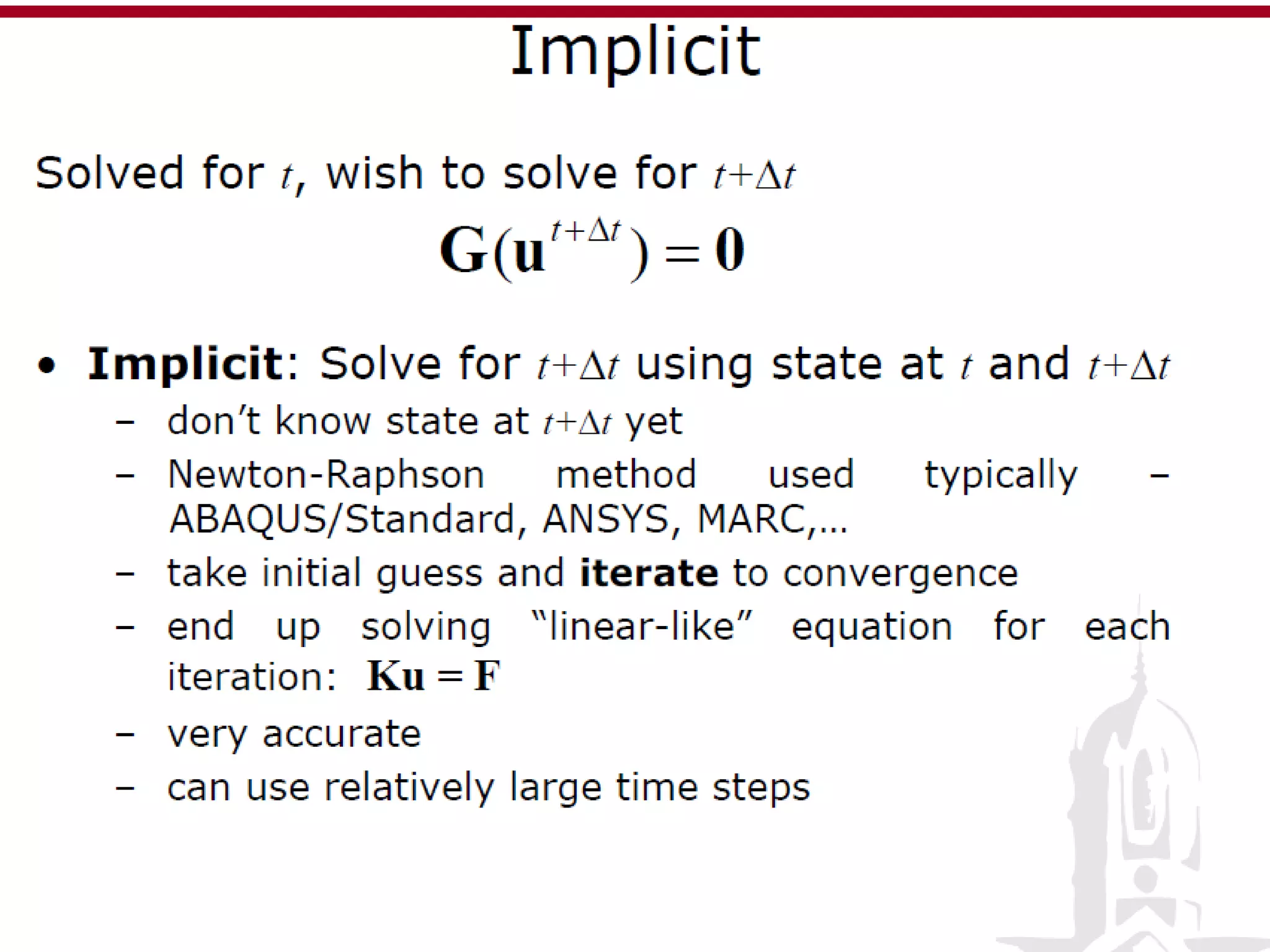

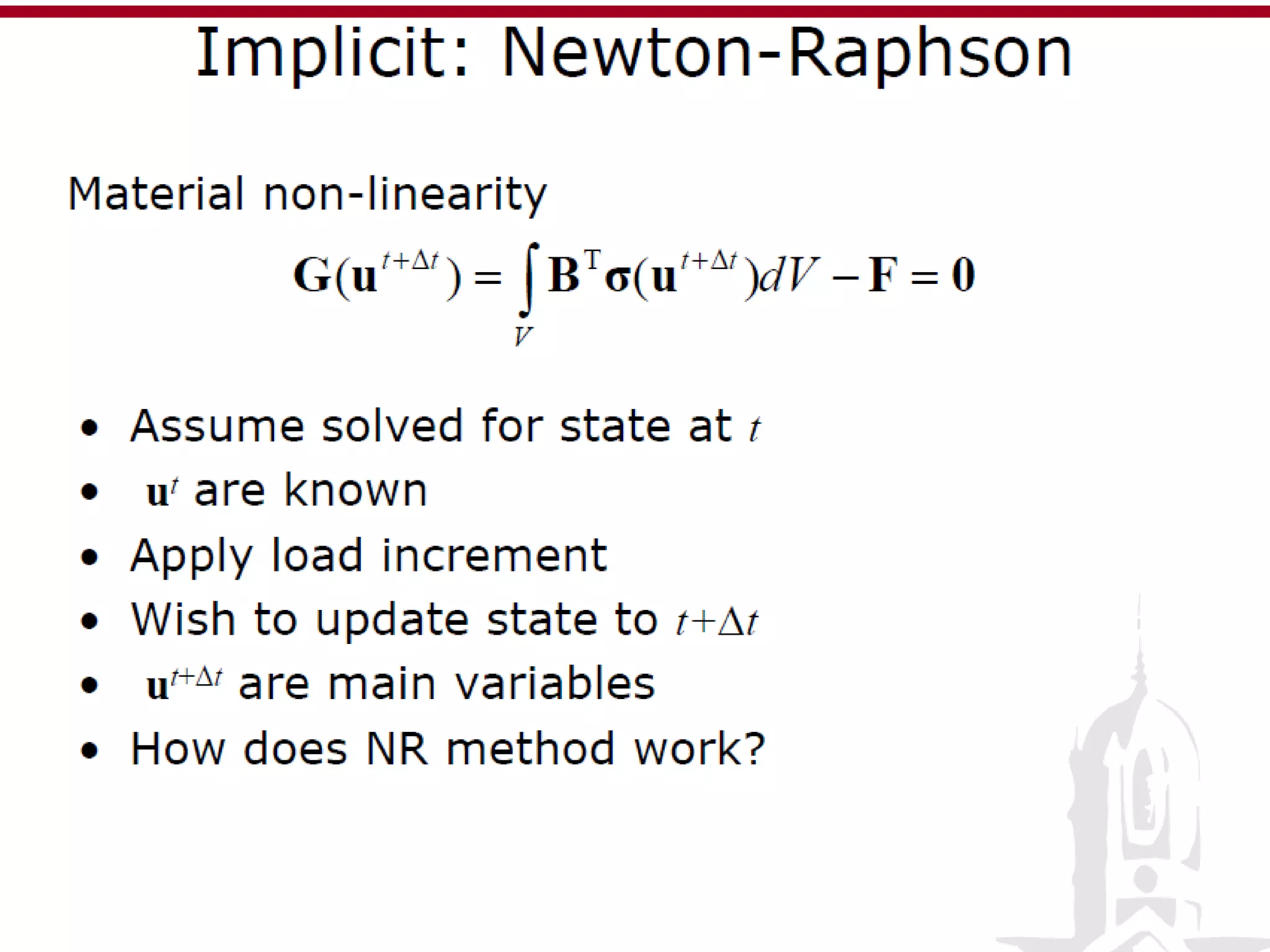
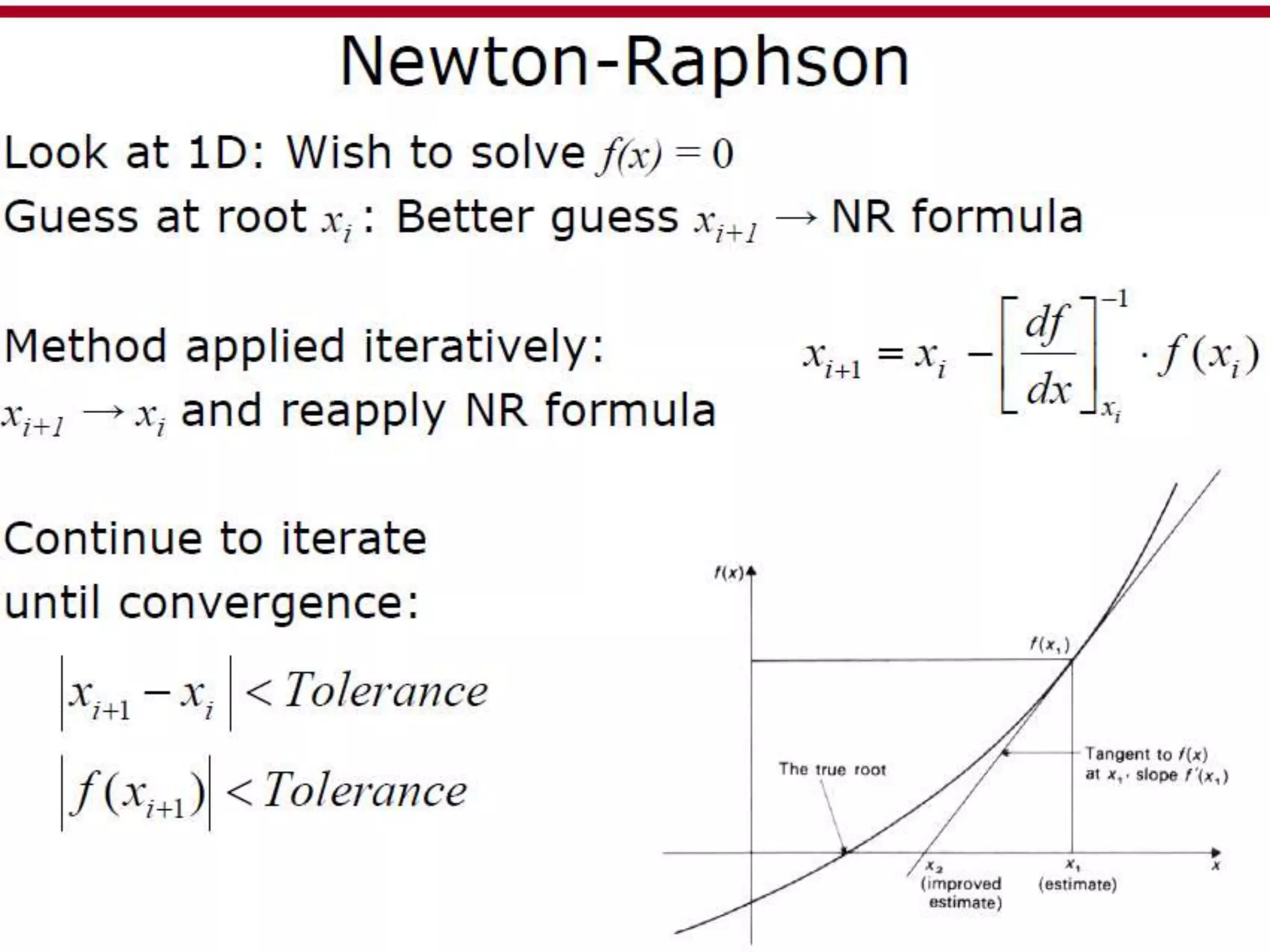
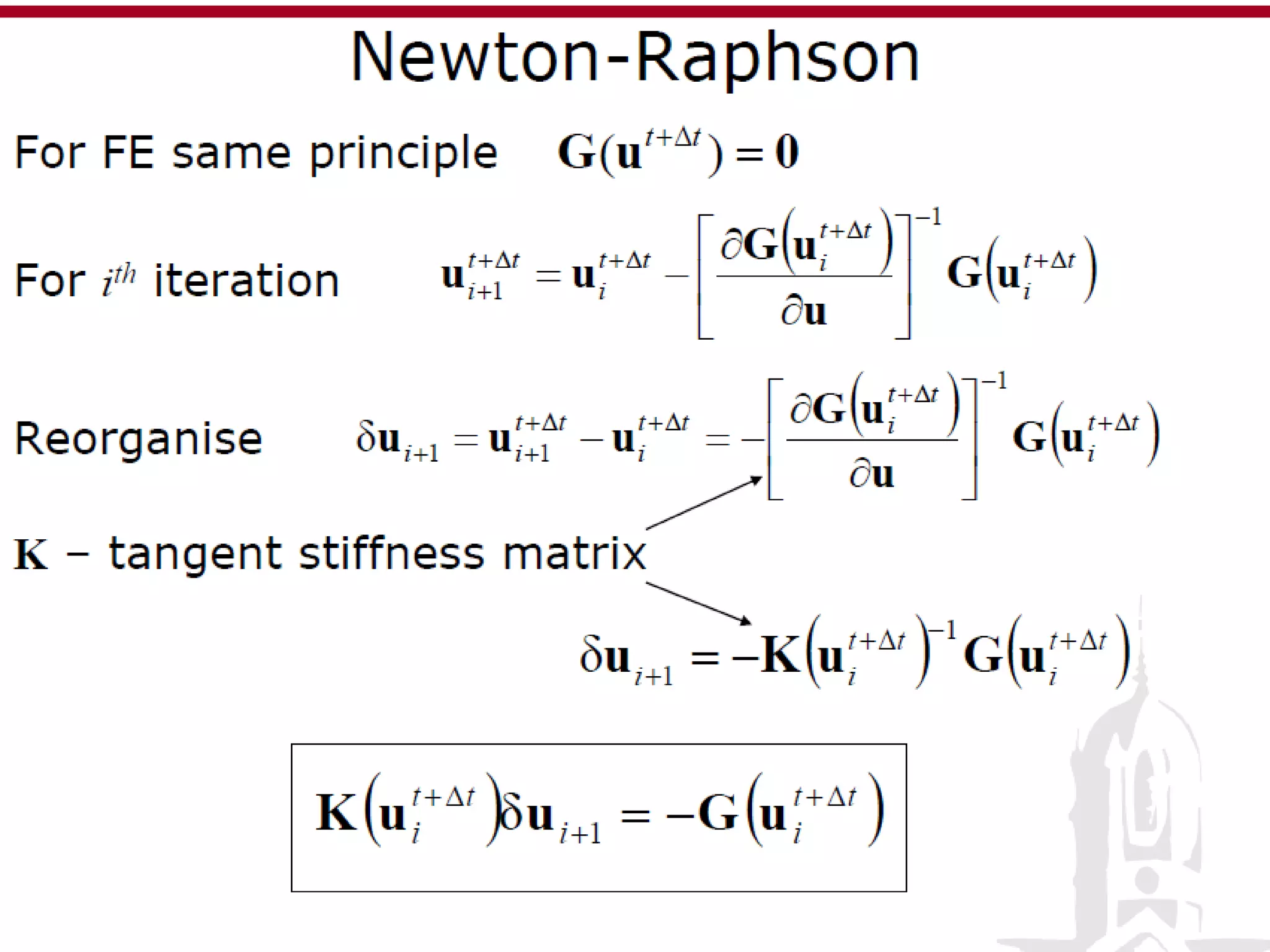
