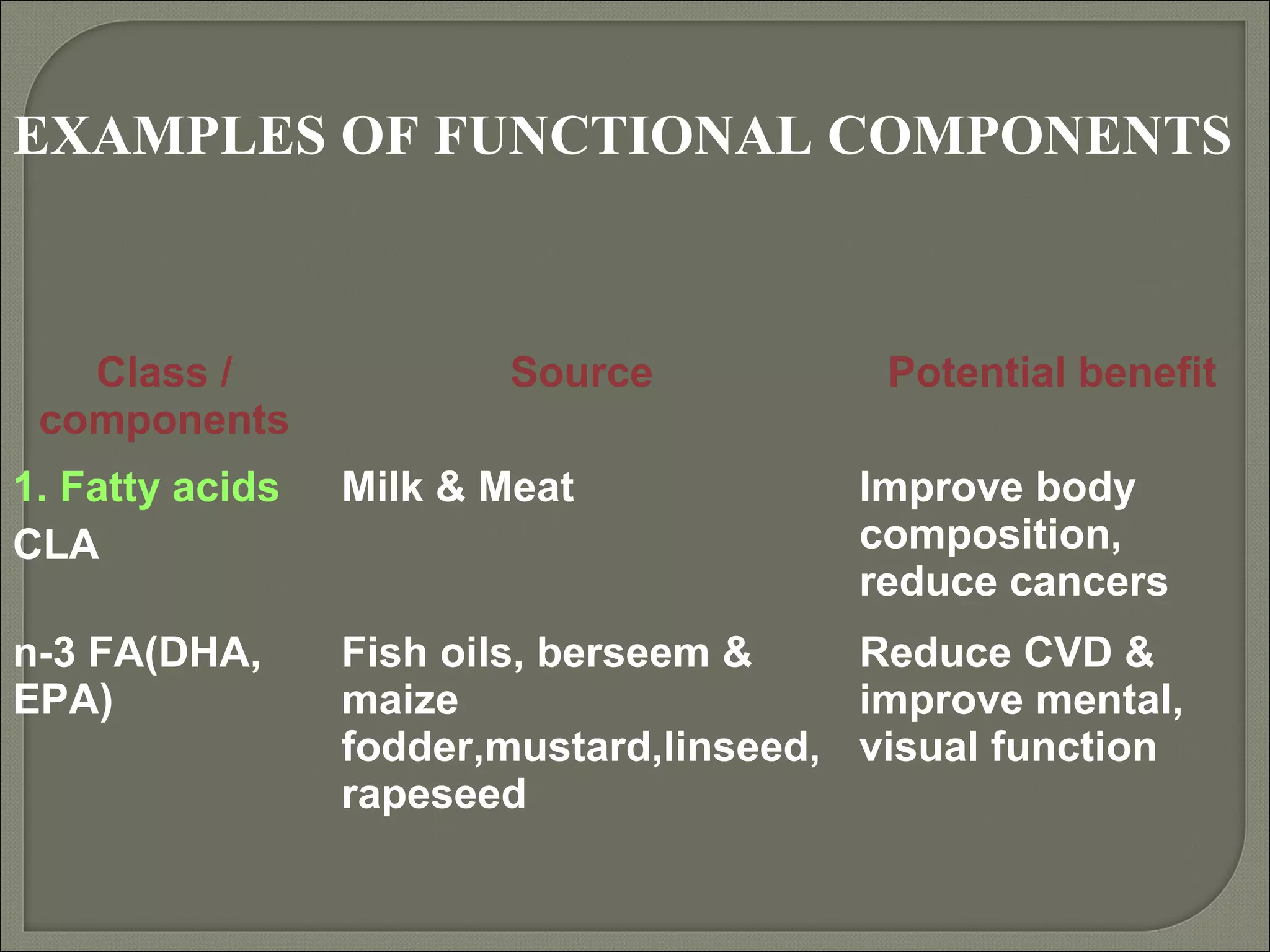
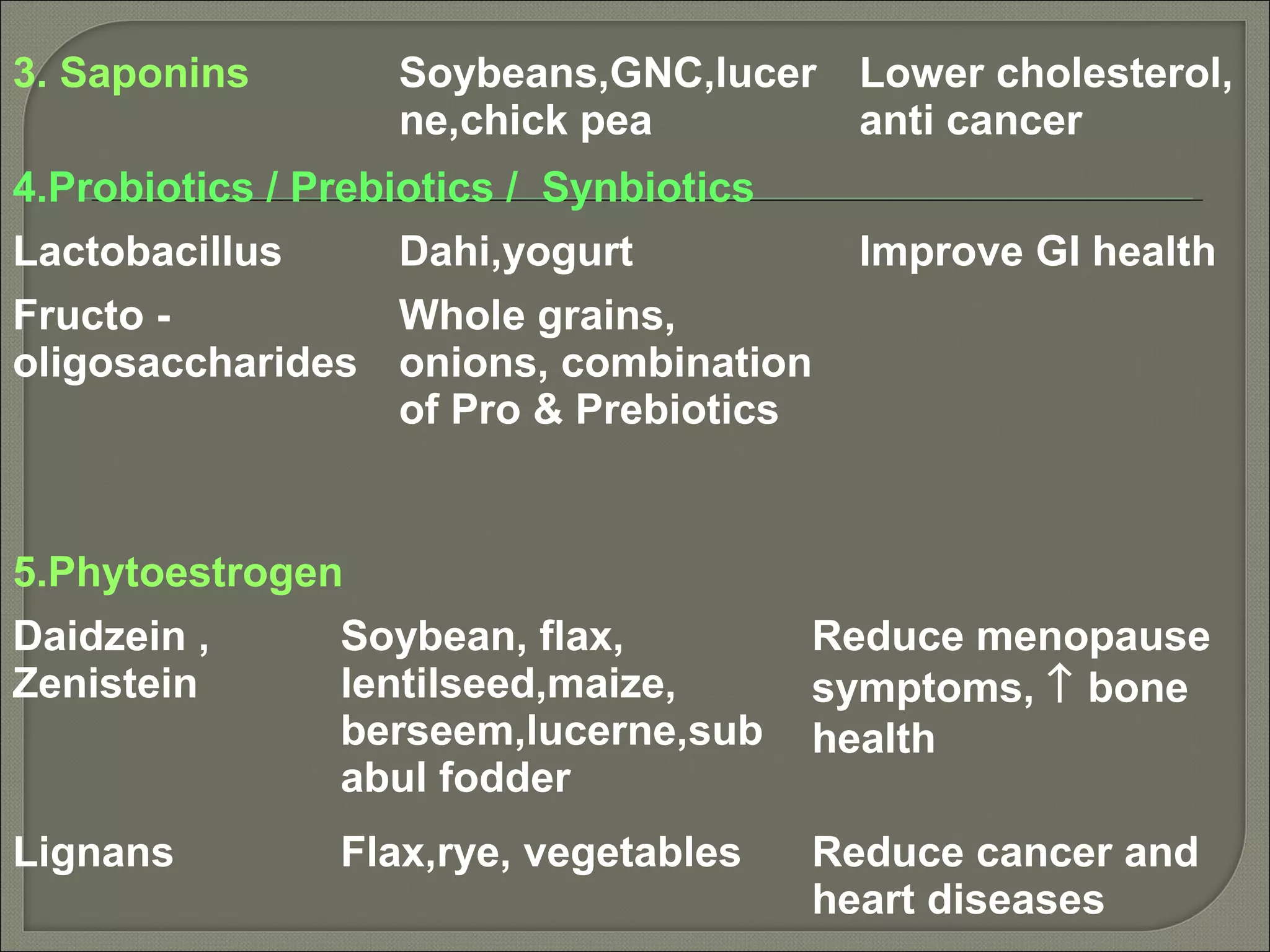
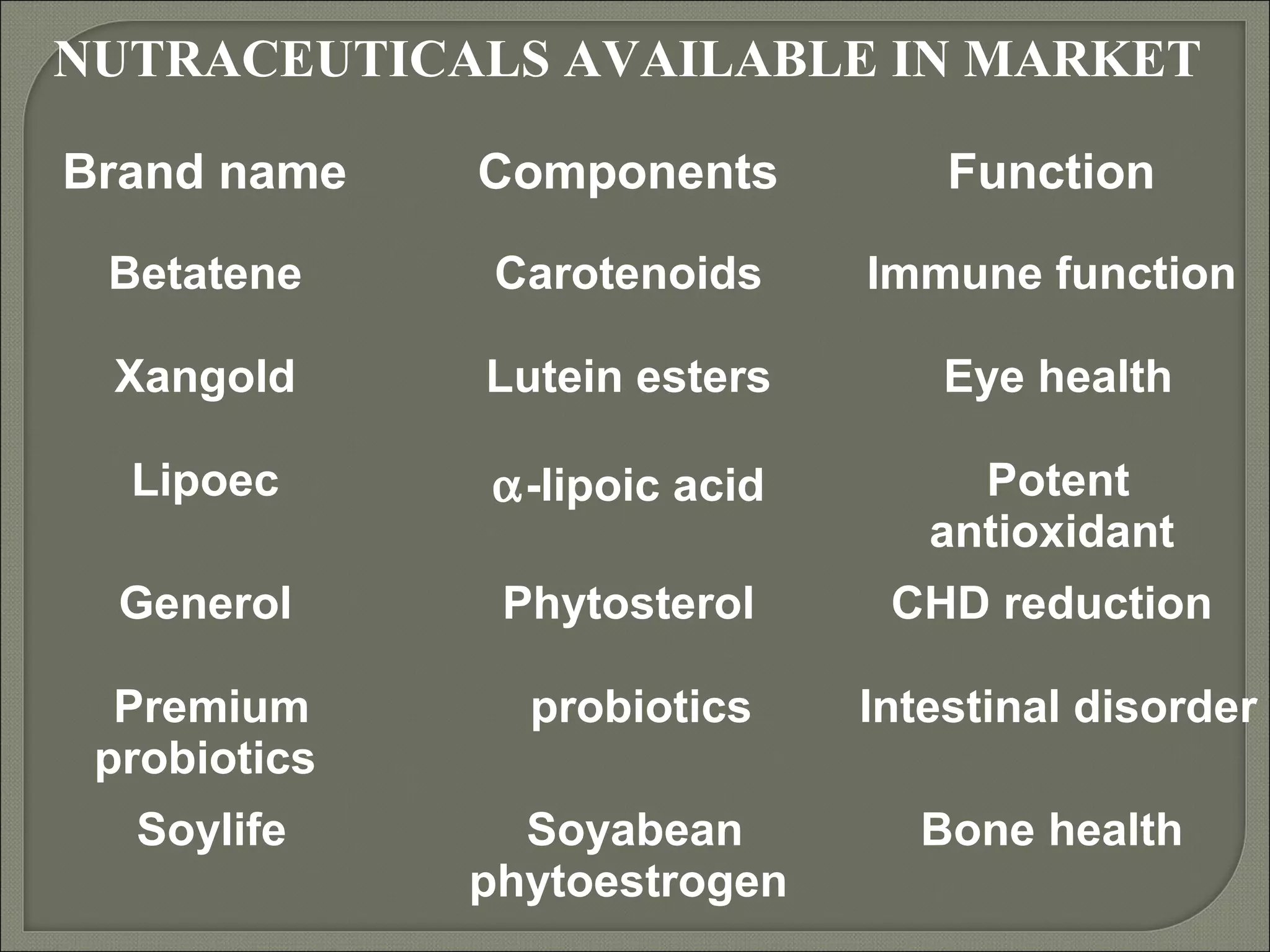
