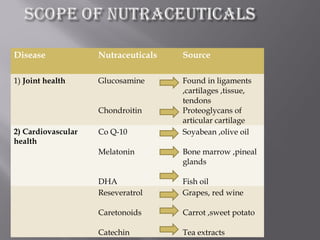
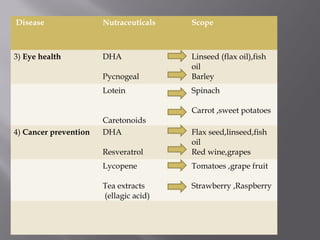
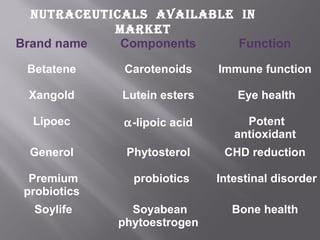
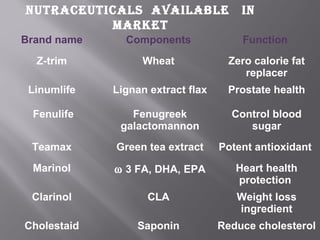
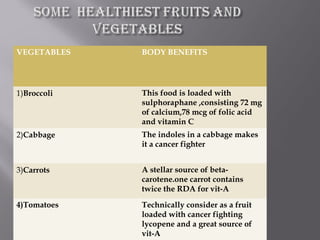
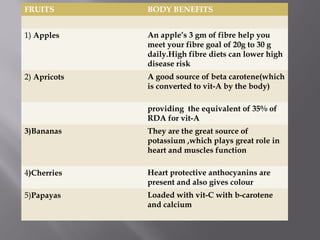
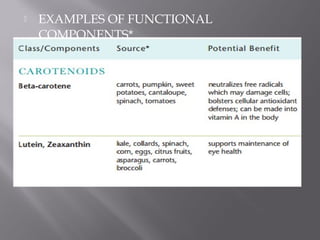
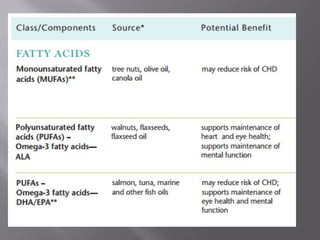
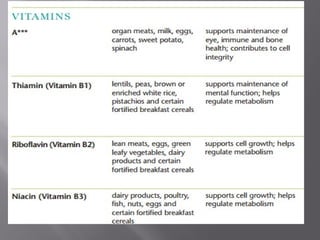
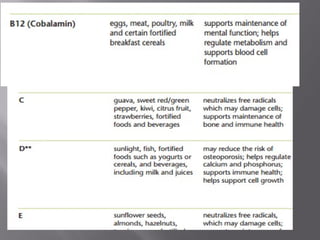
The document discusses nutraceuticals and functional foods. It defines nutraceuticals as pharmaceutical-grade nutrients that provide medicinal or health benefits. Examples given include garlic and soybeans. Functional foods are foods that have a positive health effect beyond basic nutrition, such as oatmeal providing soluble fiber to lower cholesterol. The document also discusses various vitamins, minerals, herbs and other compounds that are commonly used as nutraceuticals to promote health and reduce disease risk. It emphasizes that a diet rich in nutraceuticals, along with exercise and stress reduction, can maximize health benefits.