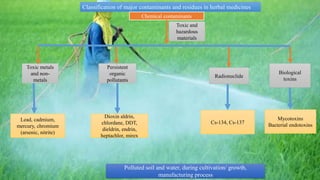
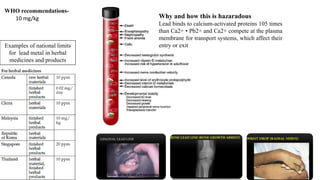
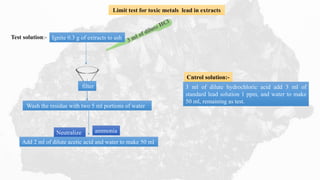
This document describes two limit test methods for determining the amount of lead in herbal medicine extracts.
Method 1 involves igniting a sample to ash, dissolving the residue, and comparing the color of the test solution to a control solution containing a known amount of lead after adding sodium sulfide. Method 2 involves heat-treating a sample, performing an atomic absorption spectrophotometry analysis using the standard addition method, and ensuring the absorbance of the test solution does not exceed the standard solution. Both methods are used to test if the amount of lead is below specified limits.