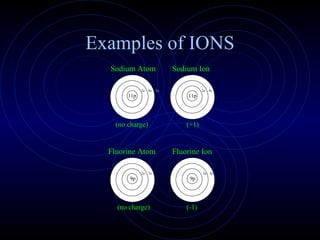
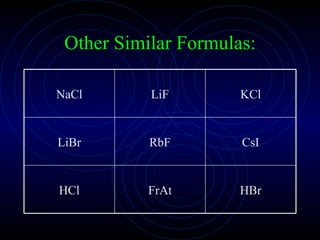
The document discusses chemical bonding and formula writing. It explains that there are two main types of bonds: ionic bonds and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms to form ions, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms. It provides examples of common ionic compounds and their formulas, such as NaCl, as well as explaining how to write formulas for compounds containing polyatomic ions like OH-. Covalent bonding is demonstrated through the example of methane, CH4, where carbon shares electrons with four hydrogen atoms to fill their outer energy levels.