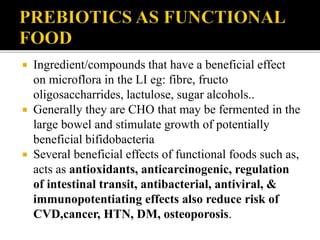
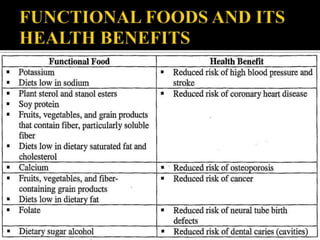
The document discusses functional foods, defined as foods providing health benefits beyond basic nutrition, including items like cereals, legumes, vegetables, and fruits, as well as probiotics and prebiotics. It highlights their role in preventing and treating various diseases, with emphasis on their nutraceutical properties and the increasing consumer demand due to rising health awareness. Functional foods contain biologically-active compounds that enhance health outcomes, making them an essential part of a balanced diet.