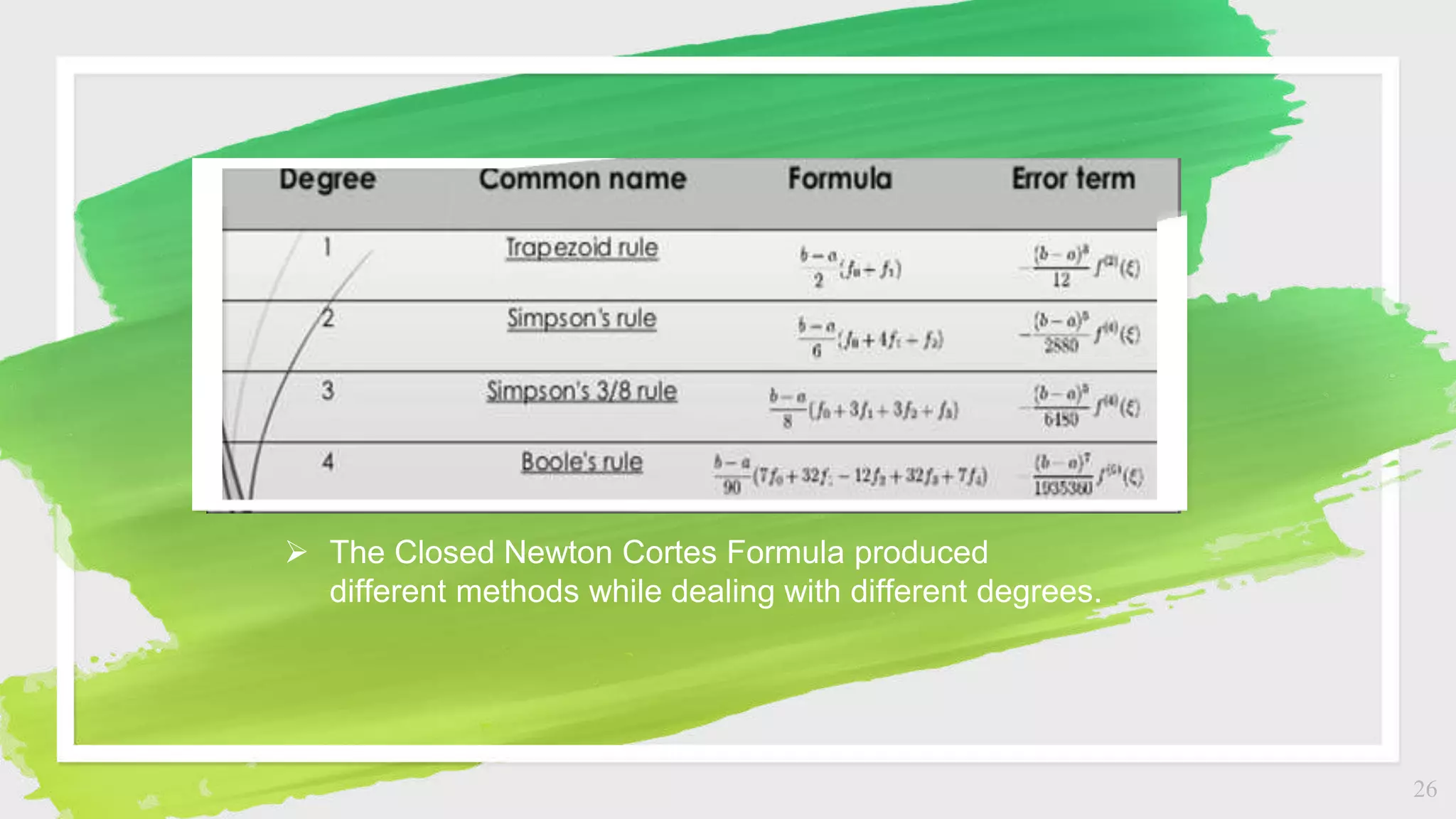
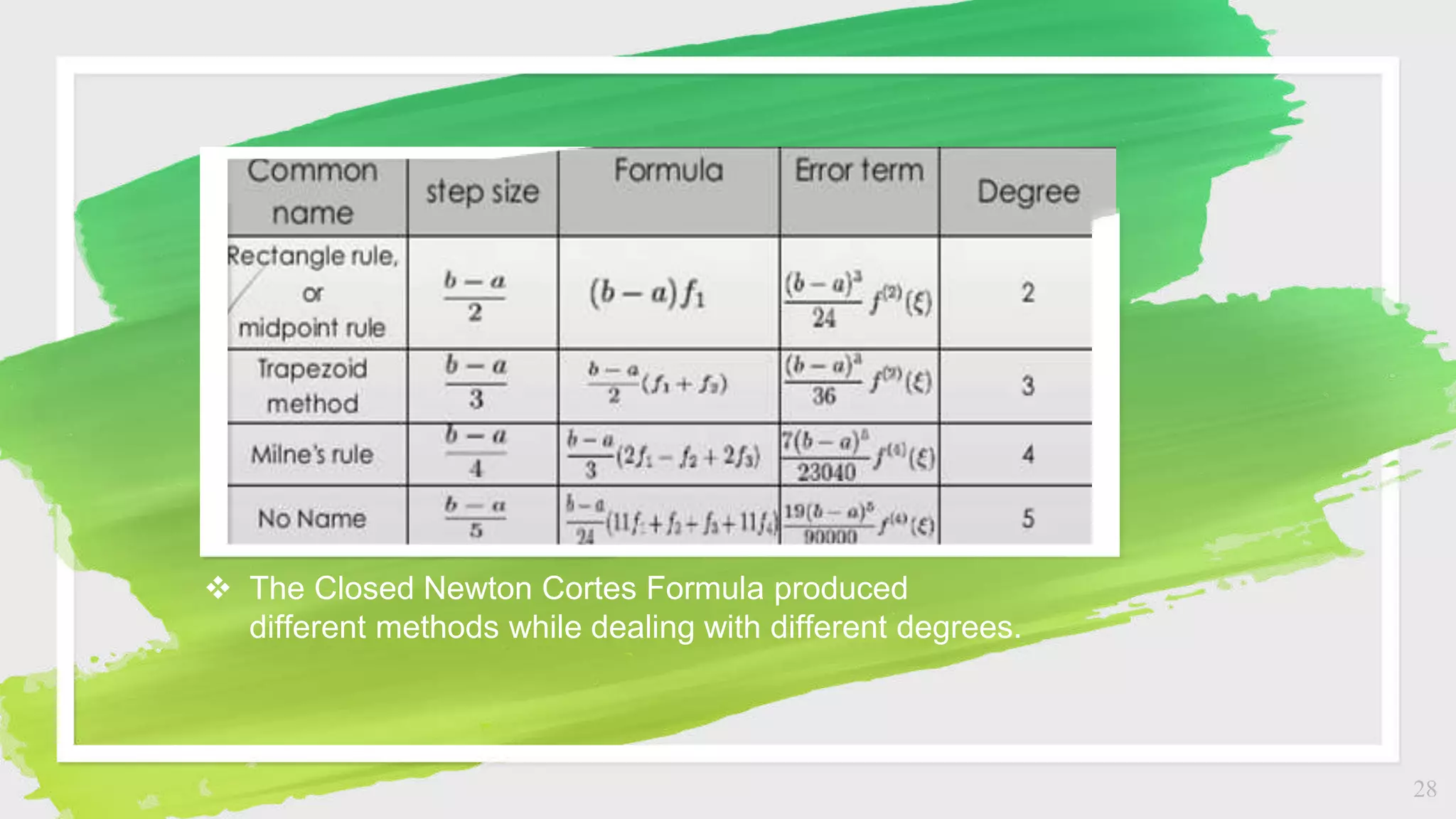
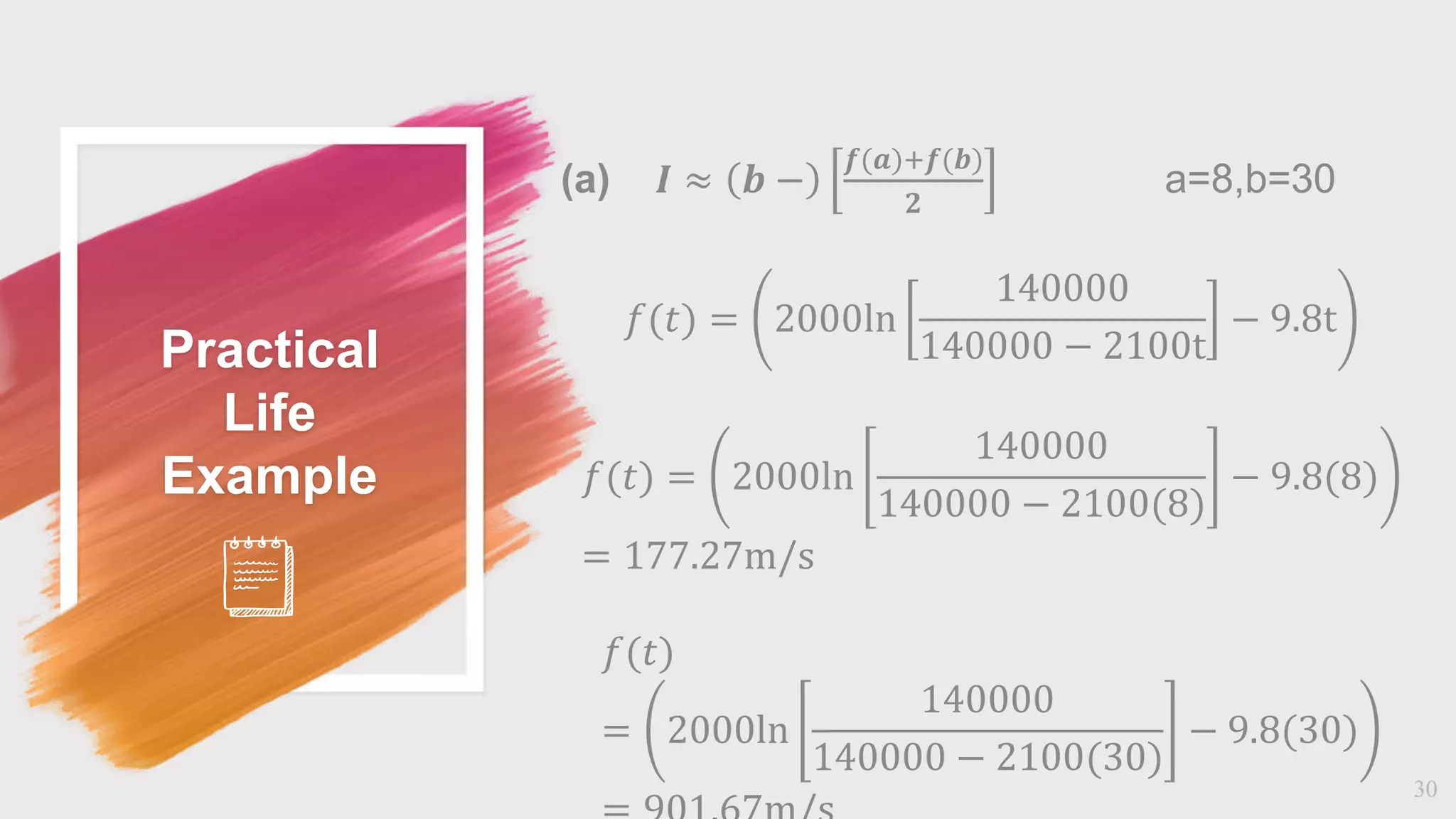
