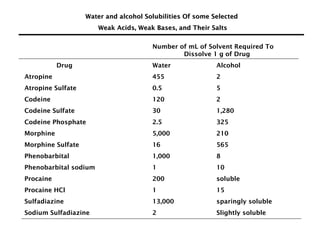
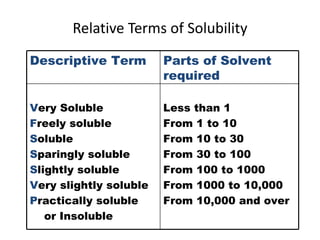
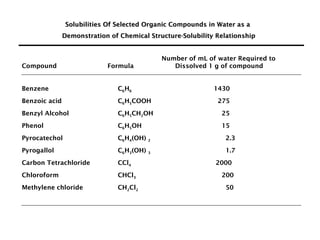
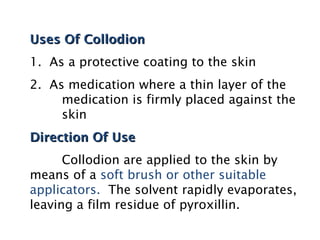
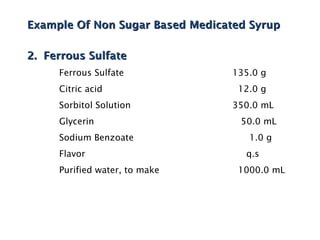
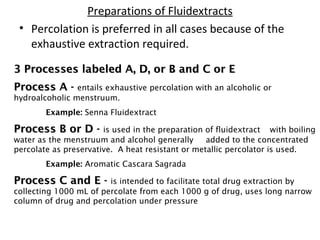
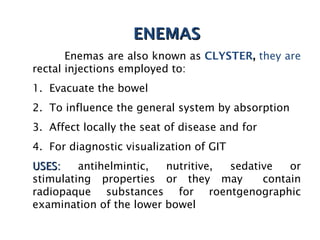
This document discusses solutions, including their physicochemical properties, types, factors affecting solubility and rate of solubility, and methods of preparation. It defines solutions as homogeneous mixtures formed via dissolving a solute in a solvent. The three main types are solid, liquid, and gaseous solutions. Key factors affecting solubility include temperature, particle size, molecular structure, pH, and presence of other substances. Methods of preparing solutions include simple dissolution, chemical reaction, and extraction. Various terms for expressing concentration and examples of oral liquid medications are also outlined.