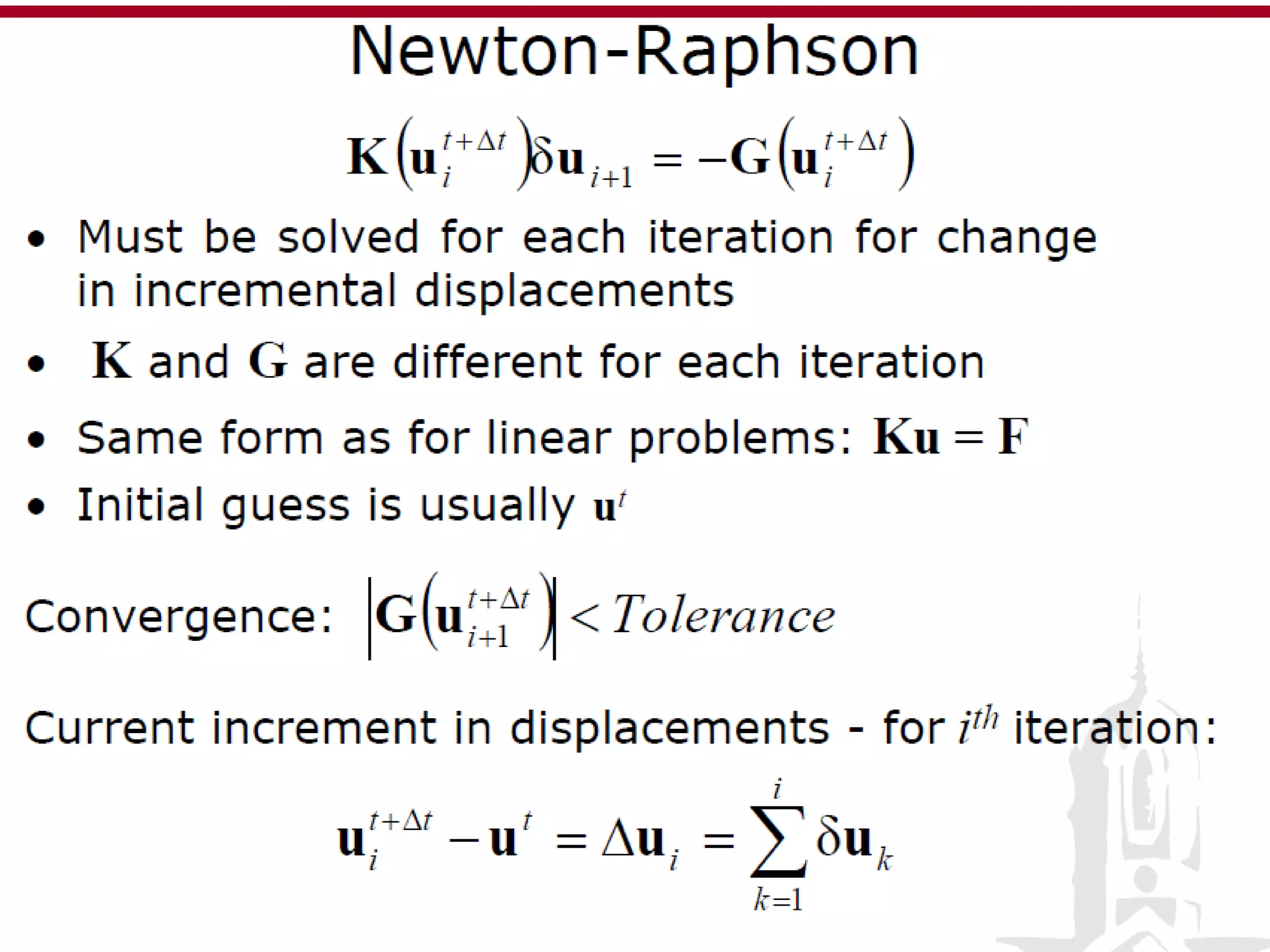
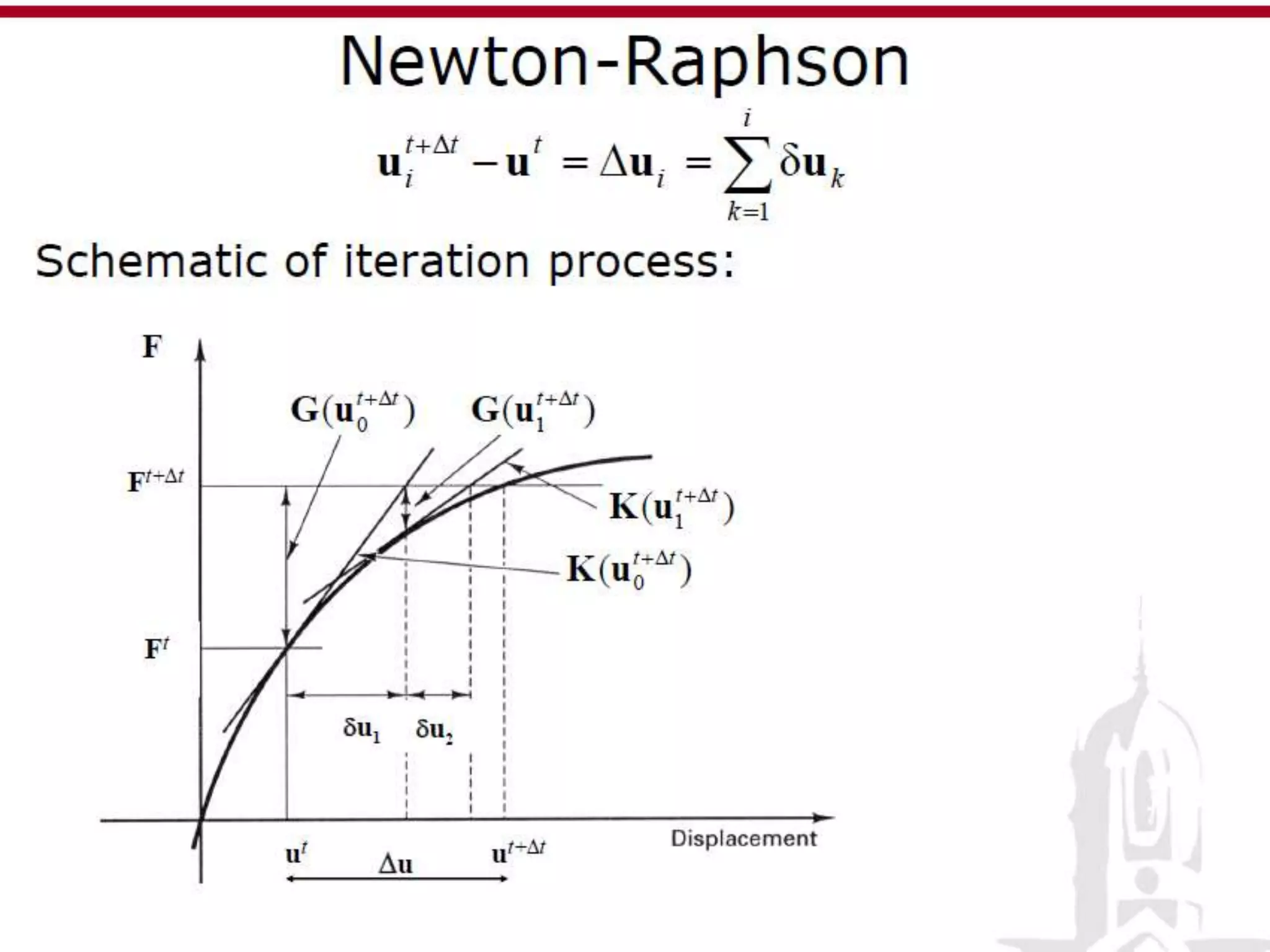
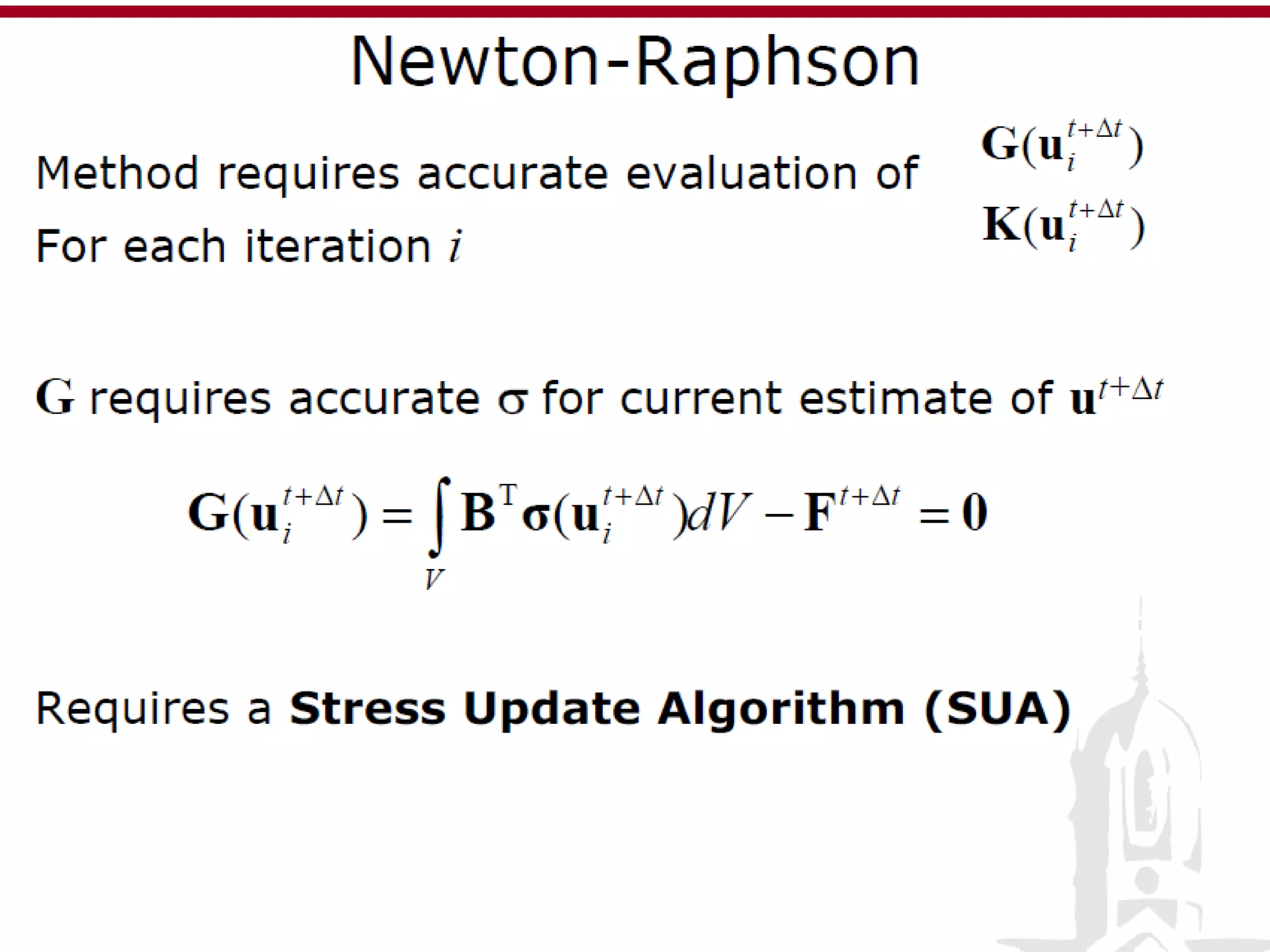
