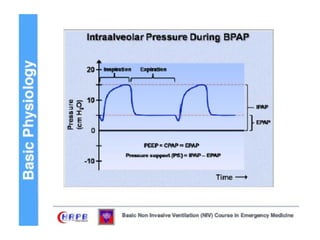
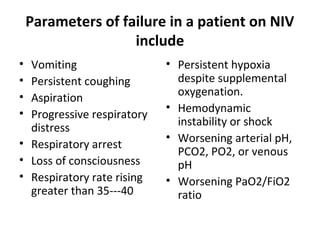
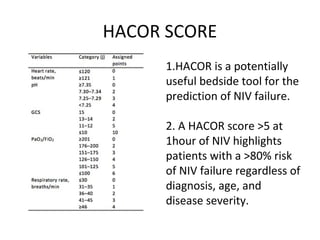
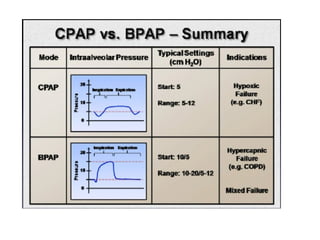
This document discusses non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) delivered via a nasal or oronasal mask for respiratory failure. NIPPV has been shown to be effective for acute pulmonary edema, respiratory failure in immunocompromised patients, and facilitating extubation in COPD patients. Factors vital for success include careful patient selection, timely initiation, a comfortable fitting interface, coaching, and monitoring. NIPPV should be used to avoid intubation rather than as an alternative. Conditions with strong evidence for NIPPV use include cardiogenic pulmonary edema, COPD exacerbations, and respiratory failure in immunocompromised patients. Contraindications include pulmonary fibrosis, ARDS with multi-organ failure, and