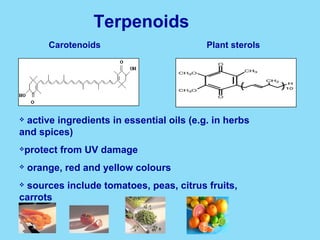
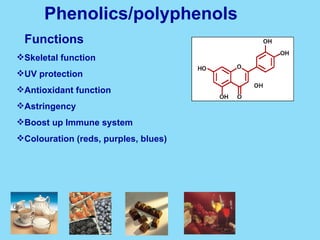
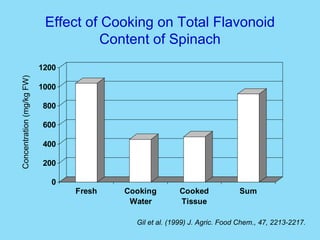
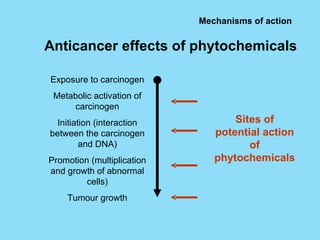
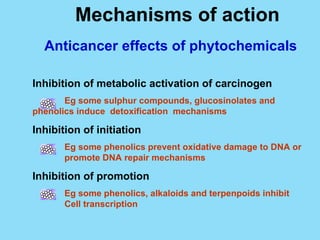
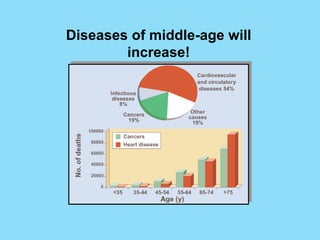
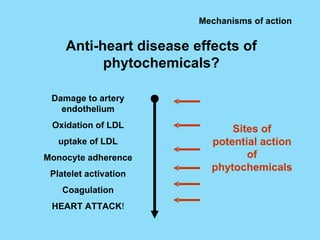
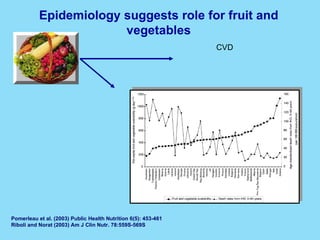
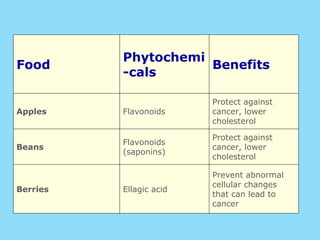
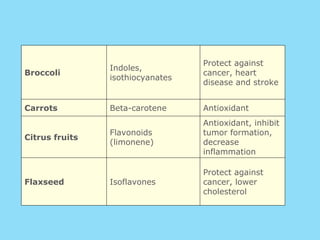
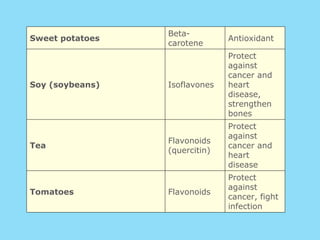
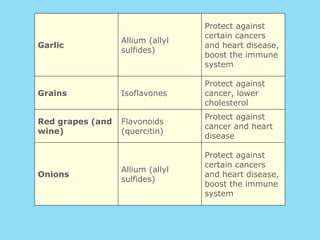
Phytochemicals, or phytonutrients, are plant compounds that may offer various health benefits, including disease prevention and enhanced immune function. There are over 3,000 identified phytochemicals with roles in detoxification, reducing inflammation, and potentially lowering cancer and heart disease risks. The consumption of a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is encouraged to maximize phytochemical intake and promote overall health.