Embed presentation
Download to read offline

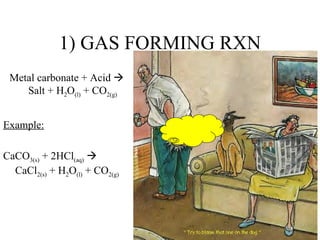




The document discusses four types of special chemical reactions: 1. Gas forming reactions involve a metal carbonate reacting with an acid to form a salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas. 2. Precipitation reactions are double displacement reactions that form an insoluble salt precipitate. 3. Neutralization reactions involve an acid reacting with a base to form a salt and water. 4. Combustion reactions involve the burning of a hydrocarbon with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.