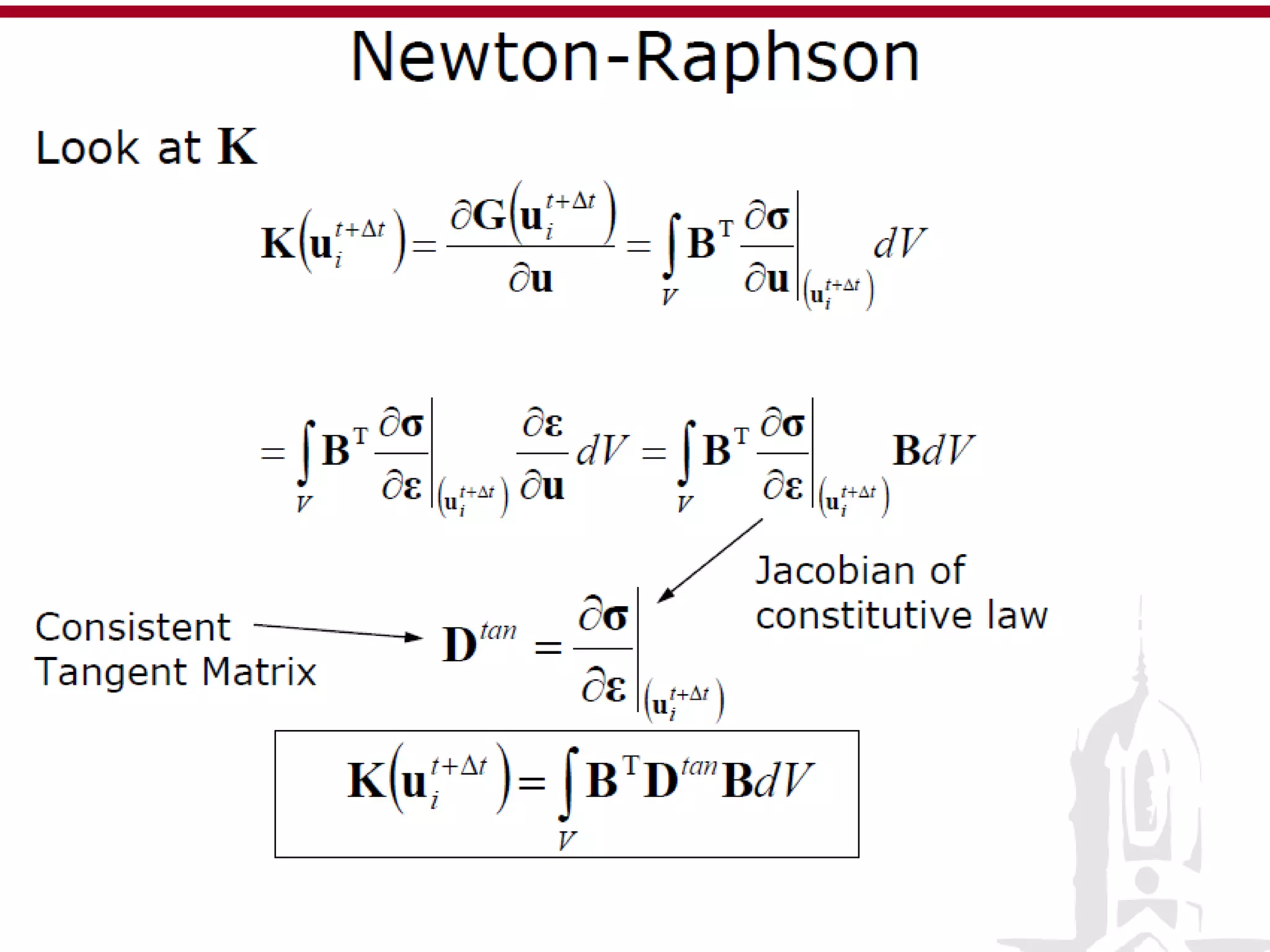

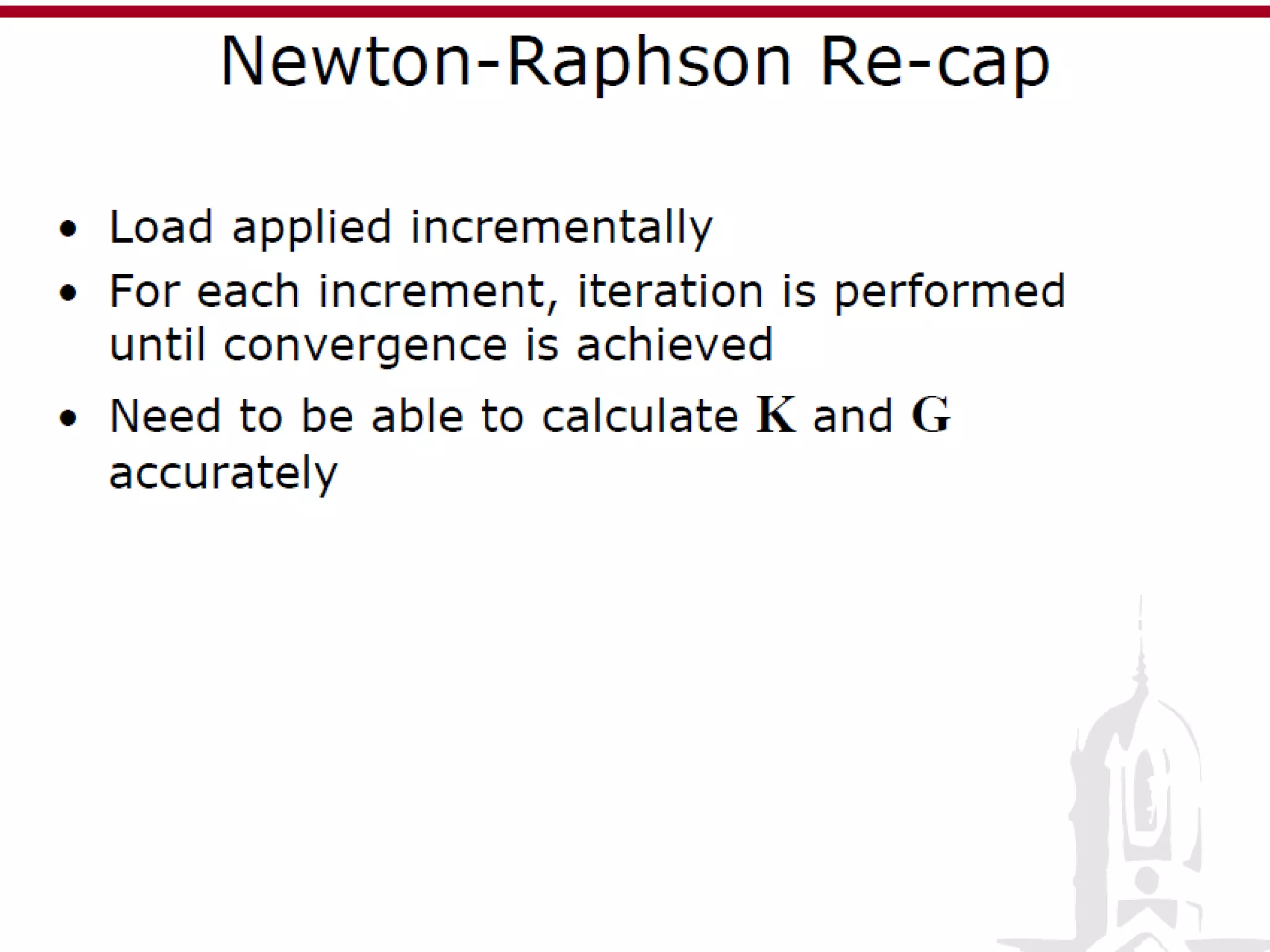
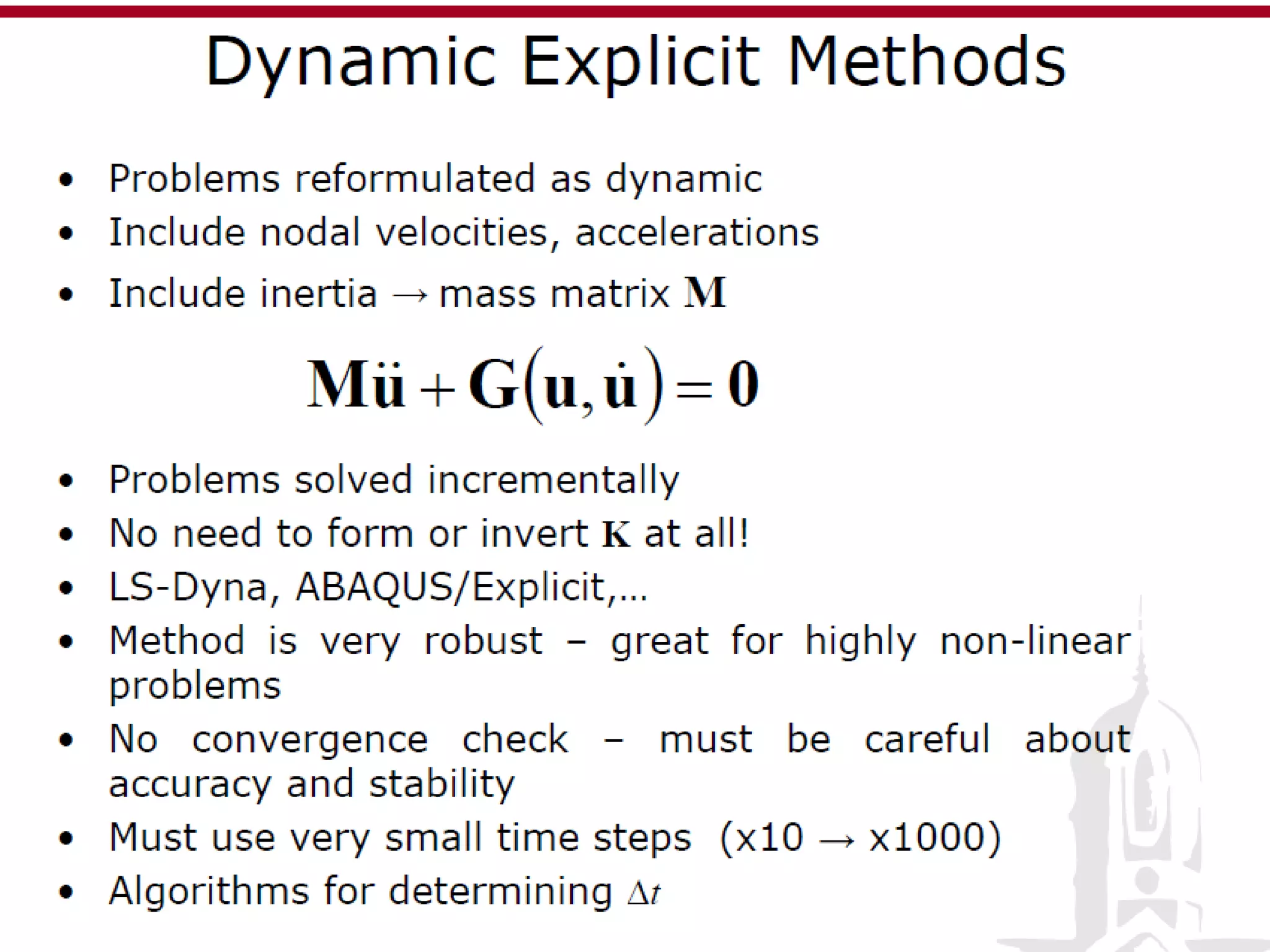
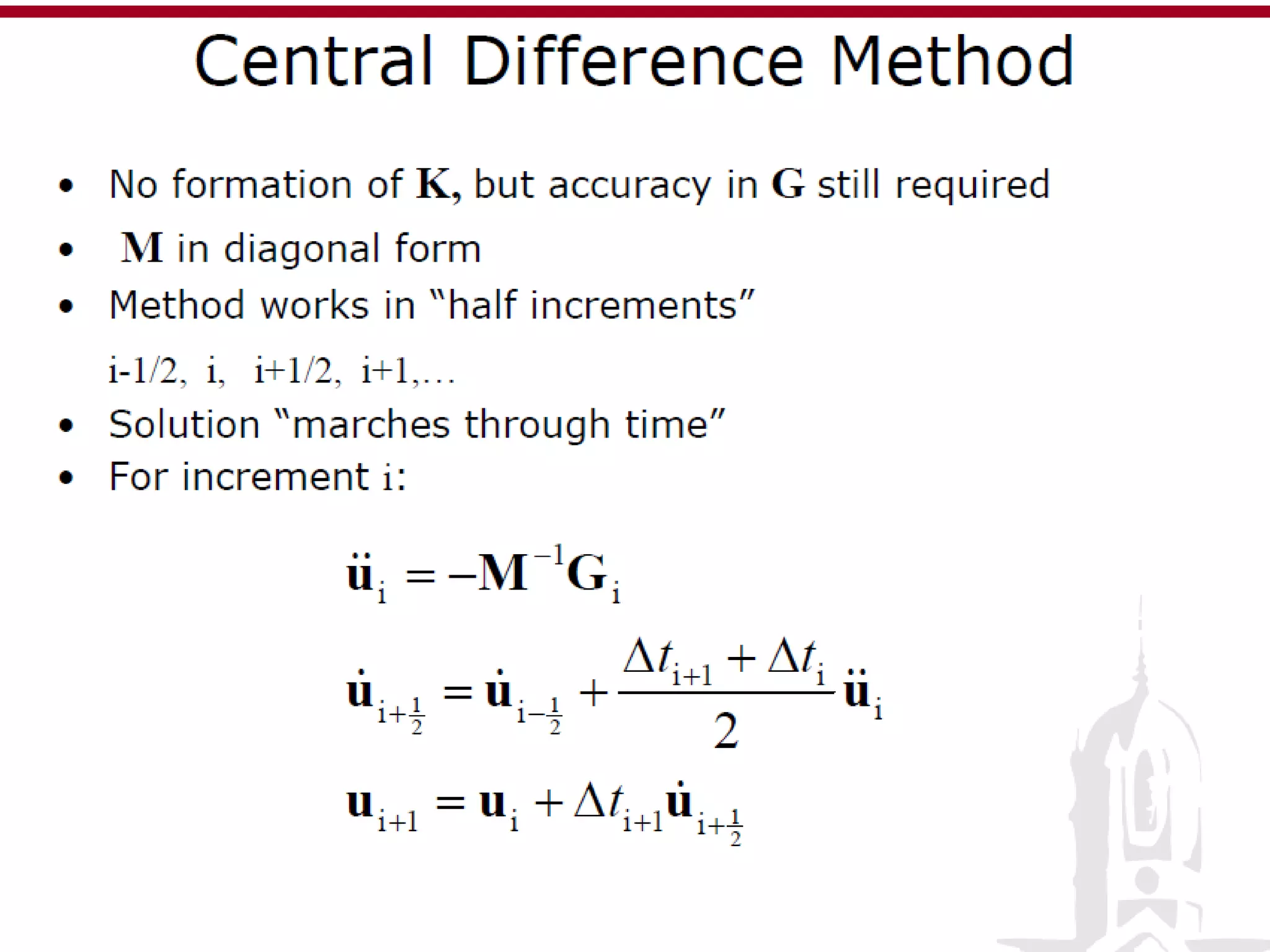