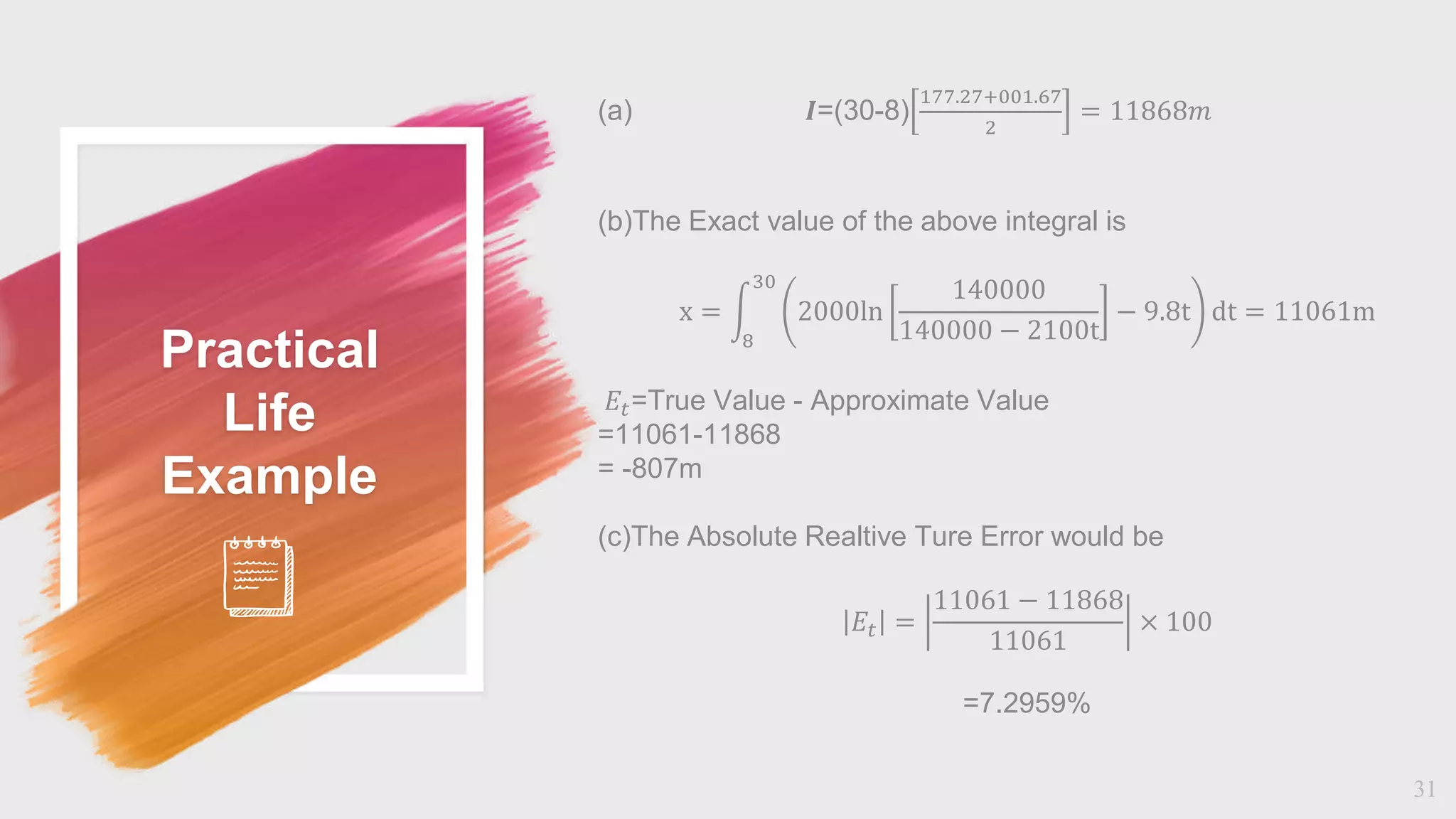
The document discusses numerical integration methods including Boole's rule, Weddle's rule, Gaussian quadrature, and Newton-Cotes formulas. Specific examples illustrate the application and accuracy of these methods for estimating definite integrals. The document highlights practical applications and error calculation techniques related to these numerical methods.









