- Transient dynamic analysis determines the time-varying response of a structure to general time-dependent loads. It accounts for inertia and damping effects.
- The basic equation of motion solved includes mass, damping, stiffness matrices, and a load vector that varies over time. At discrete time points, these equations are similar to static equilibrium equations.
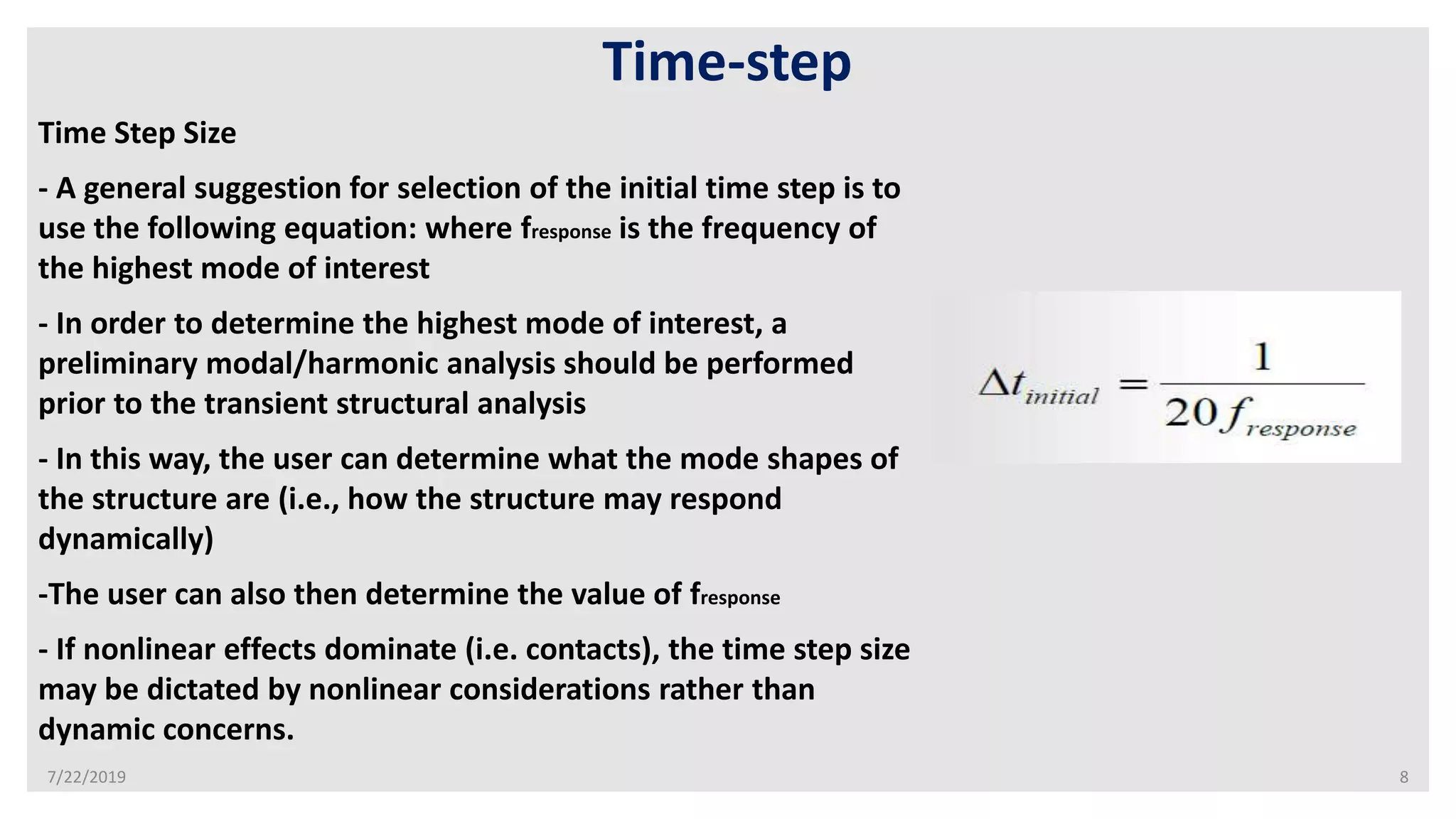
- Proper modeling of loads, time steps, and initial conditions is important for an accurate transient analysis. Loads can be applied as discrete steps or gradually ramped over time.


![7/22/2019 3
• The basic equation of motion solved by a transient dynamic analysis is where:
[M]{Ẍ} + [C]{Ẋ} + [K]{X} = F(t)
[M] = mass matrix; [C] = damping matrix; [K] = stiffness matrix; {Ẍ} = nodal acceleration
vector; {Ẋ}= nodal velocity vector; {X} = nodal displacement vector; {F(t)} = load vector
• At any given time t, these equations can be thought of as a set of "static“ equilibrium
equations that also take into account inertia forces ([M]) and damping forces ([C]).
• The ANSYS program uses the New-mark time integration method to solve these
equations at discrete time-points.
• The time increment between successive time-points is called the integration time step.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-transientanalysistheory-190722061239/75/12-transient-analysis-theory-3-2048.jpg)