Embed presentation
Downloaded 68 times

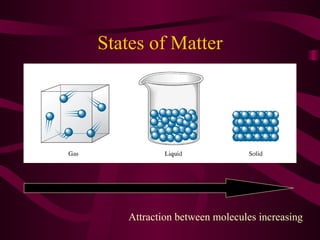
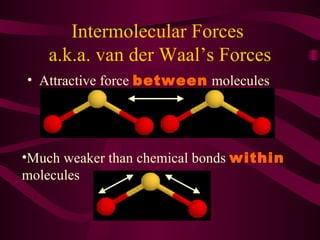





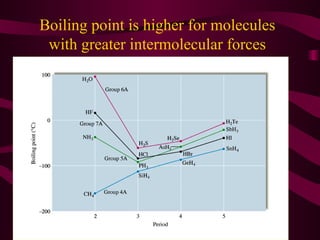
This document discusses intermolecular forces (IMFs), the attractive forces between molecules that are weaker than intramolecular chemical bonds. It describes the main types of IMFs - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding - and how their relative strengths depend on factors like molecular mass and polarity. IMFs determine key properties like a substance's boiling point, with stronger IMFs requiring more energy to overcome, resulting in higher boiling temperatures.