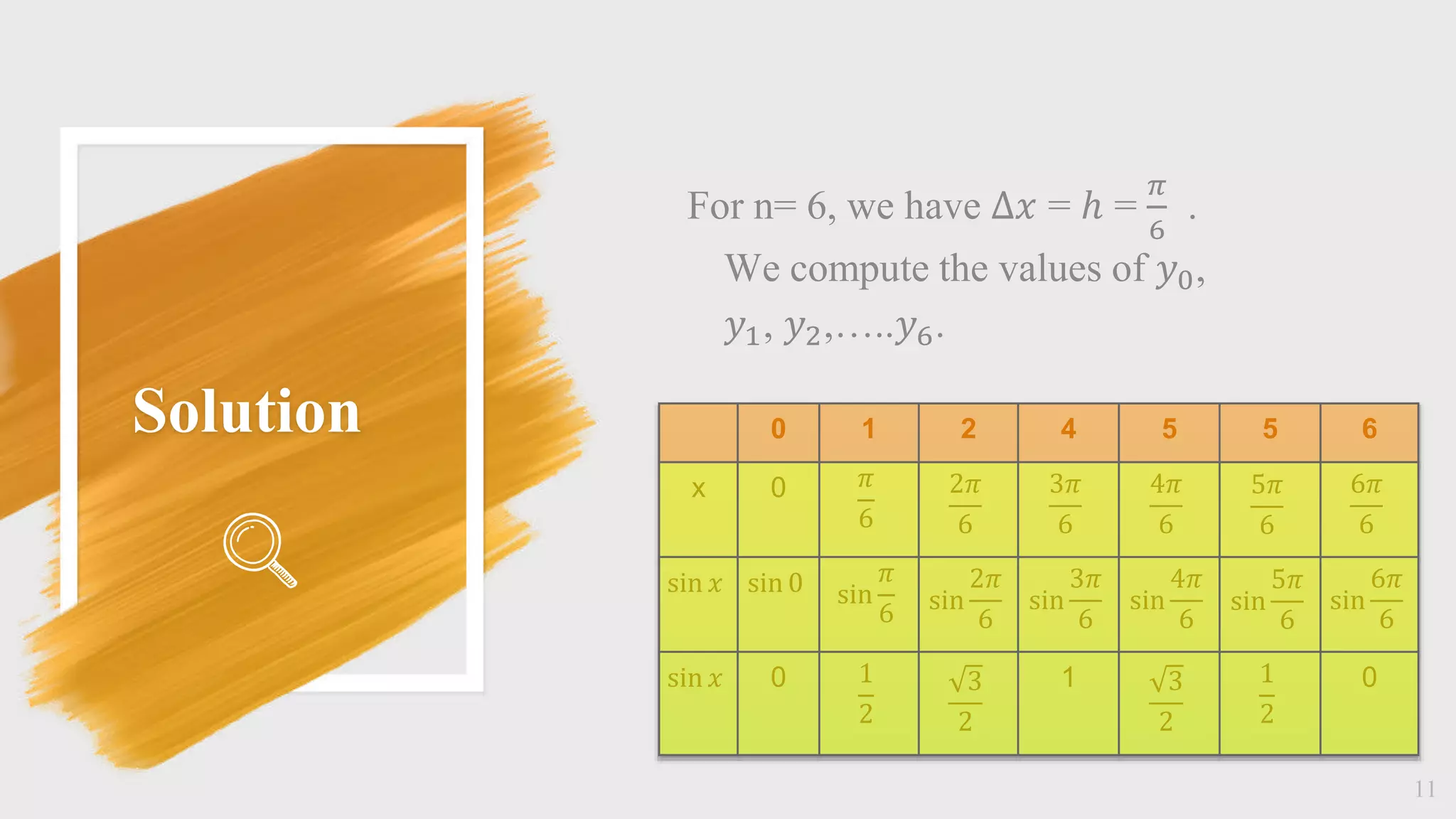
![Solution
12
SINCE THE FORMULA IS:
𝛼
𝛽
𝑦𝑑𝑥 ≈
3ℎ
10
[𝑦0+5 𝑦1+ 𝑦2 + 6 𝑦3+ 𝑦4 + 5𝑦5+ 𝑦6]
Therefore,
0
𝜋
𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥𝑑𝑥 ≈
3(
𝜋
6
)
10
[0+5
1
2
+
3
2
+6(1)+
3
2
+ 5
1
2
+0] ≈
1.999994586
Exact Solution is:
0
𝜋
𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥𝑑𝑥 = 2
Difference= 2-1.999994586 = 0.000005414](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalcomputingpresentation-220106163357/75/Newton-Cotes-Integration-Method-Open-Newton-Cotes-Closed-Newton-Cotes-Gaussian-Quadrature-rule-Weddle-s-rule-Boole-s-Rule-12-2048.jpg)











![24
It is assumed that value of the function f defined
on[a,b] is known at equally spaced point x,for i=0,.....n
where 𝑥0=a and 𝑥1=b.
Solved using Newton Cortes Formula
There are two types of Newton Cortes Formula.
1. The Closed Type
2. The Open Type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalcomputingpresentation-220106163357/75/Newton-Cotes-Integration-Method-Open-Newton-Cotes-Closed-Newton-Cotes-Gaussian-Quadrature-rule-Weddle-s-rule-Boole-s-Rule-24-2048.jpg)