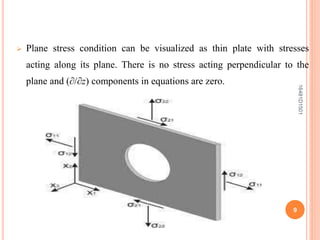
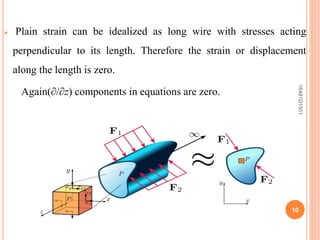
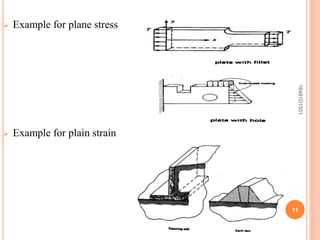
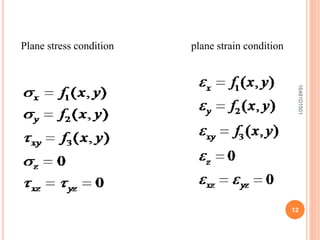
This document summarizes a seminar topic on the theory of elasticity. It discusses key concepts in elasticity including external forces, stresses, strains, displacements, assumptions of elasticity theory. It provides examples of plane stress and plane strain conditions. The purpose of elasticity theory is to analyze stresses and displacements in elastic solids and structures. Applications include designing mechanical parts and calculating stresses in beams.