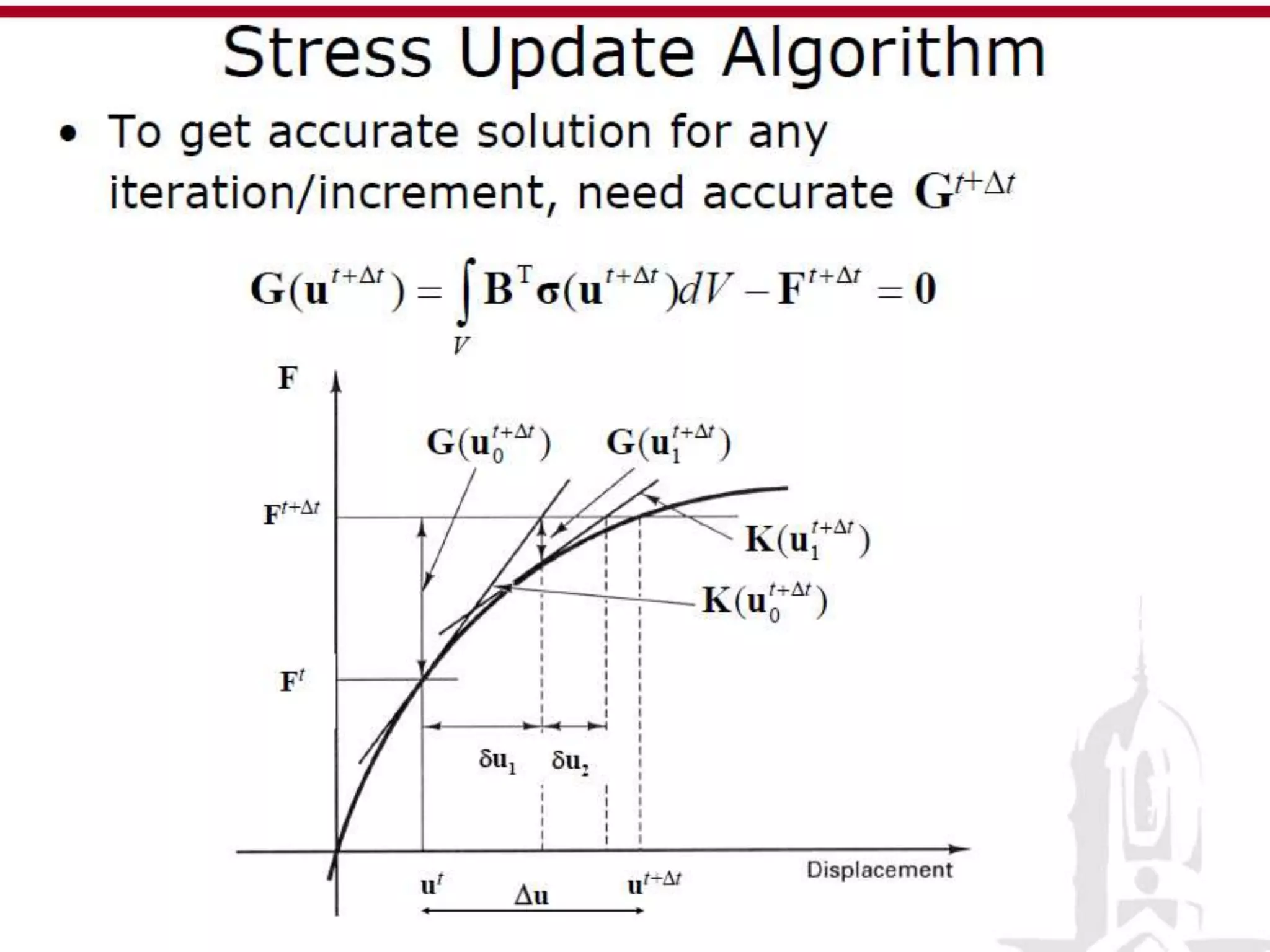
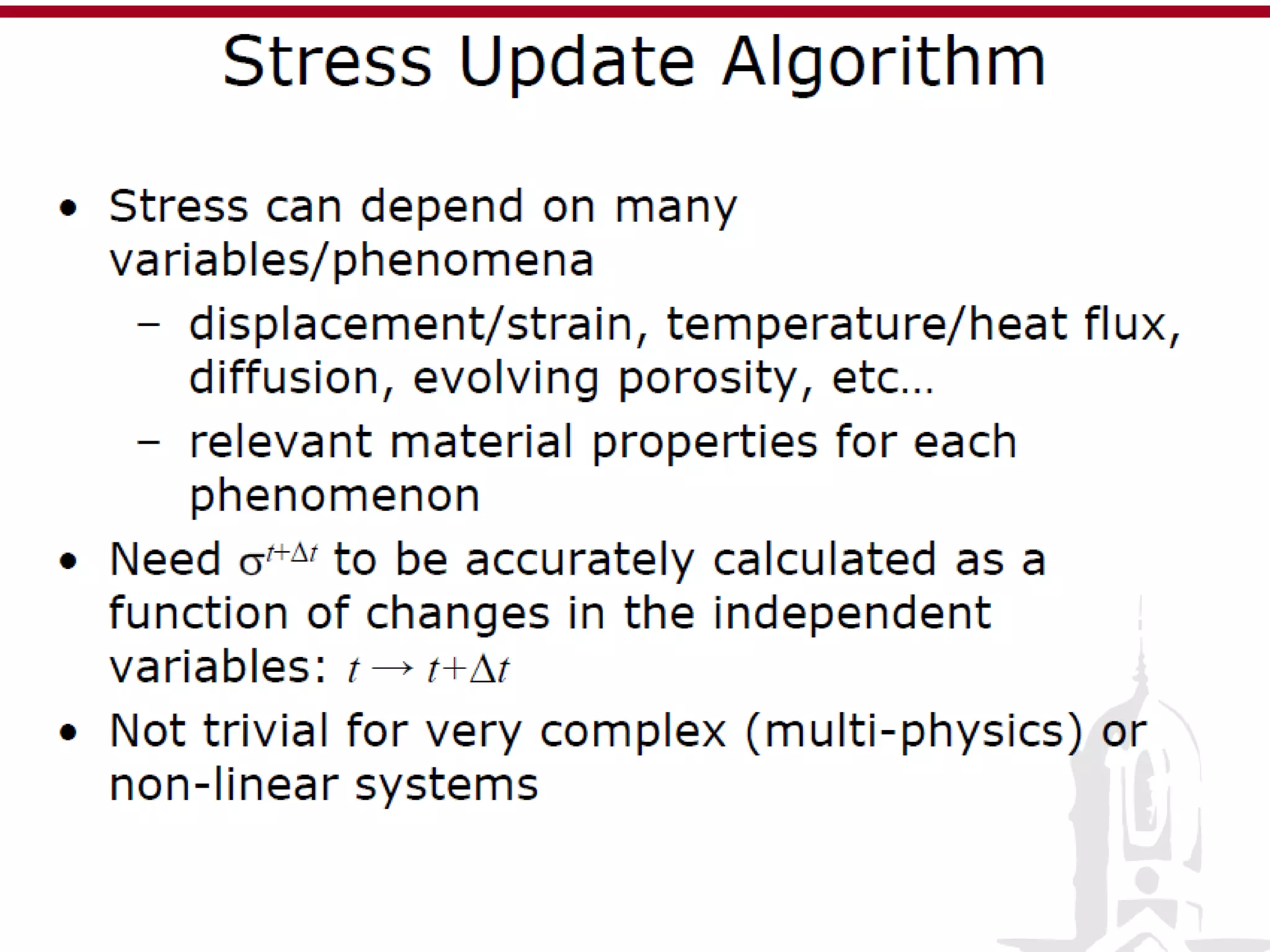



This document discusses finite element analysis and nonlinear finite element analysis. It introduces the finite element method and how it approximates solutions by dividing them into discrete elements. It explains that higher order polynomials and more nodes/elements increase accuracy. The document distinguishes between linear and nonlinear problems, with nonlinear problems not obeying Hooke's law. It lists common finite element methods for nonlinear mechanics like updated Lagrangian formulations. Finally, it discusses solution algorithms for nonlinear problems like Newton's method and line searches.





































