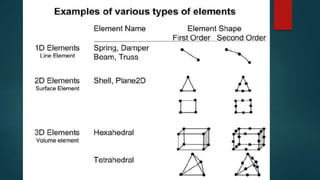
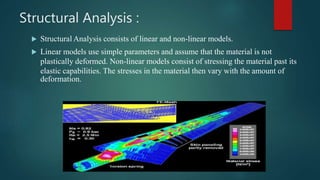
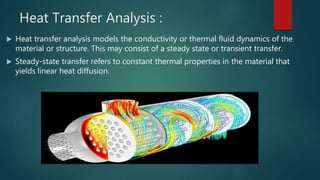
The document discusses the finite element method (FEM). FEM is a numerical technique used to find approximate solutions to partial differential equations. It divides a complex problem into small, simpler elements that are solved using relations between each other. There are three phases: pre-processing to mesh the geometry and apply properties/conditions, solution to derive equations and solve for quantities, and post-processing to validate solutions. FEM can model various problem types like static, dynamic, structural, vibrational, and heat transfer analyses. It has advantages like handling complex geometries and loadings but also disadvantages like requiring approximations and computational resources.