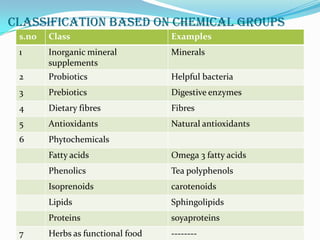
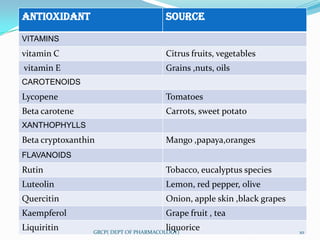
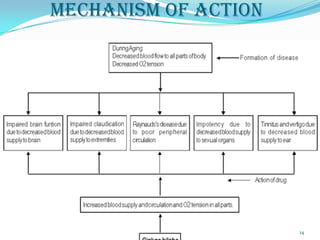
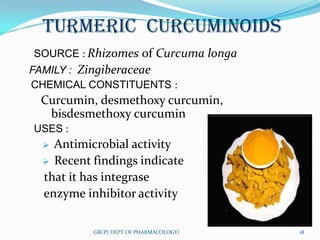
The document defines nutraceuticals as foods or food components that provide health benefits for preventing or treating disease. It classifies nutraceuticals based on their natural source, pharmacological activity, or chemical composition. Some examples of nutraceutical classes described include probiotics, prebiotics, antioxidants, phytochemicals, and herbs used as functional foods. Specific nutraceuticals discussed in more detail include flax seeds, ginkgo biloba, spirulina, karela, turmeric, soy, garlic, and tomato lycopene. The document also lists some marketed nutraceutical supplements and provides references.