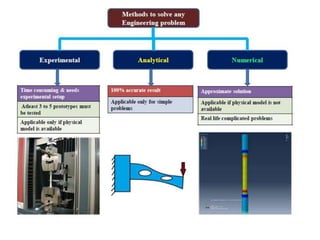
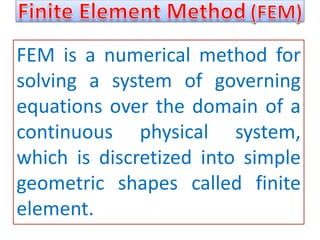
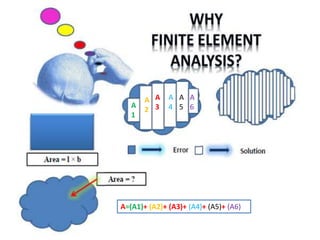
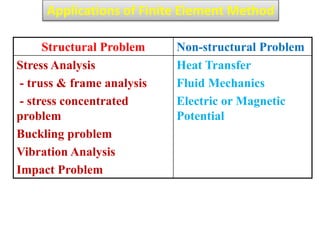
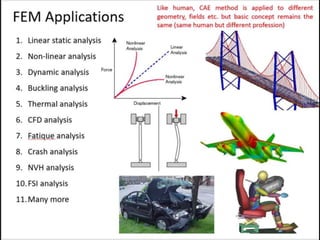
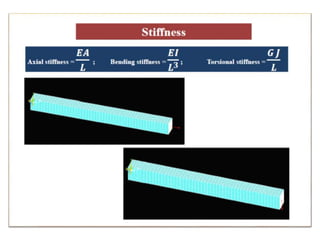
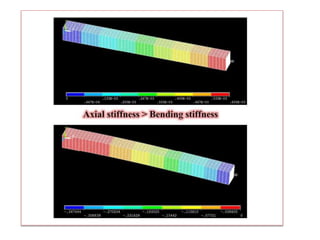
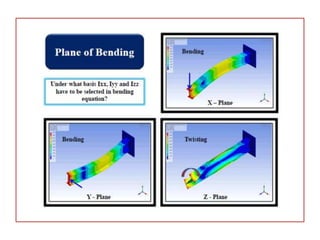
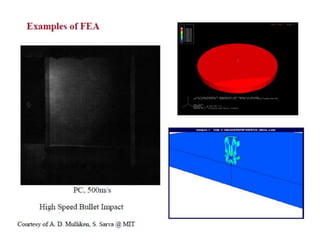
This document provides an overview of finite element analysis (FEA). It defines FEA as a numerical method for solving governing equations over the domain of a continuous physical system that is discretized into simple shapes. It lists several common structural and non-structural applications of FEA, such as stress analysis, buckling problems, vibration analysis, and heat transfer. Finally, it provides the course outline, textbooks, references, and some common FEA software packages.