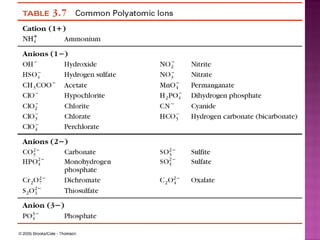
The document discusses several key concepts in chemistry including:
1) The attraction between atoms in molecules and crystalline structures is a chemical bond such as ionic bonds formed between oppositely charged ions.
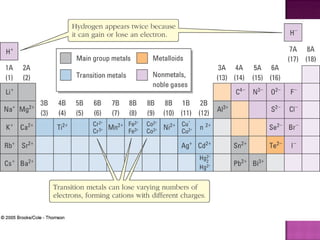
2) Metals form cations by losing electrons and bonding with other metal atoms via delocalized electrons allowing for conductivity.
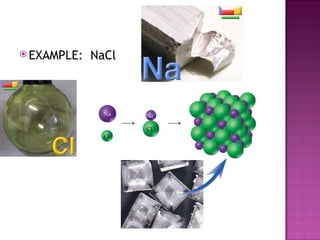
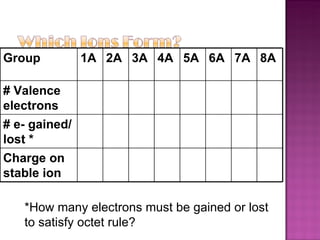
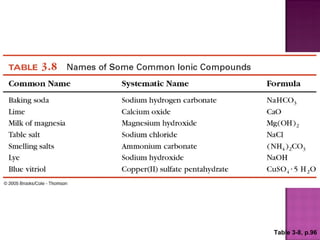
3) Ionic compounds are formed between metallic cations and nonmetallic anions with ionic bonds between oppositely charged ions that results in crystalline solids.