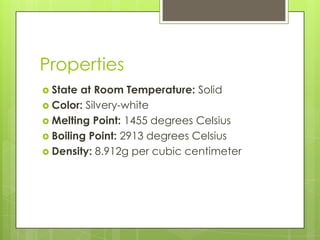
Nickel is a silvery-white metal that is solid at room temperature with a melting point of 1455 degrees Celsius. It was discovered in 1751 by Swedish chemist Axel Cronstedt, who originally believed it was copper (Kupfernickel translates to Devil's copper). Nickel is primarily found in ores and its most important properties are its high melting and boiling points. It is used as a catalyst in hydrogenation reactions, in heat regulation, in nuclear reactors, and in producing corrosion-resistant alloys and stainless steel.