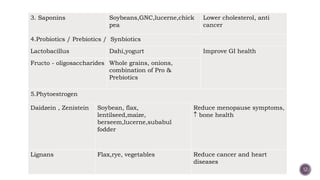
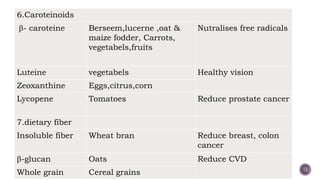
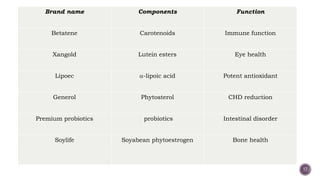
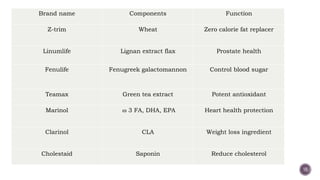
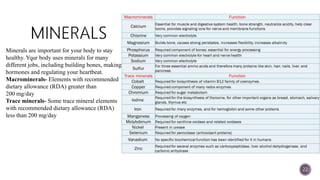
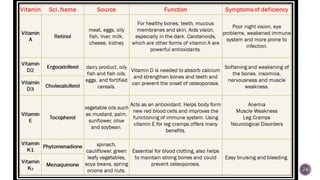
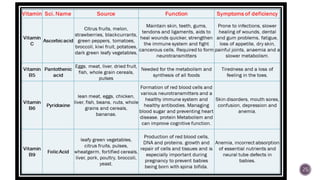
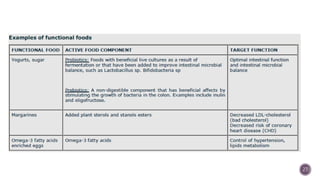
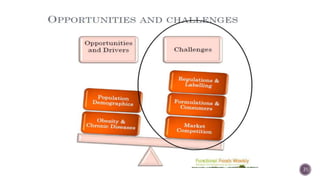
The document discusses nutraceuticals, which are products derived from food that provide health benefits and can be used as supplements or functional foods. It outlines various components of nutraceuticals, their sources, potential benefits, and the growing market for these products globally, particularly in the USA, Japan, and India. The document also emphasizes the relationship between nutraceuticals and functional foods, detailing how they can target specific health issues and the classification based on their sources and benefits.



![Introduction
Nutrition + Pharmaceuticals Term commonly used in marketing but has no regulatory
definition
The term "nutraceutical" was coined from "nutrition" and "pharmaceutical" in 1989 by
Stephen DeFelice, MD, founder and chairman of the Foundation for Innovation in Medicine
(FIM), Cranford, NJ.
[Nutr (ition) + (pharm) aceutical]
"Nutraceutical" is creating the concept that extracts from food can be used as drugs, i.e. food
supplements.
A food or part of food or nutrient,that provides health benefits, including the prevention and
treatment of a disease
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neutraceuticalsfunctionalfoodsautosaved-161122164913/85/Neutraceuticals-functional-foods-5-320.jpg)