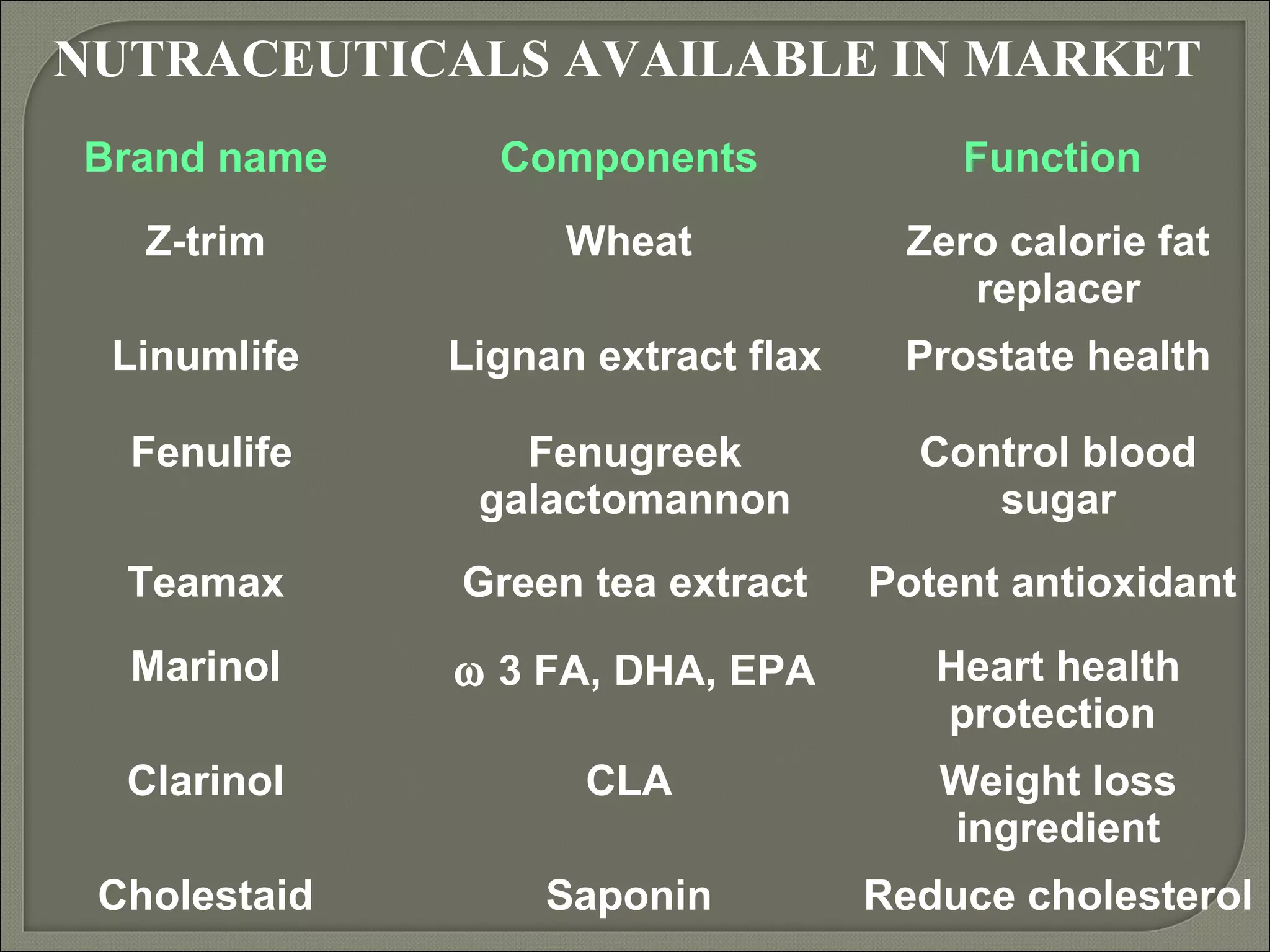
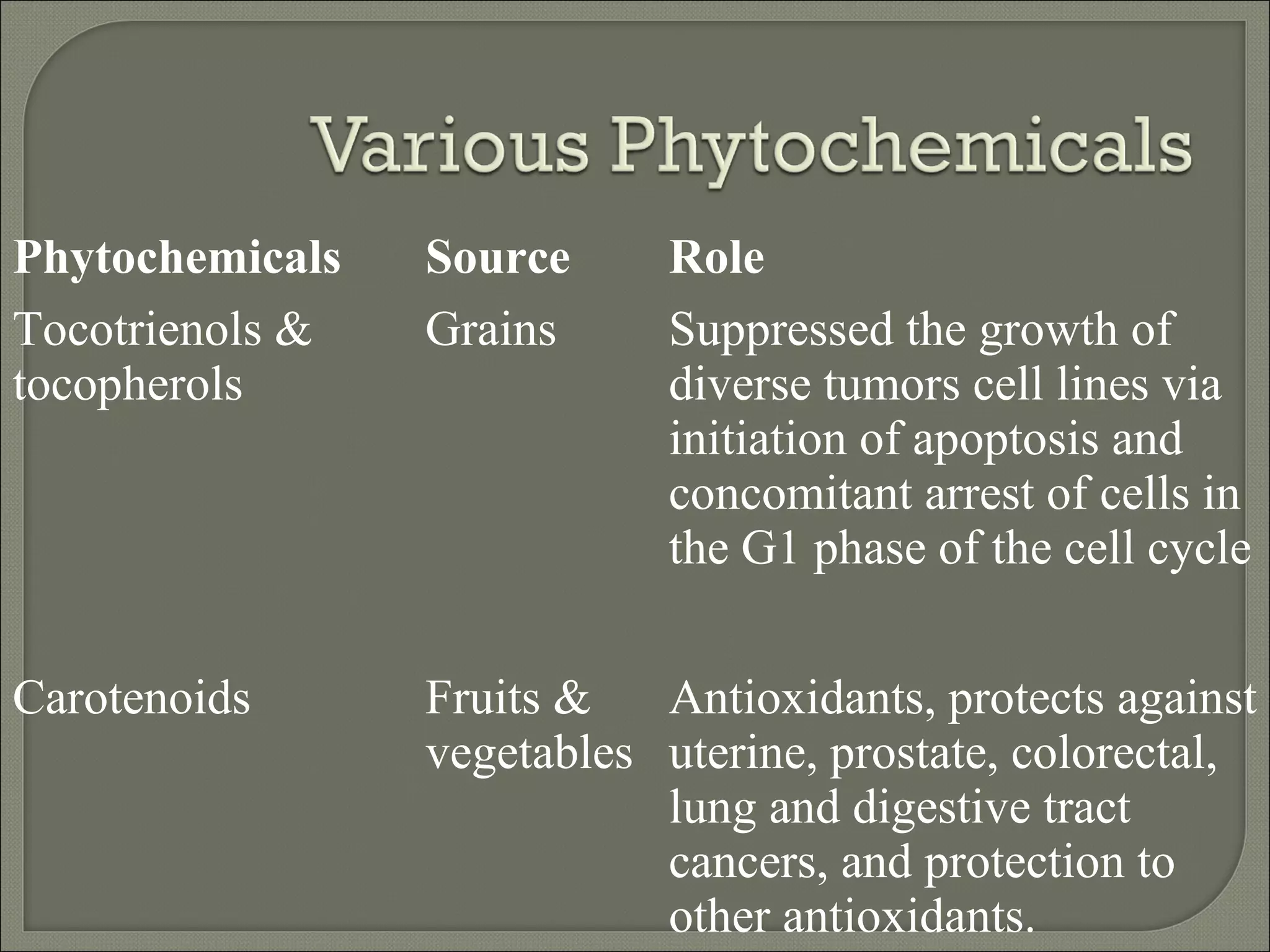
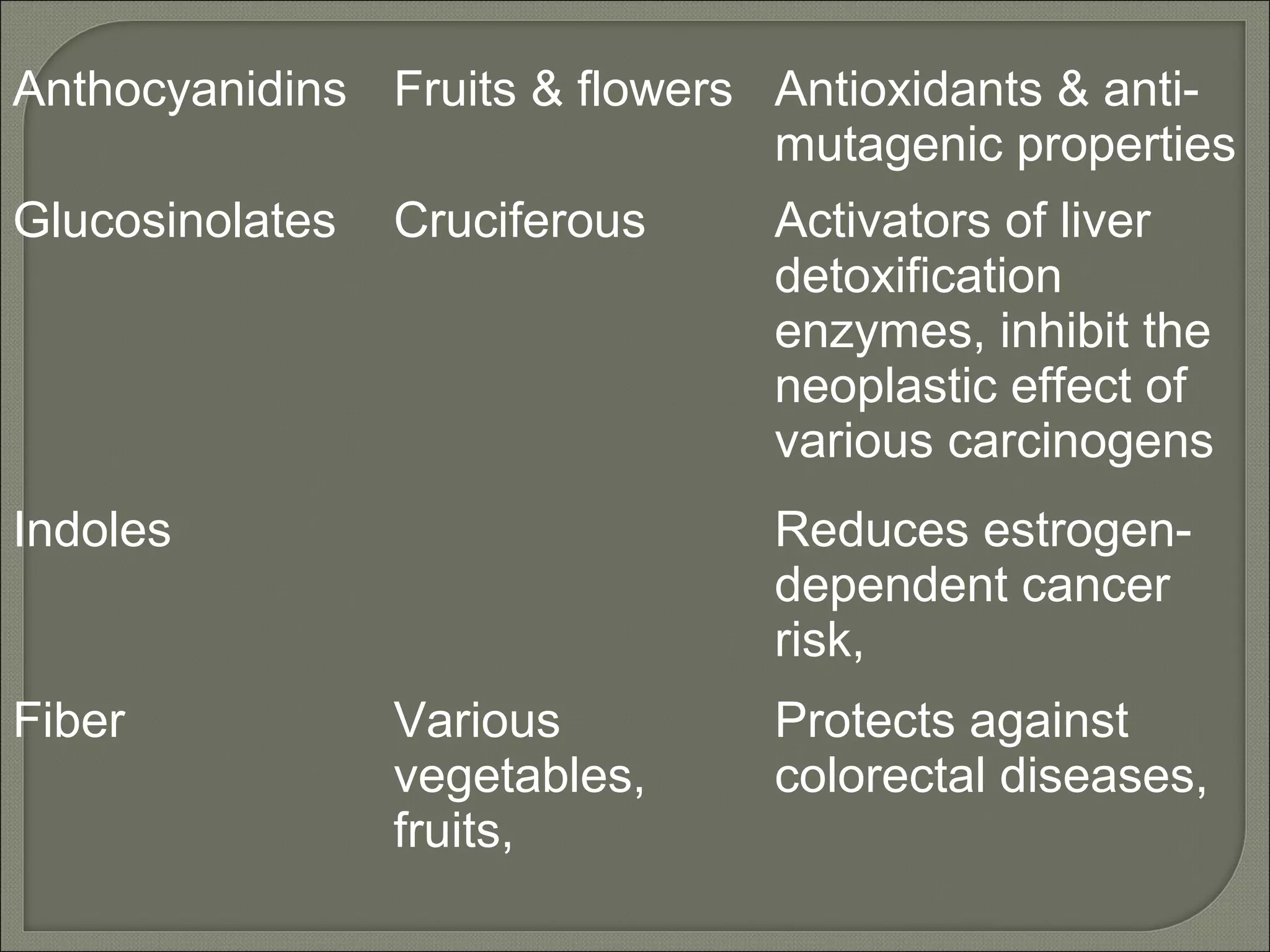
Nutraceuticals provide health benefits and can help prevent and treat diseases. They include nutrients, herbs, dietary supplements, and functional food components. Some examples that were discussed include vitamins, minerals, polyphenols, carotenoids, and phytosterols. Nutraceuticals are found naturally in many foods and their concentration can be increased through food fortification, fermentation, and dietary modifications to promote optimal health.