Embed presentation



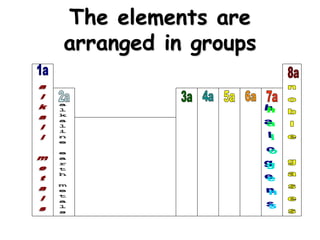
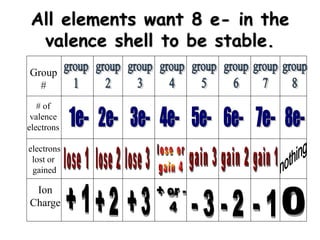
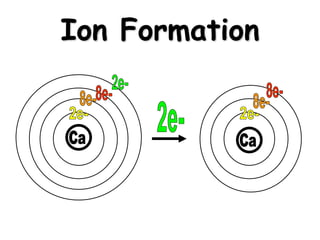

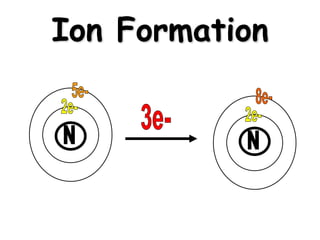




This document discusses ion formation and naming ions. It explains that atoms become ions by gaining or losing electrons to obtain a full outer electron shell of 8 electrons. It gives examples of common monatomic cations such as K+, Ca2+, and Al3+ and anions such as S2-, O2-, Br-, and N3-. The document also provides guidelines for naming ions, indicating that positive ions are called cations and named after the element, while negative ions are called anions and named by taking the element root and adding -ide.










