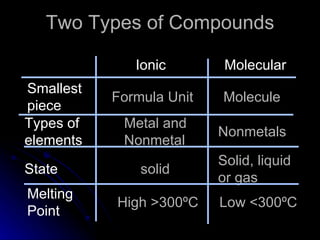
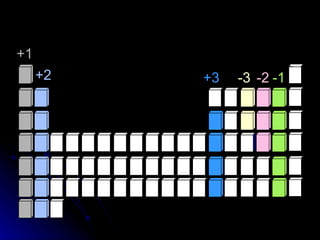
The document discusses chemical names and formulas. It explains that atoms can be neutral or ions with positive or negative charges. Compounds can be either molecular compounds made of nonmetal molecules or ionic compounds made of metal and nonmetal ions. Chemical formulas show the types and numbers of atoms in the smallest unit of a substance, whether a molecule or formula unit. The document also provides examples of naming common cations, anions, and polyatomic ions according to standard conventions by indicating charges or changing endings.